|
FIO2
Fraction of inspired oxygen (''FI''O2), corrected denoted with a capital "I", is the molar or volumetric fraction of oxygen in the inhaled gas. Medical patients experiencing difficulty breathing are provided with oxygen-enriched air, which means a higher-than-atmospheric ''FI''O2. Natural air includes 21% oxygen, which is equivalent to ''FI''O2 of 0.21. Oxygen-enriched air has a higher ''FI''O2 than 0.21; up to 1.00 which means 100% oxygen. ''FI''O2 is typically maintained below 0.5 even with mechanical ventilation, to avoid oxygen toxicity, but there are applications when up to 100% is routinely used. Often used in medicine, the ''FI''O2 is used to represent the percentage of oxygen participating in gas-exchange. If the barometric pressure changes, the ''FI''O2 may remain constant while the partial pressure of oxygen changes with the change in barometric pressure. Equations ;Abbreviated alveolar air equation :P_A \ce = \frac PAO2, PEO2, and PIO2 are the partial pressures of oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
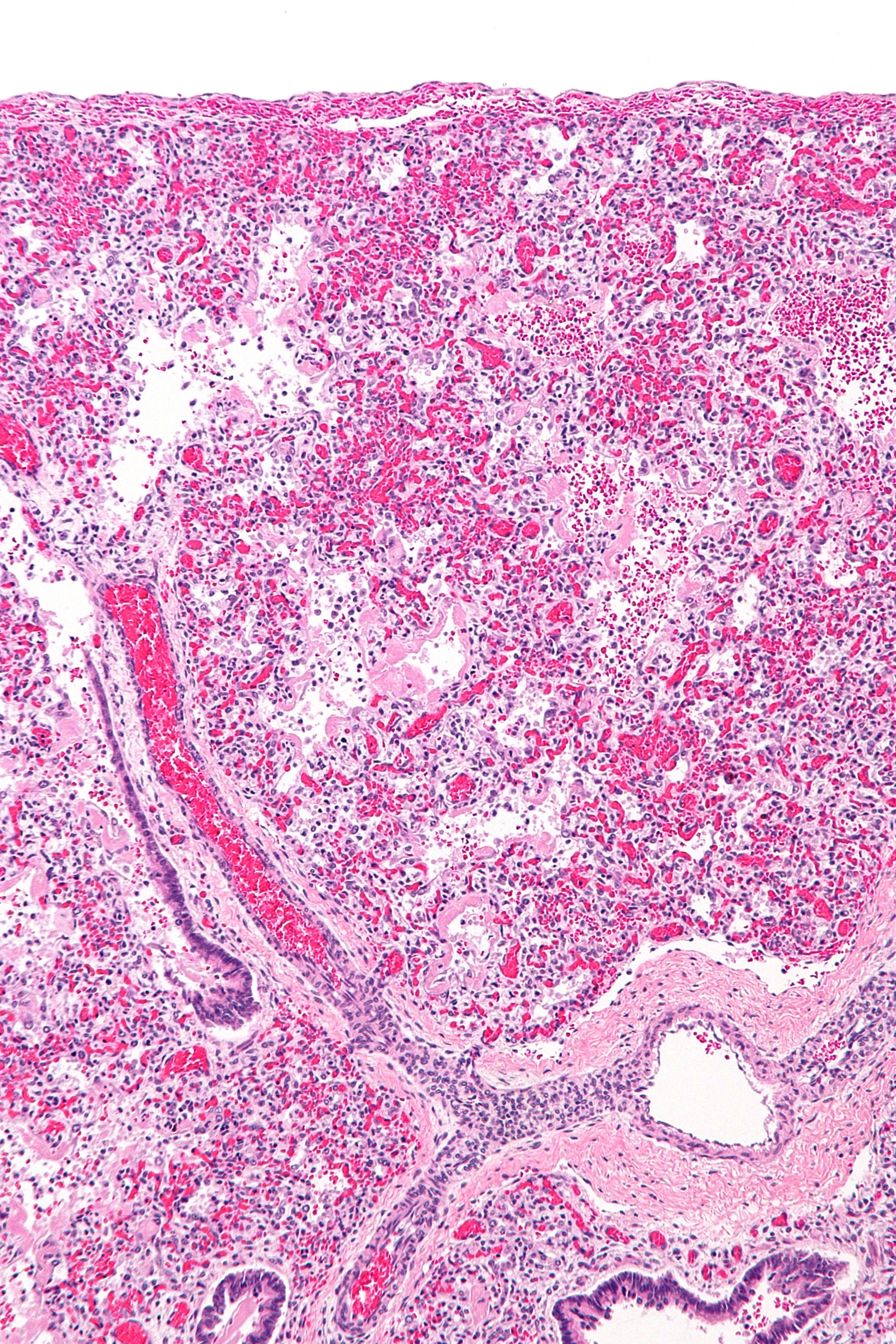
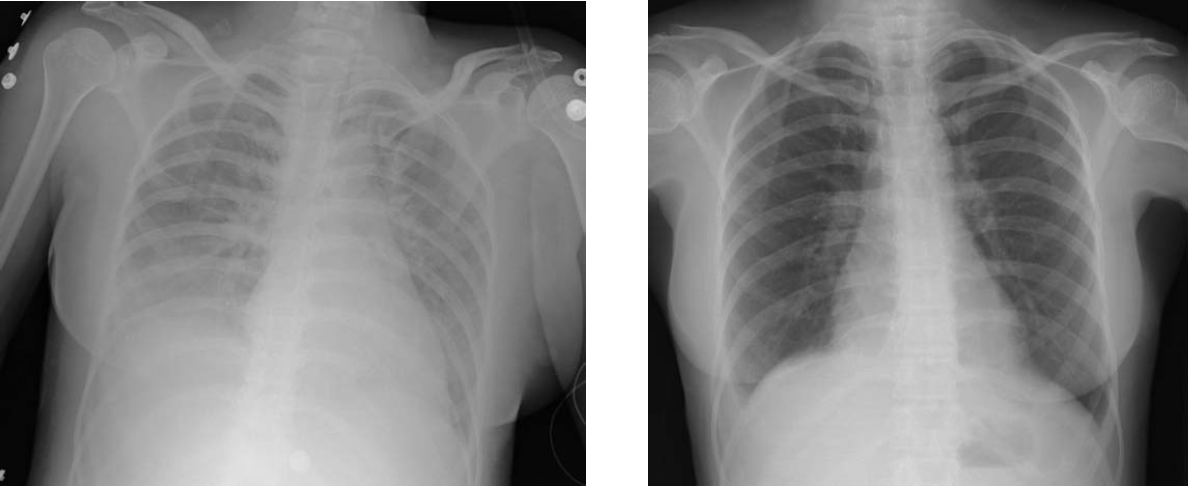
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APACHE II
APACHE II ("Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II") is a severity-of-disease classification system, one of several ICU scoring systems. It is applied within 24 hours of admission of a patient to an intensive care unit (ICU): an integer score from 0 to 71 is computed based on several measurements; higher scores correspond to more severe disease and a higher risk of death. The first APACHE model was presented by Knaus et al. in 1981. Application APACHE II was designed to measure the severity of disease for adult patients admitted to intensive care units. It has not been validated for use in children or young people aged under 16. This scoring system is used in many ways which include: # Some procedures or some medicine is only given to patients with a certain APACHE II score # APACHE II score can be used to describe the morbidity of a patient when comparing the outcome with other patients. # Predicted mortalities are averaged for groups of patients in order to speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horowitz Index
The Horowitz index or Horovitz index (also known as the Horowitz quotient or the P/F ratio) is a ratio used to assess lung function in patients, particularly those on ventilators. It is useful for evaluating the extent of damage to the lungs. The simple abbreviation as oxygenation can lead to confusion with other conceptualizations of oxygenation index. The Horowitz index is defined as the ratio of partial pressure of oxygen in blood (PaO2), in millimeters of mercury, and the fraction of oxygen in the inhaled air (FiO2) — the ''PaO2''/''FiO2 ratio''. In healthy lungs, the Horowitz index depends on age and usually falls between 350 and 450. A value below 300 is the threshold for mild lung injury, and 200 is indicative of a moderately severe lung injury. A value below 100 is a criterion for a severe injury. The Horowitz index plays a major role in the diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Three severities of ARDS are categorized based on the degree of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |