|
French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in the world, ranking seventh in combined fleet tonnage and fifth in number of naval vessels. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the U.S., U.K., China, Russia, Italy, India and Spain with its flagship being the only nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the 17th century, the French Navy is one of the oldest navies still in continual service, with precursors dating back to the Middle Ages. It has taken part in key events in French history, including the Napoleonic Wars and both world wars, and played a critical role in establishing and securing the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications (brown-water navy), open-ocean applications (blue- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzaoudzi
Dzaoudzi is a commune in the French overseas department of Mayotte, in the Indian Ocean. The commune of Dzaoudzi (sometimes called Dzaoudzi-Labattoir), made up of the twin towns of Dzaoudzi and Labattoir, is located on the small island of Petite-Terre (or Pamanzi). It was previously the capital of Mayotte, but the capital was relocated in 1977 to Mamoudzou, on the island of Grande-Terre Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe ... (Maore), the main island of Mayotte. The Foreign Legion Detachment in Mayotte has been based in Dzaoudzi (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip V of Spain, Philip of Anjou and Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters, among them Spanish Empire, Spain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of France, France, the Dutch Republic, Savoyard state, Savoy and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Related conflicts include the 1700–1721 Great Northern War, Rákóczi's War of Independence in Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867), Hungary, the Camisards revolt in southern France, Queen Anne's War in North America and minor trade wars in colonial India, India and New Spain, South America. Although weakened by over a century of continuous conflict, Spain remained a global power whose territories included the Spanish Netherlands, large parts of Italy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarchy), the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy, Sweden and Portugal. Although not the first European war to spill over to Europe's overseas colonies, the events of the war spread to such far away places as the Americas, India, and West Africa. It is for this reason that it is sometimes considered the first world war. The conflict encompassed the Glorious Revolution in England, where William of Orange deposed the unpopular James VII and II and subsequently struggled against him for control of Scotland and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Native American allies. Louis XIV of France had emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
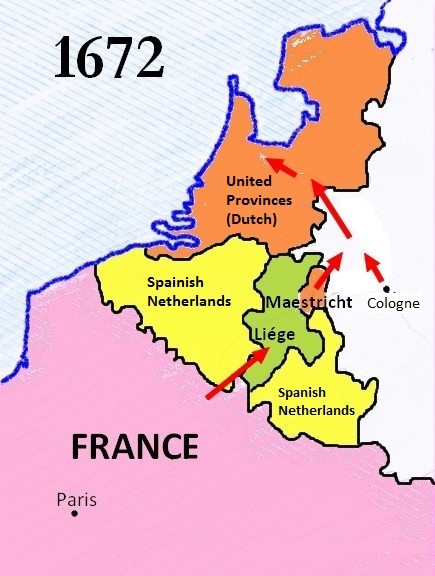
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the '' Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas and trade routes, where England tried to end the Dutch domination of world trade during a period of intense European commercial rivalry, but also as a result of political tensions. After initial English successes, the war ended in a Dutch victory. It was the second of a series of naval wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries. Background Anglo-Dutch relations Traditionally, many historians considered that the First and Second Anglo-Dutch Wars arose from commercial and maritime rivalry between England and the Netherlands. Although continuing commercial tensions formed the background to the second war, a group of ambitious English politicians and naval officers frustrated diplomatic efforts to reach any accommodation be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
The Anglo-French War () was a military conflict fought between the Kingdom of France and the Kingdom of England between 1627 and 1629. It mainly involved actions at sea.''Warfare at sea, 1500-1650: maritime conflicts and the transformation of Europe'' by Glete J Staff, Jan Glete Routledge, 2002 p.17/ref> The centrepiece of the conflict was the siege of La Rochelle (1627–28), in which the English Crown supported the French Huguenots in their fight against the French royal forces of Louis XIII of France. La Rochelle had become the stronghold of the French Huguenots, under its own governance. It was the centre of Huguenot seapower and the strongest centre of resistance against the central government. The English also launched a campaign against France's new colony in North America which led to the capture of Quebec. In 1626, France concluded a secret peace with Spain, and disputes arose around Henrietta Maria's household. Furthermore, France began building up its navy, leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current French Navy Ships
This is a list of active French Navy ships. The French Navy consists of nearly 100 vessels of the '' Force d'action navale'' (Naval action force) and the 9 submarines of the '' Forces sous-marines'' (Submarine force). Primary assets include 1 nuclear aircraft carrier, 3 amphibious assault ships, 4 air-defence-focused destroyers, 6 anti-submarine (ASW)/land attack mission-oriented destroyers, 5 general-purpose frigates, and 6 surveillance frigates. The submarine force consists of 5 nuclear attack submarines and 4 nuclear ballistic missile submarines. Integral to supporting the ''Force d'Action Navale'' at sea are the French Navy's 2 replenishment oilers, 16 mine countermeasure vessels and 8 support ships. In addition to the above units, the Navy operates 15 patrol ships (supplemented by additional coast guard vessels), 5 survey vessels, 4 experimentation ships, 4 ocean tugboats and 14 training vessels. The French Navy does not use the term "destroyer" in vessel names. Instead, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honneur, Patrie, Valeur, Discipline
{{Short description, French Navy Motto ''Honneur, patrie, valeur, discipline'' (''Honour, fatherland, valour, discipline'') is the motto of the French Navy. It is found inscribed on all ships and buildings, sometimes with each word on its separate plaque at a corner of the superstructure. Origin The motto uses words found in traditional mottos of French institutions: "''Honneur - Patrie''", and "''Valeur - Discipline''" * "''Honneur - Patrie''" is the motto of the Légion d'honneur; it has been inscribed on military flags under the First French Empire, and also became the motto of the French Navy from 1830; * "''Valeur - Discipline''" was inscribed on military flags under the late First Empire; fallen in disuse under the Bourbon Restauration, is reappeared on the flags of the French Second Republic and on the reverse of the Médaille militaire. Probably under the Second French Empire, these two mottos fused and became features of French naval ships. File:Le drapeau du 21e RI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi (, ; ar, أَبُو ظَبْيٍ ' ) is the capital and second-most populous city (after Dubai) of the United Arab Emirates. It is also the capital of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi and the centre of the Abu Dhabi Metropolitan Area. The city of Abu Dhabi is located on an island in the Persian Gulf, off the Central West Coast. Most of the city and the Emirate reside on the mainland connected to the rest of the country. , Abu Dhabi's urban area had an estimated population of 1.5 million, out of 2.9 million in the emirate of Abu Dhabi, as of 2016. The Abu Dhabi Investment Authority is headquartered in the city, and was the world's 5th largest sovereign wealth fund in 2021. Abu Dhabi itself has over a trillion US dollars worth of assets under management in a combination of various sovereign wealth funds headquartered there. Abu Dhabi houses local and federal government offices and is the home of the United Arab Emirates Government and the Supreme Petrole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area of . In antiquity, the territory, together with Ethiopia, Eritrea and Somaliland, was part of the Land of Punt. Nearby Zeila, now in Somaliland, was the seat of the medieval Adal and Ifat Sultanates. In the late 19th century, the colony of French Somaliland was established following treaties signed by the ruling Dir Somali sultans with the French, and its railroad to Dire Dawa (and later Addis Ababa) allowed it to quickly supersede Zeila as the port for southern Ethiopia and the Ogaden. It was renamed the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas in 1967. A decade later, the Djiboutian people voted for independence. This officially marked the establishment of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

