|
Family Tree Of Major Arteries
This is a list of arteries of the human body. * The aorta * The arteries of the head and neck ** The common carotid artery *** The external carotid artery *** The triangles of the neck *** The internal carotid artery ** The arteries of the brain * The arteries of the upper extremity ** The subclavian artery ** The axilla *** The axillary artery *** The brachial artery *** The radial artery *** The ulnar artery * The arteries of the trunk ** The descending aorta *** The thoracic aorta *** The abdominal aorta ** The common iliac arteries *** The hypogastric artery *** The external iliac artery * The arteries of the lower extremity ** The femoral artery ** The popliteal artery ** The anterior tibial artery ** The arteria dorsalis pedis ** The posterior tibial artery Position of artery {{Human arteries Arteries An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Iliac Artery
The external iliac arteries are two major Artery, arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. Structure The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the Pelvis, pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament. This occurs about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle. At this point they are referred to as the femoral arteries. Branches Function The external iliac artery provides the main blood supply to the legs. It passes down along the brim of the pelvis and gives off two large branches - the "inferior epigastric artery" and a "deep circumflex artery." These vessels supply blood to the muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall. The external iliac artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
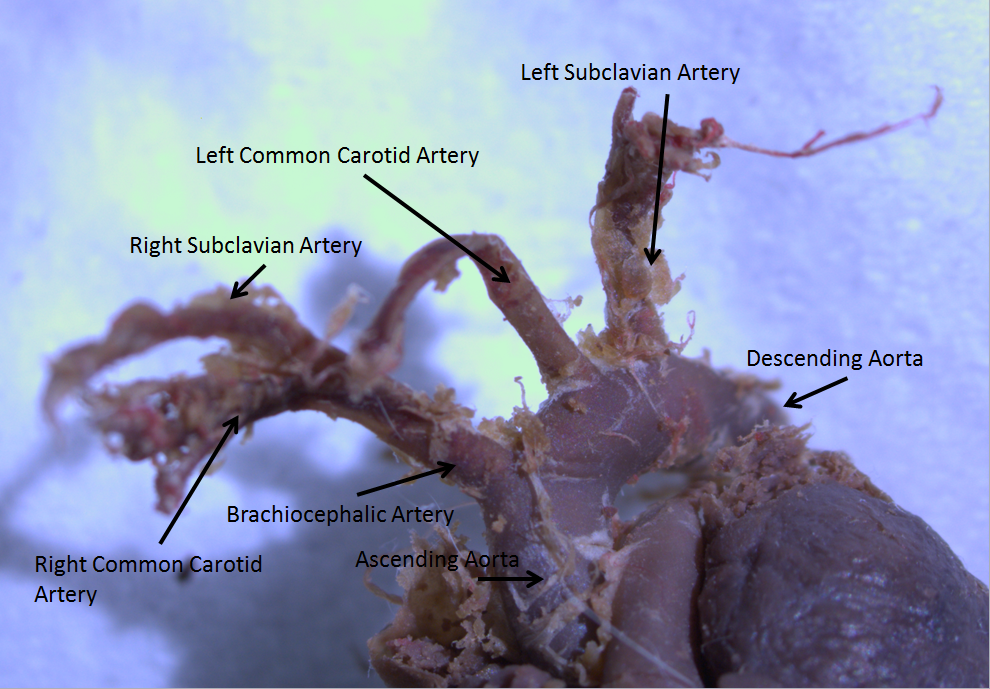
Brachiocephalic Artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck. It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic artery divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid, and the left subclavian artery, come directly off the aortic arch. However, there are two brachiocephalic veins. Structure The brachiocephalic artery arises, on a level with the upper border of the second right costal cartilage, from the start of the aortic arch, on a plane anterior to the origin of the left carotid artery. It ascends obliquely upward, backward, and to the right to the level of the upper border of the right sternoclavicular articulation, where it divides into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian arteries. The artery then cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath. and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumflex Branch Of Left Coronary Artery
The circumflex branch of left coronary artery, or left circumflex artery or circumflex artery, is a branch of the left coronary artery. Description The left circumflex artery follows the left part of the coronary sulcus, running first to the left and then to the right, reaching nearly as far as the posterior longitudinal sulcus. There have been multiple anomalies described, for example the left circumflex having an aberrant course from the right coronary artery. Branches The circumflex artery curves to the left around the heart within the coronary sulcus, giving rise to one or more left marginal arteries (also called obtuse marginal branches) as it curves toward the posterior surface of the heart. It helps form the posterior left ''ventricular branch'' or posterolateral artery. The circumflex artery ends at the point where it joins to form to the posterior interventricular artery in 15% of all cases, which lies in the posterior interventricular sulcus. In the other 85% of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Coronary Artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the heart. It supplies the right side of the heart, and the interventricular septum. Structure The right coronary artery originates above the right aortic sinus above the aortic valve. It passes through the right coronary sulcus (right atrioventricular groove), towards the crux of the heart. It gives off many branches, including the posterior interventricular artery, the right marginal artery, the conus artery, and the sinoatrial nodal artery. Segments * Proximal: starting at RCA origin, spanning half the distance to the acute margin * Middle: from proximal segment to the acute margin * Distal: from middle segment to origination point of the posterior interventricular artery, where the posterior interventricular sulcus meets the atrioven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery
The left anterior descending artery (also LAD, anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery, or anterior descending branch) is a branch of the left coronary artery. Blockage of this artery is often called the ''widow-maker infarction'' due to a high death risk. Structure It passes at first behind the pulmonary artery and then comes forward between that vessel and the left atrium to reach the anterior interventricular sulcus, along which it descends to the notch of cardiac apex. Although rare, multiple anomalous courses of the LAD have been described. These include the origin of the artery from the right aortic sinus. In 78% of cases, it reaches the apex of the heart. Branches The LAD gives off two types of branches: ''septals'' and ''diagonals''. * Septals originate from the LAD at 90 degrees to the surface of the heart, perforating and supplying the anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum. * Diagonals run along the surface of the heart and supply the lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Coronary Artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left main stem coronary artery (LMS). Branching The left coronary artery typically runs for 10 to 25 mm, and then bifurcates into the left anterior descending artery (also called the widow maker) and the left circumflex artery. Sometimes, an additional artery arises at the bifurcation of the left main artery, forming a trifurcation; this extra artery is called the ''ramus'' or ''intermediate artery''. The part that is between the aorta and the bifurcation only is known as the left main artery (LM), while the term "LCA" might refer to just the left main, or to the left main and all its eventual branches. A "first septal branch" is sometimes described. Additional images File:Coronary arteries 1.jpg, Left coronary artery File:Cardiac vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Aorta
The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum. Structure It passes obliquely upward, forward, and to the right, in the direction of the heart's axis, as high as the upper border of the second right costal cartilage, describing a slight curve in its course, and being situated, about behind the posterior surface of the sternum. The total length is about . Components The aortic root is the portion of the aorta beginning at the aortic annulus and extending to the sinotubular junction. It is sometimes regarded as a part of the ascending aorta, and sometimes regarded as a separate entity from the rest of the ascending aorta. Between each commissure of the aortic valve and opposite the cusps of the aortic valve, three small dilatations called the aortic sinuses. The sinotubular junction is the point in the ascendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Tibial Artery
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The posterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa. It is accompanied by a deep vein, the posterior tibial vein, along its course. It passes just posterior to the medial malleolus of the tibia, but anterior to the Achilles tendon. It passes into the foot deep to the flexor retinaculum of the foot. It runs through the tarsal tunnel. Branches The posterior tibial artery gives rise to: * medial plantar artery. * lateral plantar artery. * fibular artery, which is said to rise from the bifurcation of the tibial-fibular trunk and the posterior tibial artery. * calcaneal branch to the medial aspect of the calcaneus. Function The posterior tibial artery supplies oxygenated blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteria Dorsalis Pedis
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery (dorsal artery of foot) is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space (as the first dorsal metatarsal artery and the deep plantar artery). It carries oxygenated blood to the Dorsum (biology), dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during Anesthesia, anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve. Structure The dorsalis pedis artery is located 1/3 from malleolus, medial malleolus of the ankle. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery. It ends at the proximal part of the first intermetatarsal space. Here, it divides into two branches, the first dorsal metatarsal artery, and the deep plantar artery. It is covered by skin and fascia, but is fairly superficial. The dorsalis pedis communicates with the plantar blood supply of the foot through the deep plantar artery. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |