|
Fano Noise
Fano noise is a fluctuation of an electric charge obtained in a detector (in spite of constant value of the measured quantity, which is usually an energy), arising from processes in the detector. It was first described by Ugo Fano in 1947, as a fluctuation of amount of ion pairs produced by a charged particle of high energy in a gas. The amount of the ion pairs is proportional to the energy the particle loses in the gas, but with some error - due to the Fano noise. Surprisingly, the noise is usually smaller than a Poisson distribution noise (in which the variance is equal to the value - note the variance is average squared distance from the expected value), showing there is an interaction between ionization acts. A Fano factor was introduced to describe it, and the factor is almost independent of the energy measured (Fano computed it to change from 0.43 to 0.47 for ionization of atomic hydrogen by electrons of energy from 1keV to 100keV). Fano expected it to be between 1/3 and 1/2 fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugo Fano
Ugo Fano (July 28, 1912 – February 13, 2001) was an Italian American physicist, notable for contributions to theoretical physics. Biography Ugo Fano was born into a wealthy Jewish family in Turin, Italy. His father was Gino Fano, a professor of mathematics. University studies Fano earned his doctorate in mathematics at the University of Turin in 1934, under Enrico Persico, with a thesis entitled ''Sul Calcolo dei Termini Spettrali e in Particolare dei Potenziali di Ionizzazione Nella Meccanica Quantistica'' (''On the Quantum Mechanical Calculation Spectral Terms and their Extension to Ionization''). As part of his PhD examination he also made two oral presentations entitled: ''Sulle Funzioni di Due o Più Variabili Complesse'' (''On the functions of two or more complex variables'') and ''Le Onde Elettromagnetiche di Maggi: Le Connessioni Asimmetriche Nella Geometria Non Riemanniana'' (''Maggi electromagnetic waves: asymmetric connections in non-Riemannian geometry''). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson Process
In probability, statistics and related fields, a Poisson point process is a type of random mathematical object that consists of points randomly located on a mathematical space with the essential feature that the points occur independently of one another. The Poisson point process is often called simply the Poisson process, but it is also called a Poisson random measure, Poisson random point field or Poisson point field. This point process has convenient mathematical properties, which has led to its being frequently defined in Euclidean space and used as a mathematical model for seemingly random processes in numerous disciplines such as astronomy,G. J. Babu and E. D. Feigelson. Spatial point processes in astronomy. ''Journal of statistical planning and inference'', 50(3):311–326, 1996. biology,H. G. Othmer, S. R. Dunbar, and W. Alt. Models of dispersal in biological systems. ''Journal of mathematical biology'', 26(3):263–298, 1988. ecology,H. Thompson. Spatial point processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fano Factor
In statistics, the Fano factor, like the coefficient of variation, is a measure of the dispersion of a probability distribution of a Fano noise. It is named after Ugo Fano, an Italian American physicist. The Fano factor is defined as :F=\frac, where \sigma_W^2 is the variance and \mu_W is the mean of a random process in some time window ''W''. The Fano factor can be viewed as a kind of noise-to-signal ratio; it is a measure of the reliability with which the random variable could be estimated from a time window that on average contains several random events. For a Poisson process, the variance in the count equals the mean count, so ''F'' = 1 (normalization). If the time window is chosen to be infinity, the Fano factor is similar to the variance-to-mean ratio (VMR) which in statistics is also known as the index of dispersion. Use in particle detection In particle detectors, the Fano factor results from the energy loss in a collision not being purely statistical. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
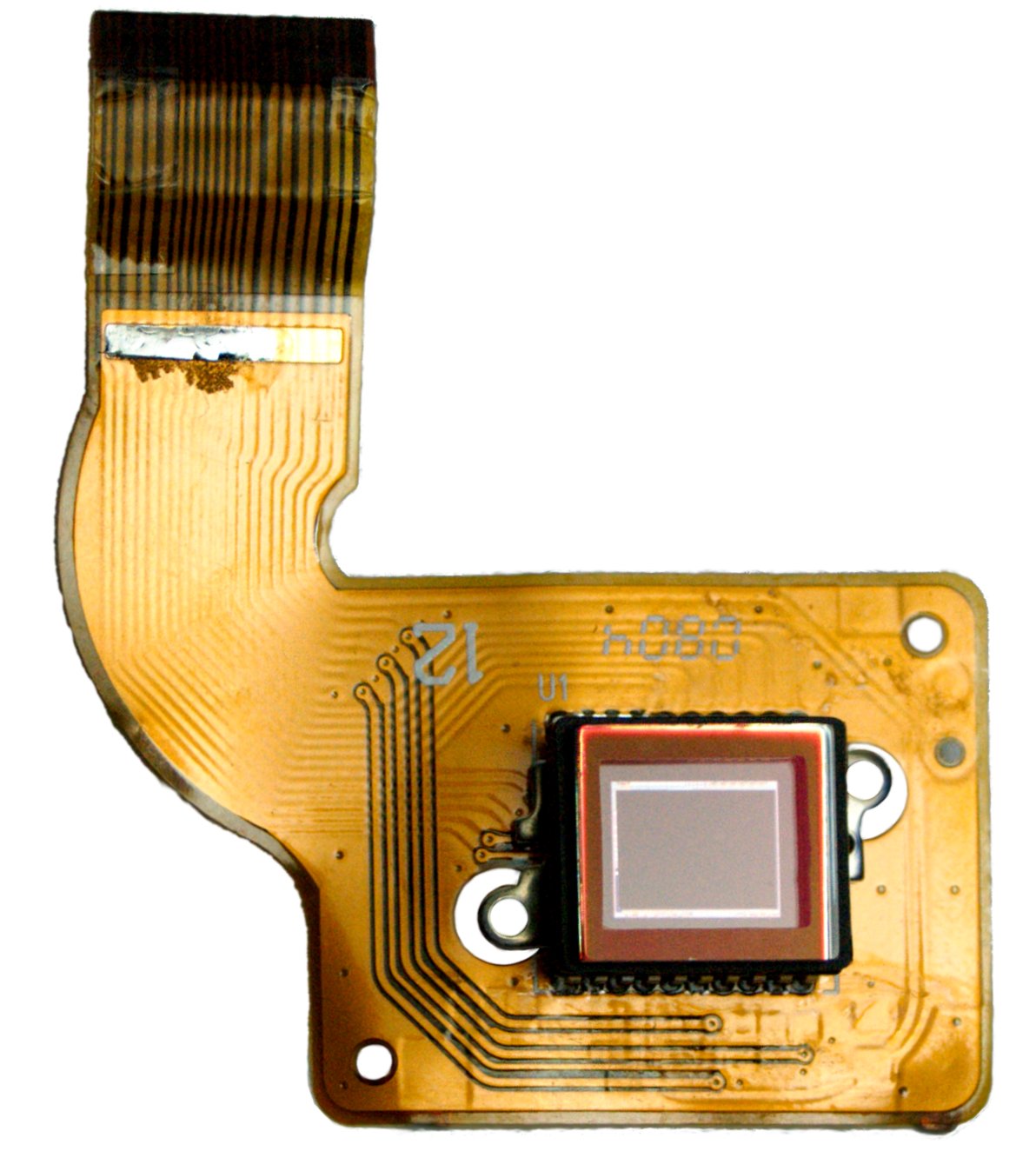
Image Sensors
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademark "COS-MO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |