|
Falset (music)
Falset is the latitude for a brasswind player's pitch-control of a harmonic by adjusting lip or air pressure. While only just sufficient in middle and high registers to allow for intonation adjustment, this latitude becomes very wide in the low register in the flattening direction. Without this ability for adjustment, the conventional system of three valves would be problematic owing to the sharpness of certain valve combinations. Previously also ''falset'' referred to falsetto. At B2 the pitch can sometimes be dropped by a fourth or more by means of what is often termed ''loose-lipping'', a slackening of the embouchure which produces ''factitious'' pitches not included in the harmonic series. This term dates at least from 1620, when Michael Praetorius wrote about falset tones in articles concerning the cornett The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. It was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombone First Position Harmonic Series
The trombone (german: Posaune, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the pitch instead of the valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide. The word "trombone" derives from Italian ''tromba'' (trumpet) and ''-one'' (a suffix meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a predominantly cylindrical bore like the trumpet, in contrast to the more conical brass instruments like the cornet, the euphonium, and the French horn. The most frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass trombone. These are treated as non-transposing instruments, reading at concert pitch in bass clef, with h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Techniques , the ability to perceive music or to create music
*
{{Music disambiguation ...
Musical is the adjective of music. Musical may also refer to: * Musical theatre, a performance art that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance * Musical film and television, a genre of film and television that incorporates into the narrative songs sung by the characters * MusicAL, an Albanian television channel * Musical isomorphism, the canonical isomorphism between the tangent and cotangent bundles See also * Lists of musicals * Music (other) * Musica (other) * Musicality Musicality (''music-al -ity'') is "sensitivity to, knowledge of, or talent for music" or "the quality or state of being musical", and is used to refer to specific if vaguely defined qualities in pieces and/or genres of music, such as melodiousness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bazooka (instrument)
The bazooka is a brass musical instrument several feet in length which incorporates telescopic tubing like the trombone. Radio comedian Bob Burns is credited with inventing the instrument in the 1910s, and popularized it in the 1930s. It was also played by jazz musicians Noon Johnson and Sanford Kendrick. Sound From its start within a lipreed mouthpiece – which may consist of nothing but the bare tube or may employ a mouthpiece which is handmade to emulate one from a low brass instrument – the air column expands into a wide length of pipe that slides freely around a narrower length of pipe, which, in turn, terminates in a widely flaring bell. Although the slide action of the bazooka appears to alter pitch, this is not the case due to the extremely wide diameter of the horn's tubing. Manipulating the horn's length changes tone quality as subtle harmonic overtones fluctuate. This effect gives the bazooka its characteristic warbling, echoing sound. All of the bazooka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombone
The trombone (german: Posaune, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips cause the Standing wave, air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the Pitch (music), pitch instead of the brass instrument valve, valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide. The word "trombone" derives from Italian ''tromba'' (trumpet) and ''-one'' (a suffix meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a predominantly cylindrical bore like the trumpet, in contrast to the more conical brass instruments like the cornet, the euphonium, and the French horn. The most frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass trombone. These are treated as trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marin Mersenne
Marin Mersenne, OM (also known as Marinus Mersennus or ''le Père'' Mersenne; ; 8 September 1588 – 1 September 1648) was a French polymath whose works touched a wide variety of fields. He is perhaps best known today among mathematicians for Mersenne prime numbers, those which can be written in the form for some integer . He also developed Mersenne's laws, which describe the harmonics of a vibrating string (such as may be found on guitars and pianos), and his seminal work on music theory, ''Harmonie universelle'', for which he is referred to as the "father of acoustics". Mersenne, an ordained Catholic priest, had many contacts in the scientific world and has been called "the center of the world of science and mathematics during the first half of the 1600s" and, because of his ability to make connections between people and ideas, "the post-box of Europe". He was also a member of the Minim religious order and wrote and lectured on theology and philosophy. Life Mersenne was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (key signatures, time signatures, and rhythmic notation); the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built." Music theory is frequently concerned with describing how musicians and composers make music, including tuning systems and composition methods among other topics. Because of the ever-expanding conception of what constitutes music, a more inclusive definition could be the consideration of any sonic phenomena, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Horn
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a list of horn players, horn player or hornist. Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of Brass instrument valve, valves by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valves, but some, especially older horns, use piston valves (similar to a trumpet's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
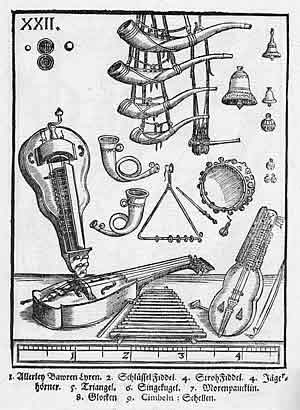
Syntagma Musicum
''Syntagma Musicum (1614-1620)'' is a musical treatise in three volumes by the German composer, organist, and music theorist Michael Praetorius. It was published in Wittenberg and Wolfenbüttel. It is one of the most commonly used research sources for seventeenth-century music theory and performance practice The second volume, ''De Organographia,'' illustrates and describes musical instruments and their use; this volume in particular became a valuable guide for research and reconstruction of early instruments in the twentieth century, and thus an integral part of the early music revival. Though never published, Praetorius intended a fourth volume on musical composition. The three extant volumes are: * I: ''Musicae Artis Analecta'' * II: ''De Organographia'' * III: ''Termini musicali'' Contents Volume One: Musicae Artis Analecta The first volume was written in Latin and divided into two parts, published separately. The first part, "on sacred or ecclesiastical music," shows Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sackbut
The term sackbut refers to the early forms of the trombone commonly used during the Renaissance music, Renaissance and Baroque music, Baroque eras. A sackbut has the characteristic telescopic slide of a trombone, used to vary the length of the tube to change Pitch (music), pitch, but is distinct from later trombones by its smaller, more cylindrically-proportioned bore (wind instruments), bore, and its less-flared bell (wind instrument), bell. Unlike the earlier slide trumpet from which it evolved, the sackbut possesses a U-shaped slide with two parallel sliding tubes, rather than just one. Records of the term ''trombone'' predate the term ''sackbut'' by two decades, and evidence for the German term ''Posaune'' is even older.Timeline of trombone history (15th century) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornett
The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. It was used in what are now called alta capellas or wind ensembles. It is not to be confused with the modern cornet. The sound of the cornett is produced by lip vibrations against a cup mouthpiece, similar to modern brass instruments. A cornett consists of a conical wooden pipe covered in leather, is about long, and has finger holes and a small horn, ivory, or bone mouthpiece. The range is from A3 to A5, however the bottom note can be lipped as far as G3 and a good player can get up to E6. Construction The ordinary treble cornett is made by splitting a length of wood and gouging out the two halves to make the gently conical, curved bore. The halves are then glued together, and the outside planed to an octagonal cross section, the whole being bound in thin black leather. Six front finger holes and a thumb hole on the back (like on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |