|
Functional Grammar (other)
Functional grammar may refer to: * Functional linguistics, a range of functionally based approaches to linguistics * Functional discourse grammar, grammar models developed by Simon C. Dik that explain how utterances are shaped based on the goals of language users * Systemic functional grammar, a grammatical description developed by Michael Halliday * Danish functional linguistics, a strand of functional linguistics associated with linguists at the University of Copenhagen * Lexical functional grammar Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, an ..., a variety of generative grammar initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan * Role and reference grammar, a model of grammar developed by William Foley and Robert Van Valin, Jr. {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Linguistics
Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic functionalism spawned in the 1920s to 1930s from Ferdinand de Saussure's systematic structuralist approach to language (1916). Functionalism sees functionality of language and its elements to be the key to understanding linguistic processes and structures. Functional theories of language propose that since language is fundamentally a tool, it is reasonable to assume that its structures are best analyzed and understood with reference to the functions they carry out. These include the tasks of conveying meaning and contextual information. Functional theories of grammar belong to structural and, broadly, humanistic linguistics, considering language as being created by the community, and linguistics as relating to systems theory. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Discourse Grammar
Functional grammar (FG) and functional discourse grammar (FDG) are grammar models and theories motivated by functional theories of grammar. These theories explain how linguistic utterances are shaped, based on the goals and knowledge of natural language users. In doing so, it contrasts with Chomskyan transformational grammar. Functional discourse grammar has been developed as a successor to functional grammar, attempting to be more psychologically and pragmatically adequate than functional grammar. The top-level unit of analysis in functional discourse grammar is the discourse move, not the sentence or the clause. This is a principle that sets functional discourse grammar apart from many other linguistic theories, including its predecessor functional grammar. History Functional grammar (FG) is a model of grammar motivated by functions, as Dik's thesis pointed towards issues with generative grammar and its analysis of coordination back then, and proposed to solve them with a ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
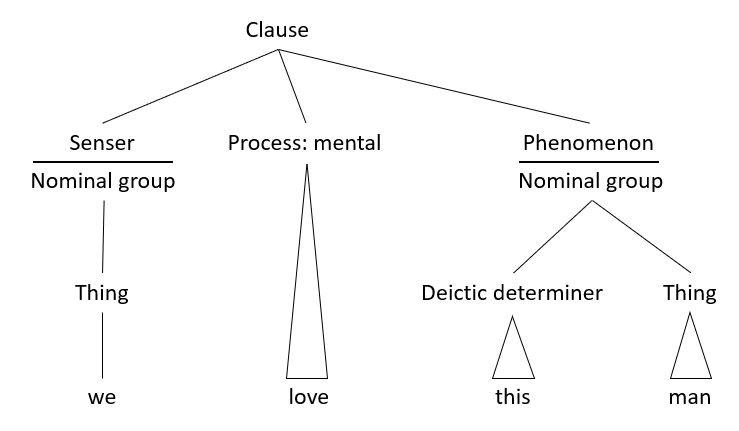
Systemic Functional Grammar
Systemic functional grammar (SFG) is a form of grammatical description originated by Michael Halliday. It is part of a social semiotics, semiotic approach to language called ''systemic functional linguistics''. In these two terms, ''systemic'' refers to the view of language as "a network of systems, or interrelated sets of options for making meaning"; ''functional'' refers to Halliday's view that language is as it is because of what it has evolved to do (see Metafunction). Thus, what he refers to as the ''multidimensional architecture of language'' "reflects the multidimensional nature of human experience and interpersonal relations." Influences Halliday describes his grammar as built on the work of Ferdinand de Saussure, Saussure, Louis Hjelmslev, Bronisław Malinowski, Malinowski, J.R. Firth, and the Prague school linguists. In addition, he drew on the work of the American anthropological linguists Franz Boas, Boas, Edward Sapir, Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf, Whorf. His "main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Functional Grammar
Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, and a representation of grammatical functions such as subject and object, similar to dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to the theory of transformational grammar which was current in the late 1970s. It mainly focuses on syntax, including its relation with morphology and semantics. There has been little LFG work on phonology (although ideas from optimality theory have recently been popular in LFG research). Some recent work combines LFG with Distributed Morphology in Lexical-Realizational Functional Grammar.Ash Asudeh, Paul B. Melchin & Daniel Siddiqi (2021). ''Constraints all the way down: DM in a representational model of grammar''. In ''WCCFL 39 Proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |