|
French Frigate Vertu (1794)
''Vertu'' was a 40-gun French frigate designed by engineer Segondat. She served in Sercey's squadron in the Indian Ocean, and in Saint-Domingue. She was captured by the Royal Navy at the end of the Blockade of Saint-Domingue when the island surrendered to the British. After her capture the Navy sailed her to Britain but never commissioned her, and finally sold her in 1810. French career Ordered as ''Vertu'' at the heigh of the Reign of Terror, the frigate was commissioned in Lorient. In May 1793, she sailed from Brest to Île-d'Aix under Captain Montagniès-Laroque She took part in the Croisière du Grand Hiver in December 1794, and escorted the 74-gun ''Redoutable'' after she broke her cables upon departure.Troude, vol.2, p. 366 On 3 February, a violent gust of wind damaged Sercey's naval division, which was readying for a transit to Mauritius and a campaign in the Indian Ocean, damaging ''Cocarde'';Troude, vol.3, p. 16 ''Vertu'', under Lhermite, was chosen to replace her. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Régénérée (1794)
''Régénérée'' was a 40-gun ''Cocarde''-class frigate of the French Navy. The British captured her in 1801 at the fall of Alexandria, named her HMS ''Alexandria'', sailed her back to Britain, but never commissioned her. She was broken up in 1804. Service In 1796, she was commanded by captain Willaumez, in a squadron under Sercey. On 15 May 1796 '' ''Forte'' '', ''Vertu'', ''Seine'', and ''Régénérée'' were cruising between St Helena and the Cape of Good Hope hoping to capture British East Indiamen when they encountered the British whaler on her way to Walvis Bay. The French took off her crew, except for two seamen and a boy, and put ''Forte''s fourth officer and 13-man prize crew aboard ''Lord Hawkesbury'' with orders to sail to Île de France. On her way there one of the British seamen, who was at the helm, succeeded in running her aground on the east coast of Africa a little north of the Cape, wrecking her. There were no casualties, but the prize crew became Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockade Of Saint-Domingue
The Blockade of Saint-Domingue was a naval campaign fought during the first months of the Napoleonic Wars in which a series of British Royal Navy squadrons blockaded the French-held ports of Cap Français and Môle-Saint-Nicolas on the northern coast of the French colony of Saint-Domingue, soon to become Haiti, after the conclusion of the Haitian Revolution on 1 January 1804. In the summer of 1803, when war broke out between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and the French Consulate, Saint-Domingue had been almost completely overrun by Haitian forces commanded by Jean-Jacques Dessalines. In the north of the country, the French forces were isolated in the two large ports of Cap Français and Môle-Saint-Nicolas and a few smaller settlements, all supplied by a French naval force based primarily at Cap Français. At the outbreak of war on 18 May 1803, the Royal Navy immediately despatched a squadron under Sir John Duckworth, 1st Baronet, Sir John Duckwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle De France (Mauritius)
Isle de France () was the name of the Indian Ocean island which is known as Mauritius and its dependent territories between 1715 and 1810, when the area was under the French East India Company and a part of the French colonial empire. Under the French, the island witnessed major changes. The increasing importance of agriculture led to the importation of slaves and the undertaking of vast infrastructural works that transformed Port Louis into a major capital, port, warehousing, and commercial centre. During the Napoleonic Wars, Isle de France became a base from which the French navy, including squadrons under Rear Admiral Linois or Commodore Jacques Hamelin, and corsairs such as Robert Surcouf, organised raids on British merchant ships. The raids (see Battle of Pulo Aura and Mauritius campaign of 1809–1811) continued until 1810 when the British sent a strong expedition to capture the island. The first British attempt, in August 1810, to attack Grand Port resulted in a Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
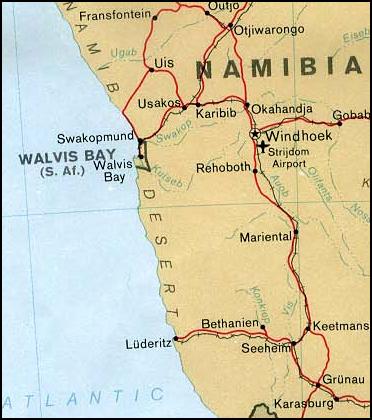
Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay ( en, lit. Whale Bay; af, Walvisbaai; ger, Walfischbucht or Walfischbai) is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies. It is the second largest city in Namibia and the largest coastal city in the country. The city covers a total area of of land. The bay is a safe haven for sea vessels because of its natural deepwater harbour, protected by the Pelican Point sand spit, being the only natural harbour of any size along the country's coast. Being rich in plankton and marine life, these waters also drew large numbers of southern right whales, attracting whalers and fishing vessels. A succession of colonists developed the location and resources of this strategic harbour settlement. The harbour's value in relation to the sea route around the Cape of Good Hope had caught the attention of world powers since it was discovered by the outside world in 1485. This explains the complicated political status of Walvis Bay down the years. The town is situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales. Terminology The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japan, still dedicates a single factory ship for the industry. The vessels used by aboriginal whaling communities are much smaller and are used for various purposes over the course of the year. The ''whale catcher'' was developed during the age of steam, and then driven by diesel engines throughout much of the twentieth century. It was designed with a harpoon gun mounted at its bow and was fast enough to chase and catch rorquals such as the fin whale. At first, whale catchers either brought the whales they killed to a whaling station, a settlement ashore where the carcasses could be processed, or to its factory ship anchored in a sheltered bay or inlet. With the later development of the slipway at the ship's stern, whale catchers were able ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indiamen
East Indiaman was a general name for any sailing ship operating under charter or licence to any of the East India trading companies of the major European trading powers of the 17th through the 19th centuries. The term is used to refer to vessels belonging to the Austrian, Danish, Dutch, English, French, Portuguese, or Swedish companies. Some of the East Indiamen chartered by the British East India Company were known as "tea clippers". In Britain, the East India Company held a monopoly granted to it by Queen Elizabeth I of England in 1600 for all English trade between the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Horn. This grant was progressively restricted during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, until the monopoly was lost in 1834. English (later British) East Indiamen usually ran between England, the Cape of Good Hope and India, where their primary destinations were the ports of Bombay, Madras and Calcutta. The Indiamen often continued on to China before returning to England via t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, based on the misbelief that the Cape was the dividing point between the Atlantic and Indian oceans, and have nothing to do with north or south. In fact, by looking at a map, the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas about to the east-southeast. The currents of the two oceans meet at the point where the warm-water Agulhas current meets the cold-water Benguela current and turns back on itself. That oceanic meeting point fluctuates between Cape Agulhas and Cape Point (about east of the Cape of Good Hope). When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward. Thus, the first mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about and has a population of 4,439 per the 2021 census. It was named after Helena, mother of Constantine I. It is one of the most remote islands in the world and was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese enroute to the Indian subcontinent in 1502. For about four centuries the island was an important stopover for ships from Europe to Asia and back, while sailing around the African continent, until the opening of the Suez canal. St Helena is the United Kingdom's second-oldest overseas territory after Bermuda. Saint Helena is known for being the site of Napoleon's second exile, following his final defeat in 1815. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Seine (1798)
''Seine'' was a 38-gun French ''Seine''-class frigate that the Royal Navy captured in 1798 and commissioned as the fifth-rate HMS ''Seine''. On 20 August 1800, ''Seine'' captured the French ship in a single ship action that would win for her crew the Naval General Service Medal. ''Seine's'' career ended in 1803 when she hit a sandbank near the Texel. French career ''Seine'' was a 40-gun frigate built between May 1793 and March 1794 at Le Havre, having been launched on 19 December 1793. ''Seine''s career with the French Navy lasted less than five years. On 14 July 1794 she and captured the 16-gun sloop-of-war in the Atlantic. In late 1794, L'Hermitte's squadron sailed for Norway. It comprised the frigates ''Seine'', under L'Hermitte, ''Galathée'', under Labutte, and , under Le Bozec. The squadron found itself blocked by cold and damage in a Norwegian harbour during the entire winter of 1794–95, sustaining over 250 dead from illness out of a total complement of 880. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Forte (1794)
''Forte'' was a French 42-gun frigate, lead ship of her class. Career French service Launched on 26 September 1794 and commissioned two months later under Commander Beaulieu-Leloup, ''Forte'' was part of a large frigate squadron under contre-amiral Sercey, also comprising , , ''Vertu'', , and . The division sailed to Ile de France to raid commerce in the Indian Ocean. On 15 May 1796 ''Forte'', ''Vertu'', ''Seine'', and ''Régénérée'' were cruising between St Helena and the Cape of Good Hope hoping to capture British East Indiamen when they encountered the British whaler on her way to Walvis Bay. The French took off her crew, except for two seamen and a boy, and put ''Forte''s fourth officer and 13-man prize crew aboard ''Lord Hawkesbury'' with orders to sail to Île de France. On her way there one of the British seamen, who was at the helm, succeeded in running her aground on the east coast of Africa a little north of the Cape, wrecking her. There were no casualties, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Cocarde (1794)
The ''Cocarde'' ("Cockade") was a 40-gun ''Cocarde'' class frigate of the French Navy. Ordered as ''Cocarde nationale'', she was launched on 29 April 1794 in Saint Malo and commissioned in July under Lieutenant Allanic. Under Captain Quérangal, she took part in the Battle of Groix. She later took part in the Expédition d'Irlande The French expedition to Ireland, known in French as the ''Expédition d'Irlande'' ("Expedition to Ireland"), was an unsuccessful attempt by the French Republic to assist the outlawed Society of United Irishmen, a popular rebel Irish republica .... She was renamed ''Cocarde'' in June 1796. In 1802, she served in the Caribbean. A series of beachings damaged her sails and hull to the point where she was condemned and broken up in 1803. Sources and references * {{DEFAULTSORT:Cocarde Cocarde-class frigates Age of Sail frigates of France 1794 ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)