|
Frozen Mirror Image Method
Frozen mirror image method (or method of frozen images) is an extension of the method of images for magnet- superconductor systems that has been introduced by Alexander Kordyuk in 1998 to take into account the magnetic flux pinning phenomenon. The method gives a simple representation of the magnetic field distribution generated by a magnet (a system of magnets) outside an infinitely flat surface of a perfectly hard (with infinite pinning force) type-II superconductor in more general field cooled (FC) case, i.e. when the superconductor goes into superconducting state been already exposed to the magnetic field. The difference from the mirror image method, which deals with a perfect type-I superconductor (that completely expels the magnetic field, see the Meissner effect), is that the perfectly hard superconductor screens the variation of the external magnetic field rather than the field itself. Description The name originates from the replacement of certain elements in the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frozen Image Method
Frozen may refer to: * the result of freezing * a paralysis response in extreme cases of fear Films * ''Frozen'' (1997 film), a film by Wang Xiaoshuai * ''Frozen'' (2005 film), a film by Juliet McKoen * ''Frozen'' (2007 film), a film by Shivajee Chandrabhushan * ''Frozen'' (2010 American film), a thriller film by Adam Green * ''Frozen'' (2010 Hong Kong film), a film by Derek Kwok * ''Frozen'' (franchise), a Disney media franchise based on the 2013 film ** ''Frozen'' (2013 film), a Disney animated film inspired by Hans Christian Andersen's ''The Snow Queen'' **'' Frozen Fever'' (2015), a short sequel to the film ''Frozen'' (2013) ** ''Olaf's Frozen Adventure'' (2017), a featurette short sequel to the film ''Frozen'' (2013) ** '' Frozen II'' (2019), the sequel to the film ''Frozen'' (2013) * Frozen (advertisement), a 2014 political advertisement Music Albums * ''Frozen'' (album), by Sentenced, released in 1998 * ''Frozen'' (EP), an EP by Curve * ''Frozen'' (soundtra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Temperature Superconductors
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previously known superconductors, which function at even colder temperatures close to absolute zero. In absolute terms, these "high temperatures" are still far below ambient, and therefore require cooling. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986, by IBM researchers Bednorz and Müller, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled by using liquid nitrogen, as opposed to the previously known superconductors which require expensive and hard-to-handle coolants, primarily liquid helium. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bean's Critical State Model
Bean's critical state model, introduced by C. P. Bean in 1962, gives a macroscopic explanation of the irreversible magnetization behavior ( hysteresis) of hard Type-II superconductors. Assumptions Hard superconductors often exhibit hysteresis in magnetization measurements. C. P. Bean postulated for the Shubnikov phase an extraordinary shielding process due to the microscopic structure of the materials. He assumed lossless transport with a critical current density ''Jc(B)'' ''(Jc(B→0) = const.'' and ''Jc(B→∞) = 0)''. An external magnetic field is shielded in the Meissner phase (''H < Hc1'') in the same way than in a soft superconductor. In the Shubnikov phase ''(Hc1 < H < Hc2)'', the critical current flows below the surface within a depth necessary to reduce the field in the inside of the superconductor to ''Hc1''. Explanation of the irreversible magnetization [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
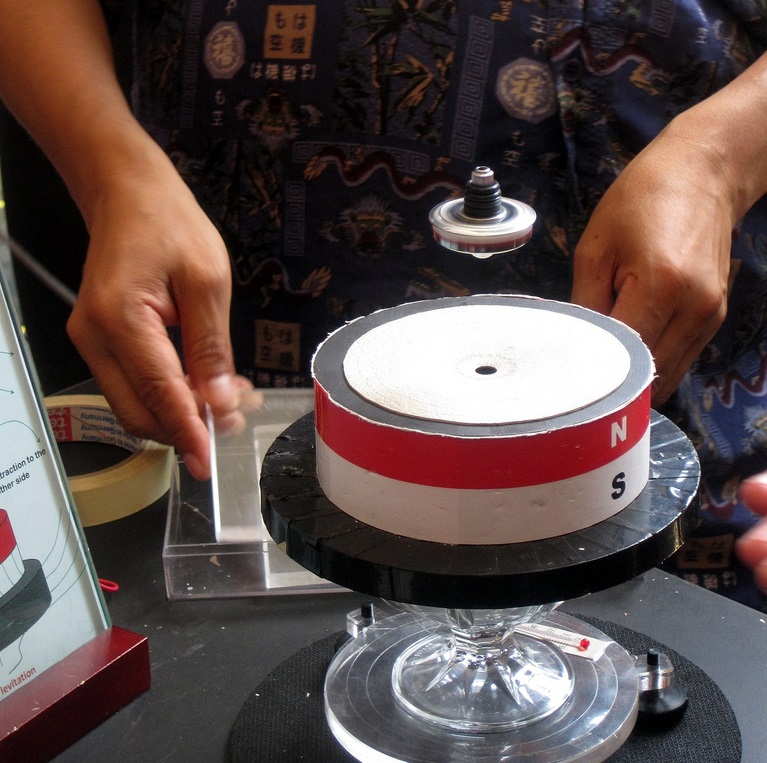
Magnetic Levitation
Magnetic levitation (maglev) or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces. The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are ''lifting forces'': providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and ''stability'': ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized. Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, contactless melting, magnetic bearings and for product display purposes. Lift Magnetic materials and systems are able to attract or repel each other with a force dependent on the magnetic field and the area of the magnets. For example, the simplest example of lift would be a simple dipole magnet positioned in the magnetic fields of another dipole magnet, oriented with like poles facing each other, so that the force between mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Method Of Images
The method of images (or method of mirror images) is a mathematical tool for solving differential equations, in which the domain of the sought function is extended by the addition of its mirror image with respect to a symmetry hyperplane. As a result, certain boundary conditions are satisfied automatically by the presence of a mirror image, greatly facilitating the solution of the original problem. The domain of the function is not extended. The function is made to satisfy given boundary conditions by placing singularities outside the domain of the function. The original singularities are inside the domain of interest. The additional (fictitious) singularities are an artifact needed to satisfy the prescribed but yet unsatisfied boundary conditions. Method of image charges The method of image charges is used in electrostatics to simply calculate or visualize the distribution of the electric field of a charge in the vicinity of a conducting surface. It is based on the fact that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Journal Of Physics
The ''European Journal of Physics'' is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal dedicated to maintaining and improving the standard of physics education in higher education. The journal, published since 1980, is now published by IOP Publishing on behalf of the European Physical Society. The current editor-in-chief is Mojca Čepič of the Ljubljana University, Slovenia. It does not include original research in physics, but rather: *Surveys of research at a level accessible to students *Original insights into the derivation of results *Descriptions of new laboratory exercises *Scholarly or reflective articles at appropriate levels *Descriptions of successful original student projects *Discussions of the history and philosophy of physics. *Reports of new developments in methods for teaching physics and in the physics curriculum. The journal had an Impact factor of 0.781 for 2020, according to the Journal Citation Reports. It is indexed In Chemical Abstracts, Engineering Index/Ei C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Education
Science education is the teaching and learning of science to school children, college students, or adults within the general public. The field of science education includes work in science content, science process (the scientific method), some social science, and some teaching pedagogy. The standards for science education provide expectations for the development of understanding for students through the entire course of their K-12 education and beyond. The traditional subjects included in the standards are physical, life, earth, space, and human sciences. Historical background The first person credited with being employed as a science teacher in a British public school was William Sharp, who left the job at Rugby School in 1850 after establishing science to the curriculum. Sharp is said to have established a model for science to be taught throughout the British public school system.Bernard Leary, 'Sharp, William (1805–1896)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textbook
A textbook is a book containing a comprehensive compilation of content in a branch of study with the intention of explaining it. Textbooks are produced to meet the needs of educators, usually at educational institutions. Schoolbooks are textbooks and other books used in schools. Today, many textbooks are published in both print and digital formats. History The history of textbooks dates back to ancient civilizations. For example, Ancient Greeks wrote educational texts. The modern textbook has its roots in the mass production made possible by the printing press. Johannes Gutenberg himself may have printed editions of ''Ars Minor'', a schoolbook on Latin grammar by Aelius Donatus. Early textbooks were used by tutors and teachers (e.g. alphabet books), as well as by individuals who taught themselves. The Greek philosopher Socrates lamented the loss of knowledge because the media of transmission were changing. Before the invention of the Greek alphabet 2,500 years ago, knowledge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancelation of the magnetic field in the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the superco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAGLEV
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of friction. Such trains rise approximately off the track. There are both high speed, intercity maglev systems (over ), and low speed, urban maglev systems ( to ) being built and under construction and development. With maglev technology, the train travels along a guideway of electromagnets which control the train's stability and speed. While the propulsion and levitation require no moving parts, the bogies can move in relation to the main body of the vehicle and some technologies require support by retractable wheels at low speeds under . This compares with electric multiple units that may have several dozen parts per bogie. Maglev trains can therefore in some cases be quieter and smoother than conventional trains and have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Transactions On Magnetics
''IEEE Transactions on Magnetics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers the basic physics of magnetism, magnetic materials, applied magnetics, magnetic devices, and magnetic data storage. The editor-in-chief is Pavel Kabos (National Institute of Standards and Technology). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Science Citation Index, Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences, Scopus, CSA databases, and EBSCOhost. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a recent impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 1.7. References External links * {{Official website, 1=http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=20 Physics journals Materials science journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |