|
Function Block Diagram
The Function Block Diagram (FBD) is a graphical language for programmable logic controller design, that can describe the function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks. Input and output variables are connected to blocks by connection lines. Inputs and outputs of the blocks are wired together with connection lines or links. Single lines may be used to connect two logical points of the diagram: * An input variable and an input of a block * An output of a block and an input of another block * An output of a block and an output variable The connection is oriented, meaning that the line carries associated data from the left end to the right end. The left and right ends of the connection line must be of the same type. Multiple right connection, also called divergence, can be used to broadcast information from its left end to each of its right ends. All ends of the connection must be of the same type. Function Block Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBS Maximum
FBS may refer to: People * Frederik Batti Sorring, known as FBS, Indonesian politician Schools * Faith Baptist School (other) * France Business School, in France * Friern Barnet School, in London * Friends Boys' School, one of two Ramallah Friends Schools in the West Bank Science and medicine * Failed back syndrome * Fasting blood sugar * Fetal bovine serum * ''Frontiers in Bioscience'', an academic journal * Function-Behaviour-Structure ontology * Lees-Haley Fake Bad Scale Other uses * Federal Bureau of Statistics of the Government of Pakistan * Fellow of the Burgon Society, in the United Kingdom * Friday Harbor Seaplane Base, in Washington, United States * Fukuoka Broadcasting System, a Japanese TV station * Furness Building Society, a British financial institution * NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, part of college football in the United States See also * FB (other) FB, Fb, or fb may refer to: Arts and media * F♭ (musical note) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. Dick Morley is considered as the father of PLC as he had invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for General Motors in 1968. PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems. They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact. Programs to control machine operation are typically stored in battery-backed-up or non-volatile memory. PLCs were first deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects which are also studied are controllability and observability. Control theory is used in control sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Configuration
In communications or computer systems, a configuration of a system refers to the arrangement of each of its functional units, according to their nature, number and chief characteristics. Often, configuration pertains to the choice of hardware, software, firmware, and documentation. Along with its architecture, the configuration of a computer system affects both its function and performance See also * Auto-configuration * Configuration management - In multiple disciplines, a practice for managing change ** Software configuration management * Configuration file - In software, a data resource used for program initialization *Configure script (computing) A configure script is an executable script designed to aid in developing a program to be run on a wide number of different computers. It matches the libraries on the user's computer, with those required by the program before compiling it from ... * Configurator * Settings (Windows) References * Federal Standard 1037C Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate a normalization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of ''standardization'' is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions. History Early examples Standard weights and measures were developed by the Indus Valley civilization.Iwata, Shigeo (2008), "Weights and Measures in the Indus Valley", ''Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures (2nd edition)'' edited by Helaine Selin, pp. 2254–2255, Springer, . The centralized wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 61131-3
IEC 61131-3 is the third part (of 10) of the open international standard IEC 61131 for programmable logic controllers. It was first published in December 1993 by the IEC; the current (third) edition was published in February 2013. Part 3 of ''IEC 61131'' deals with basic software architecture and programming languages of the control program within PLC. It defines three graphical and two textual programming language standards: * Ladder diagram (LD), graphical * Function block diagram (FBD), graphical * Structured text (ST), textual * Instruction list (IL), textual (deprecated in 3rd edition of the standard) * Sequential function chart (SFC), has elements to organize programs for sequential and parallel control processing, graphical. Data types * Elementary Data Type ** Bit Strings – groups of on/off values *** BOOL - 1 bit (0,1) *** BYTE – 8 bit (1 byte) *** WORD – 16 bit (2 byte) *** DWORD – 32 bit (4 byte) *** LWORD – 64 bit (8 byte) ** INTEGER – whol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control There are two common classes of control action: open loop and closed loop. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Control System
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerised control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localising control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision. Distributed control systems first emerged in large, high value, safety critical process industries, and were attractive because the DCS manufacturer would supply both the local control level and central supervisory equipment as an integrated package, thus reducing design integration risk. Today the functionality of Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) and DCS systems are very similar, but DCS tends to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladder Logic
Ladder logic was originally a written method to document the design and construction of relay racks as used in manufacturing and process control. Each device in the relay rack would be represented by a symbol on the ladder diagram with connections between those devices shown. In addition, other items external to the relay rack such as pumps, heaters, and so forth would also be shown on the ladder diagram. Ladder logic has evolved into a programming language that represents a program by a graphical diagram based on the circuit diagrams of relay logic hardware. Ladder logic is used to develop software for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in industrial control applications. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical rails and a series of horizontal rungs between them. While ladder diagrams were once the only available notation for recording programmable controller programs, today other forms are standardized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
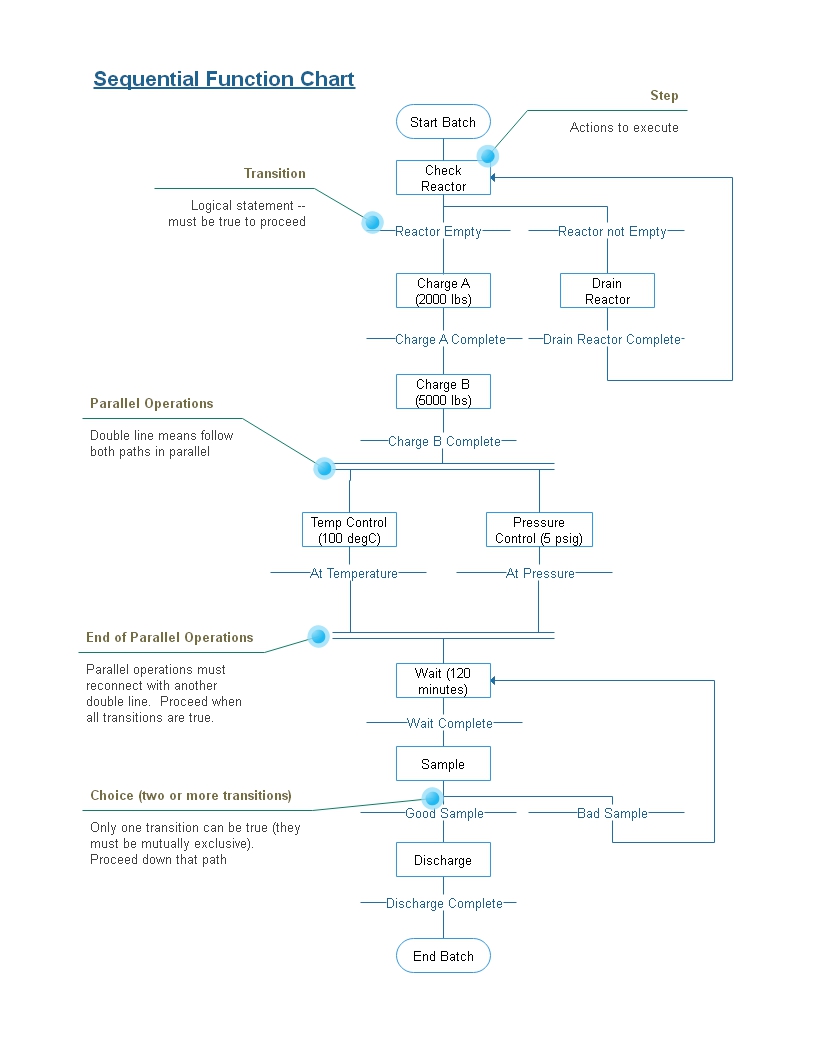
Sequential Function Chart
Sequential function chart (SFC) is a visual programming language used for programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It is one of the five languages defined by IEC 61131-3 standard. The SFC standard is defined as ''Preparation of function charts for control systems'', and was based on (itself based on binary Petri nets). It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps. Main components of SFC are: * Steps with associated actions; * Transitions with associated logic conditions; * Directed links between steps and transitions. Steps in an SFC diagram can be active or inactive. Actions are only executed for active steps. A step can be active for one of two motives: * It is an initial step as specified by the programmer. * It was activated during a scan cycle and not deactivated since. Steps are activated when all steps above it are active and the connecting transition is superable (i.e. its associated condition is true). When a transition is passed, all steps above are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Text
Structured text, abbreviated as ST or STX, is one of the five languages supported by the IEC 61131-3 standard, designed for programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It is a high level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to: People and fictional characters * Pascal (given name), including a list of people with the name * Pascal (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name ** Blaise Pascal, Fren ..., on which it is based. All of the languages share IEC61131 Common Elements. The variables and function calls are defined by the common elements so different languages within the IEC 61131-3 standard can be used in the same program. Complex statements and nested instructions are supported: * Iteration loops (REPEAT-UNTIL; WHILE-DO) * Conditional execution (IF-THEN-ELSE; CASE) * Functions (SQRT(), SIN()) Sample program (* simple state machine *) TxtState := STATES tateMachine CAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)