|
Falconidae
The falcons and caracaras are around 60 species of diurnal birds of prey that make up the family Falconidae (representing all extant species in the order Falconiformes). The family is divided into three subfamilies, Herpetotherinae, which includes the laughing falcon and forest falcons, Polyborinae, which includes the caracaras, '' Spiziapteryx'' and Falconinae, the falcons and kestrels (''Falco'') and falconets (''Microhierax''). Description Falcons and caracaras are small to medium-sized birds of prey, ranging in size from the black-thighed falconet, which can weigh as little as , to the gyrfalcon, which can weigh as much as . They have strongly hooked bills, sharply curved talons and excellent eyesight. The plumage is usually composed of browns, whites, chestnut, black and grey, often with barring of patterning. There is little difference in the plumage of males and females, although a few species have some sexual dimorphism in boldness of plumage. Distribution and habit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon
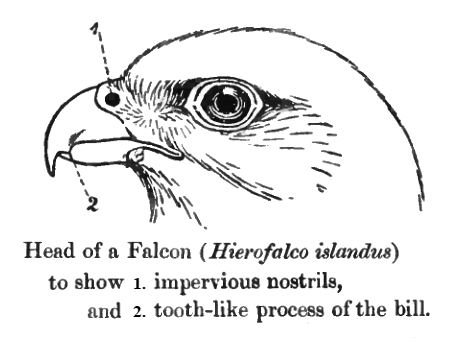
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peregrine Falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falconidae. A large, Corvus (genus), crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey back, barred white underparts, and a black head. The peregrine is renowned for its speed, reaching over during its characteristic hunting stoop (high-speed dive), making it the fastest bird in the world, as well as the Fastest animals, fastest member of the animal kingdom. According to a ''National Geographic (U.S. TV channel), National Geographic'' TV program, the highest measured speed of a peregrine falcon is . As is typical for avivore, bird-eating raptors, peregrine falcons are Sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic, with females being considerably larger than males. The peregrine's breeding range includes land regions from the Arctic tundra to the tropics. It can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caracara (subfamily)
Caracaras are birds of prey in the family Falconidae. They are traditionally placed in subfamily Polyborinae with the forest falcons, but are sometimes considered to constitute their own subfamily, Caracarinae, or classified as members of the true falcon subfamily, Falconinae. Caracaras are principally birds of South and Central America, just reaching the southern United States. Unlike the ''Falco'' falcons in the same family, the birds in the five relevant genera are not fast-flying aerial hunters, but are comparatively slow and are often scavengers (a notable exception being the red-throated caracara). Species Distribution The caracaras are found throughout much of the Americas. The range of the crested caracara extends as far north as the states of Arizona, Texas, and Florida in the United States. In the Southern Hemisphere, the striated caracara inhabits the Falkland Islands and Tierra del Fuego, just off the coast of the southernmost tip of South America. Taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyborinae
Caracaras are birds of prey in the family Falconidae. They are traditionally placed in subfamily Polyborinae with the forest falcons, but are sometimes considered to constitute their own subfamily, Caracarinae, or classified as members of the true falcon subfamily, Falconinae. Caracaras are principally birds of South and Central America, just reaching the southern United States. Unlike the ''Falco'' falcons in the same family, the birds in the five relevant genera are not fast-flying aerial hunters, but are comparatively slow and are often scavengers (a notable exception being the red-throated caracara). Species Distribution The caracaras are found throughout much of the Americas. The range of the crested caracara extends as far north as the states of Arizona, Texas, and Florida in the United States. In the Southern Hemisphere, the striated caracara inhabits the Falkland Islands and Tierra del Fuego, just off the coast of the southernmost tip of South America. Taxonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpetotherinae
Herpetotherinae is a subfamily of falconid birds of prey that includes eight species in two genera '' Herpetotheres'' (laughing falcons) and '' Micrastur'' (forest falcons). Both genera are found in South America and the subfamily is basal to the other falconid subfamilies where they split off around 30.2 million years ago in the Oligocene epoch. The two herpetotherine genera split around 20 million years ago in the Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ... epoch. References Birds of prey Bird subfamilies {{Falconiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falconinae
Falconinae is a subfamily of falconid birds of prey that includes 44 species in three genera. It includes ''Microhierax'' (the typical falconets), ''Polihierax'' (the pygmy falcons), and '' Falco'' (the falcons). Molecular data since 2015 has found support in the grouping of these genera, with ''Polihierax'' being paraphyletic in respect to ''Falco''. Falconinae and their sister taxon, Polyborinae, split off from Herpetotherinae around 30.2 million years ago in the Oligocene epoch. Falconines split off from the polyborines around 20 million years ago in the Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ... epoch. References Birds of prey Bird subfamilies {{Falconiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falconiformes
The order Falconiformes () is represented by the extant family Falconidae (falcons and caracaras) and a handful of enigmatic Paleogene species. Traditionally, the other bird of prey families Cathartidae (New World vultures and condors), Sagittariidae (secretarybird), Pandionidae (ospreys), Accipitridae (hawks) were classified in Falconiformes. A variety of comparative genome analysis published since 2008, however, found that falcons are part of a clade of birds called Australaves, which also includes seriemas, parrots and passerines. Within Australaves falcons are more closely related to the parrot-passerine clade (Psittacopasserae), which together they form the clade Eufalconimorphae. The hawks and vultures occupy a basal branch in the clade Afroaves in their own clade Accipitrimorphae, closer to owls and woodpeckers. See below cladogram of Telluraves relationships based on Braun & Kimball (2021): The fossil record of Falconiformes ''sensu stricto'' is poorly documented. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laughing Falcon
The laughing falcon (''Herpetotheres cachinnans''), also called the snake hawk (erroneously, since it is not a hawk), is a medium-sized bird of prey in the falcon family ( Falconidae), the only member of the genus ''Herpetotheres''. This Neotropical species is a specialist snake-eater. Its common and scientific names both refer to its distinctive voice. Taxonomy Its English name comes from its loud voice, as does the specific name ''cachinnans'', Latin for "laughing aloud" or "laughing immoderately". The generic name ''Herpetotheres'' refers to its preferred food; it is Latinized Ancient Greek, derived from '' rpeton'' (ἑρπετόν, " reptile") + ''therizein'' (θερίζειν, "to mow down"). Its relationships with other members of the Falconidae are unclear. Traditionally it has been placed in the subfamily Polyborinae with the caracaras and forest falcons, but the American Ornithologists' Union's North American Check-list Committee now places it in the same subfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spot-winged Falconet
The spot-winged falconet (''Spiziapteryx circumcincta'') is a species of bird of prey in the family Falconidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Spiziapteryx''. It is found in Argentina, southeastern Bolivia, Paraguay, and Uruguay, where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forest and subtropical or tropical dry shrubland. Taxonomy The holotype specimen A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ... of ''Harpagus curcumcinctus'' KaupProc. Zool. Soc. London (1851) 1852, p.43. is held in the collections of National Museums Liverpool at World Museum, with accession number D959. The specimen was collected from “Chili” by Thomas Bridges on 22 June 1848 and came to the Liverpool national collection via the 13th Earl of Derby’s collection which was bequea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Falcon
Forest falcons are members of the genus ''Micrastur'', part of the family Falconidae. They are endemic to the Americas, found from Mexico in the north, south through Central America and large parts of South America, and as far south as northern Argentina. Most are restricted to humid tropical and subtropical forests, but the two most widespread species, the collared and the barred forest falcon, also range into drier and more open habitats. Forest falcons, like most ''Accipiter''-type hawks (but unlike other falcons), are adapted for agility in thick cover rather than outright speed in the open air. They have short wings, long tails, and extraordinarily acute hearing. While generally visually inconspicuous, their songs are commonly heard. Their diet is a mixture of birds, mammals, and reptiles. Hunting is often performed in goshawk fashion: the bird takes up a perch in an inconspicuous position and waits for a prey species to pass, then strikes with a short, rapid pursuit. Fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrfalcon
The gyrfalcon ( or ) (), the largest of the falcon species, is a bird of prey. The abbreviation gyr is also used. It breeds on Arctic coasts and tundra, and the islands of northern North America and the Eurosiberian region. It is mainly a resident there also, but some gyrfalcons bird migration, disperse more widely after the breeding season, or in winter. Individual Vagrancy (biology), vagrancy can take birds for long distances. Its plumage varies with location, with birds being coloured from all-white to dark brown. These colour variations are called Polymorphism (biology), morphs. Like other falcons, it shows sexual dimorphism, with the female much larger than the male. For centuries, the gyrfalcon has been valued as a Falconry, hunting bird. Typical prey includes the ptarmigan and waterfowl, which it may take in flight; it also takes fish and mammals. Taxonomy and etymology The gyrfalcon was Species description, formally described by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kestrel
The term kestrel (from french: crécerelle, derivative from , i.e. ratchet) is the common name given to several species of predatory birds from the falcon genus ''Falco''. Kestrels are most easily distinguished by their typical hunting behaviour which is to hover at a height of around over open country and swoop down on ground prey, usually small mammals, lizards or large insects, while other falcons are more adapted for active hunting during flight. Kestrels are notable for usually having mostly brown in their plumage. Description Most species termed kestrels appear to form a distinct clade among the falcons, as suggested by comparison of mtDNA cytochrome ''b'' sequence data and morphology. This seems to have diverged from other ''Falco'' around the Miocene–Pliocene boundary (Messinian to Zanclean, or about 7–3.5 mya). The most basal "true" kestrels are three species from Africa and its surroundings which lack a malar stripe, and in one case have—like other falcons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)