|
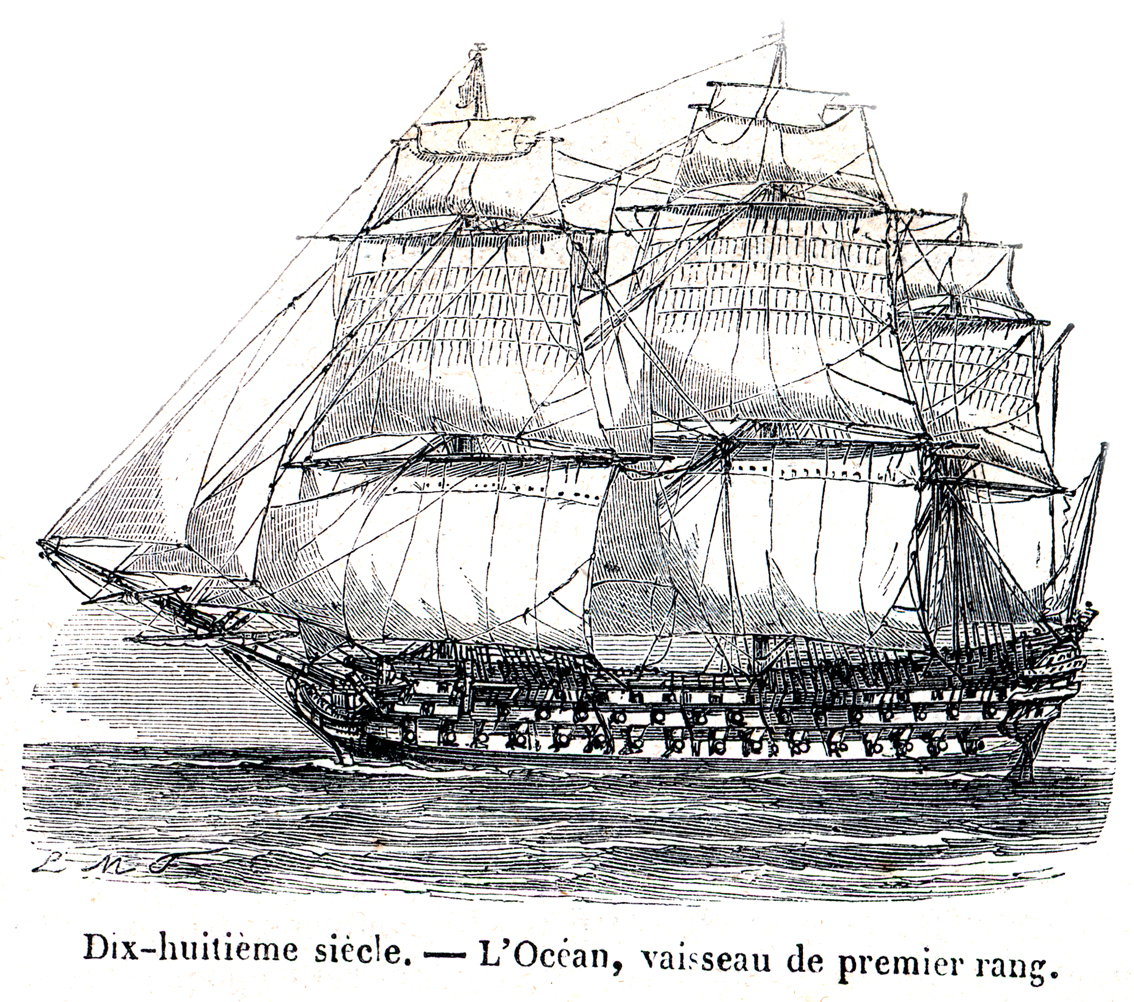
French Ship Océan (1790)
''Océan'' was a 118-gun first-rate three-decker ship of the line of the French Navy, lead ship''Commerce de Marseille'' was ordered after ''États de Bourgogne'' (which was later renamed ''Océan''), but launched before her; therefore, the ship type is alternatively called ''Commerce de Marseille'' class or ''Océan'' class of her class. She was funded by a don des vaisseaux donation from the Estates of Bourgogne. She was ordered as ''États de Bourgogne'' and was launched at Brest in 1790. Like many French ships of the line during the Revolutionary period, she was renamed several times, becoming ''Côte d'Or'' in January 1793, ''Montagne'' in October 1793, ''Peuple'' on 17 May 1795, and a matter of weeks later again renamed, to ''Océan''. She served until 1855. A large model of a generic ''Océan''-class ship, named ''Océan'', at the scale can be seen at the Musée de la Marine in Paris. Career As the largest ship of the line in the Brest fleet, the ship spent muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Battery
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facilitate better battlefield communication and command and control, as well as to provide dispersion for its constituent gunnery crews and their systems. The term is also used in a naval context to describe groups of guns on warships. Land usage Historically the term "battery" referred to a cluster of cannon in action as a group, either in a temporary field position during a battle or at the siege of a fortress or a city. Such batteries could be a mixture of cannon, howitzer, or mortar types. A siege could involve many batteries at different sites around the besieged place. The term also came to be used for a group of cannon in a fixed fortification, for coastal or frontier defence. During the 18th century "battery" began to be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Decommissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Basque Roads
The Battle of the Basque Roads, also known as the Battle of Aix Roads (French: ''Bataille de l'île d'Aix'', also ''Affaire des brûlots'', rarely ''Bataille de la rade des Basques''), was a major naval battle of the Napoleonic Wars, fought in the narrow Basque Roads at the mouth of the Charente River on the Biscay coast of France. The battle, which lasted from 11–24 April 1809, was unusual in that it pitted a hastily-assembled squadron of small and unorthodox British Royal Navy warships against the main strength of the French Atlantic Fleet, the circumstances dictated by the cramped, shallow coastal waters in which the battle was fought. The battle is also notorious for its controversial political aftermath in both Britain and France. In February 1809 the French Atlantic Fleet, blockaded in Brest on the Breton coast by the British Channel Fleet, attempted to break out into the Atlantic and reinforce the garrison of Martinique. Sighted and chased by British blockade squadrons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacharie Allemand
Zacharie Jacques Théodore Allemand (1 May 1762, in Port-Louis, Morbihan, Port-Louis – 2 March 1826, in Toulon) was a French admiral. Biography Early career Allemand was born to a captain of the East Indian Company. Orphaned at an early age, he started his sailing career at 12 as an apprentice on ''Superbe'', an East Indiaman. In 1778, at the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, American War of Independence, he volunteered for Navy service of ''Sévère'', in Suffren's squadron. By the end of the war, Allemand had risen to lieutenant de frégate and served on French ship Annibal (1779), ''Annibal''. He later went on to serve on the fluyts ''Baleine'' and ''Outarde'' in the Indian Ocean. In late 1786, Allemand returned to France to benefit from a reform of the Navy by which he could obtain a permanent commission of ''sous-lieutenant de vaisseau'' for his service. In this capacity, he served on a number of frigates in the Caribbean and off America. French Revolution an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer specifically to the Spanish-held Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, now the Dominican Republic. The borders between the two were fluid and changed over time until they were finally solidified in the Dominican War of Independence in 1844. The French had established themselves on the western portion of the islands of Hispaniola and Tortuga by 1659. In the Treaty of Ryswick of 1697, Spain formally recognized French control of Tortuga Island and the western third of the island of Hispaniola. In 1791, slaves and some Dominican Creoles took part in the Vodou ceremony Bois Caïman and planned the Haitian Revolution. The slave rebellion later allied with Republican French forces following the abolition of slavery in the colony in 1793, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Leclerc (general, Born 1772)
Charles Victoire Emmanuel Leclerc (17 March 1772 – 2 November 1802) was a French Army general who served under Napoleon Bonaparte during the French Revolution. He was husband to Pauline Bonaparte, sister to Napoleon. In 1801, he was sent to Saint-Domingue (Haiti), where an expeditionary force under his command captured and deported the Haitian leader Toussaint L'Ouverture, as part of an unsuccessful attempt to reassert imperial control over the Saint-Domingue government. Leclerc died of yellow fever during the failed expedition. Biography To 1801 Leclerc started his military career in 1791 during the French Revolution as one of the army volunteers of Seine-et-Oise and passed through the ranks of sous-lieutenant in the 12th Cavalry, then aide-de-camp to general Lapoype. He was made a captain and divisional chief of staff during the siege of Toulon, at which he first allied himself to Napoleon Bonaparte. Following the revolutionary success there, he campaigned along the Rhine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorient
Lorient (; ) is a town ('' commune'') and seaport in the Morbihan department of Brittany in western France. History Prehistory and classical antiquity Beginning around 3000 BC, settlements in the area of Lorient are attested by the presence of Megalith, megalithic architecture. Ruins of Roman roads (linking Vannes to Quimper and Port-Louis, Morbihan, Port-Louis to Carhaix) confirm Gallo-Roman presence. Founding In 1664, Jean-Baptiste Colbert founded the French East Indies Company. In June 1666, an Ordonnance, ordinance of Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV granted lands of Port-Louis, Morbihan, Port-Louis to the company, along with Faouédic on the other side of the roadstead. One of its directors, Denis Langlois, bought lands at the confluence of the Scorff and the Blavet rivers, and built slipways. At first, it only served as a subsidiary of Port-Louis, where offices and warehouses were located. The following years, the operation was almost abandoned, but in 1675, durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Groix
The Battle of Groix was a large naval engagement which took place near the island of Groix off the Biscay coast of Brittany on 23 June 1795 ( 5 messidor an III) during the French Revolutionary Wars. The battle was fought between elements of the British Channel Fleet and the French Atlantic Fleet, which were cruising in the region on separate missions. The British fleet, commanded by Admiral Lord Bridport, was covering an invasion convoy carrying a French Royalist army to invade Quiberon, while the French under Vice-admiral Villaret de Joyeuse had sailed a week earlier to rescue a French convoy from attack by a British squadron. The French fleet had driven off the British squadron in a battle on 17 June known as Cornwallis's Retreat, and were attempting to return to their base at Brest when Bridport's force of 14 ships of the line appeared on 22 June. Villaret, believing that the stronger British fleet would destroy his own 12 ships of the line, ordered his force to fall ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious First Of June
The Glorious First of June (1 June 1794), also known as the Fourth Battle of Ushant, (known in France as the or ) was the first and largest fleet action of the naval conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the First French Republic during the French Revolutionary Wars. The action was the culmination of a campaign that had criss-crossed the Bay of Biscay over the previous month in which both sides had captured numerous merchant ships and minor warships and had engaged in two partial, but inconclusive, fleet actions. The British Channel Fleet under Admiral Lord Howe attempted to prevent the passage of a vital French grain convoy from the United States, which was protected by the French Atlantic Fleet, commanded by Rear-Admiral Villaret-Joyeuse. The two forces clashed in the Atlantic Ocean, some west of the French island of Ushant on 1 June 1794. During the battle, Howe defied naval convention by ordering his fleet to turn towards the French and for each of his ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Thomas Villaret De Joyeuse
Louis-Thomas Villaret de Joyeuse (29 May 1747Granier, p.87Some biographers give a date of 1750 (Levot, p.541). Granier quotes the registers of Sainte-Marie parish. – 24 July 1812Levot, p.544) was a French admiral. Villaret was born at Auch. After serving in the Indies under Suffren, he rose in rank during the early stages of the French Revolution. He was in command of the French fleet during the Glorious First of June, where despite being handed a heavy tactical defeat, he ensured the passage of a vital grain convoy to France. He led the French fleet during the disastrous Croisière du Grand Hiver and failed to prevent a British fleet from successfully retreating, with his last battle being a defeat off Groix. He was relieved when he refused to serve for the disastrous Expédition d'Irlande. Villaret was then elected at the Council of Five Hundred. He joined the Club de Clichy, a party promoting colonies and slavery, and harbouring Royalist sympathies. After the Coup of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_underway_2009.jpg)




