|
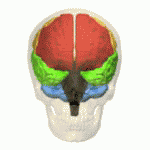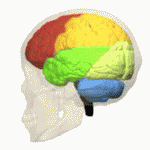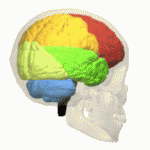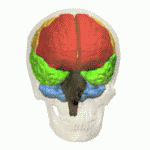
Frontal Lobe Injury
The frontal lobe of the human brain is both relatively large in mass and less restricted in movement than the posterior portion of the brain. It is a component of the cerebral system, which supports goal directed behavior. This lobe is often cited as the part of the brain responsible for the ability to decide between good and bad choices, as well as recognize the consequences of different actions. Because of its location in the anterior part of the head, the frontal lobe is arguably more susceptible to injuries. Following a frontal lobe injury, an individual's abilities to make good choices and recognize consequences are often impaired. Memory impairment is another common effect associated with frontal lobe injuries, but this effect is less documented and may or may not be the result of flawed testing. Damage to the frontal lobe can cause increased irritability, which may include a change in mood and an inability to regulate behavior. Particularly, an injury of the frontal lobe c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Lobes Animation Small2
4 (four) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is tetraphobia, considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically 3, three. The sum of the first four prime numbers 2, two + 3, three + 5, five + 7, seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an Parity (mathematics), odd prime number, 17 (number), seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, 3, three and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
The Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) is a neuropsychological test of set-shifting, which is the capability to show flexibility when exposed to changes in reinforcement.E. A. Berg. (1948). A simple objective technique for measuring flexibility in thinking J. Gen. Psychol. 39: 15-22. The WCST was written by David A. Grant and Esta A. Berg. ''The Professional Manual for the WCST'' was written by Robert K. Heaton, Gordon J. Chelune, Jack L. Talley, Gary G. Kay, and Glenn Curtiss. Method Stimulus cards are shown to the participant and the participant is then instructed to match the cards. They are not given instructions on how to match the cards but are given feedback when the matches they make are right or wrong. When the test was first released the method of showing the cards was done with an evaluator using paper cards with the evaluator on one side of the desk facing the participant on the other. The test takes approximately 12–20 minutes to carry out using manual scoring which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressive Aphasia
Expressive aphasia, also known as Broca's aphasia, is a type of aphasia characterized by partial loss of the ability to produce language ( spoken, manual, or written), although comprehension generally remains intact. A person with expressive aphasia will exhibit effortful speech. Speech generally includes important content words but leaves out function words that have more grammatical significance than physical meaning, such as prepositions and articles. This is known as "telegraphic speech". The person's intended message may still be understood, but their sentence will not be grammatically correct. In very severe forms of expressive aphasia, a person may only speak using single word utterances.ASHA.orgAppendix: Common Classifications of Aphasia. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.asha.org/Practice-Portal/Clinical-Topics/Aphasia/Common-Classifications-of-Aphasia/ Typically, comprehension is mildly to moderately impaired in expressive aphasia due to difficulty understanding complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobotomy
A lobotomy, or leucotomy, is a form of neurosurgical treatment for psychiatric disorder or neurological disorder (e.g. epilepsy) that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal cortex. The surgery causes most of the connections to and from the prefrontal cortex, the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, to be severed. In the past, this treatment was used for treating psychiatric disorders as a mainstream procedure in some countries. The procedure was controversial from its initial use, in part due to a lack of recognition of the severity and chronicity of severe and enduring psychiatric illnesses, so it was claimed to be an inappropriate treatment. Frontal lobe surgery, including lobotomy, is the second most common surgery for epilepsy to this day, and usually done on one side of the brain, unlike lobotomies for psychiatric disorder which were done on both sides of the brain. The originator of the procedure, Portuguese neurologist António Egas Moniz, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourmand Syndrome
Gourmand syndrome is a very rare and benign eating disorder that usually occurs six to twelve months after an injury to the frontal lobe. Those with the disorder usually have a right hemisphere frontal or temporal brain lesion typically affecting the cortical areas, basal ganglia or limbic structures. These people develop a new, post-injury passion for gourmet food. There are two main aspects of gourmand syndrome: first, the fine dining habits and changes to taste, and second, the obsessive component, which may result in craving and preservation. Gourmand syndrome can be related to, and shares biological features with, addictive and obsessive disorders. The syndrome was first characterised in 1997. Signs and symptoms * A new-found obsession for fine foods * Wanting to write, talk, eat, about refined foods Causes It is believed that the frontotemporal circuits, normally involved in healthy eating, can, when injured, cause gourmand syndrome in patients. History Only 36 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe Disorder
Frontal lobe disorder, also frontal lobe syndrome, is an impairment of the frontal lobe that occurs due to disease or frontal lobe injury. The frontal lobe of the brain plays a key role in executive functions such as motivation, planning, social behaviour, and speech production. Frontal lobe syndrome can be caused by a range of conditions including head trauma, tumours, neurodegenerative diseases, Neurodevelopmental disorders, neurosurgery and cerebrovascular disease. Frontal lobe impairment can be detected by recognition of typical signs and symptoms, use of simple screening tests, and specialist neurological testing. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of frontal lobe disorder can be indicated by dysexecutive syndrome which consists of a number of symptoms which tend to occur together. Broadly speaking, these symptoms fall into three main categories; cognitive (movement and speech), emotional or behavioral. Although many of these symptoms regularly co-occur, it is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Brain Injuries
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic brain injury), mechanism ( closed or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death. Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardized Tests
A standardized test is a test that is administered and scored in a consistent, or "standard", manner. Standardized tests are designed in such a way that the questions and interpretations are consistent and are administered and scored in a predetermined, standard manner. Any test in which the same test is given in the same manner to all test takers, and graded in the same manner for everyone, is a standardized test. Standardized tests do not need to be high-stakes tests, time-limited tests, or multiple-choice tests. A standardized test may be any type of test: a written test, an oral test, or a practical skills performance test. The questions can be simple or complex. The subject matter among school-age students is frequently academic skills, but a standardized test can be given on nearly any topic, including driving tests, creativity, athleticism, personality, professional ethics, or other attributes. The opposite of standardized testing is ''non-standardized testing'', in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subjectivity
Subjectivity in a philosophical context has to do with a lack of objective reality. Subjectivity has been given various and ambiguous definitions by differing sources as it is not often the focal point of philosophical discourse.Bykova, Marina F. (February 2018). "On the Problem of Subjectivity: Editor's Introduction". ''Russian Studies in Philosophy''. 56: 1-5 - via EBSCOhost. However, it is related to ideas of consciousness, agency, personhood, philosophy of mind, reality, and truth. Three common definitions include that subjectivity is the quality or condition of: * Something being a ''subject'', narrowly meaning an individual who possesses conscious experiences, such as perspectives, feelings, beliefs, and desires. Solomon, Robert C. "Subjectivity," in Honderich, Ted. '' Oxford Companion to Philosophy (Oxford University Press, 2005), p.900. * Something being a ''subject'', broadly meaning an entity that has agency, meaning that it acts upon or wields power over some other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-taking
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas ( business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Control
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence (e.g., reasoning and problem-solving). Executive functions gradually develop and change across the lifespan of an individual and can be improved at any time over the course of a person's life. Similarly, these cognitive processes can be adversely affected by a variety of events which affect an individual. Both neuropsychological tests (e.g., the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |