|
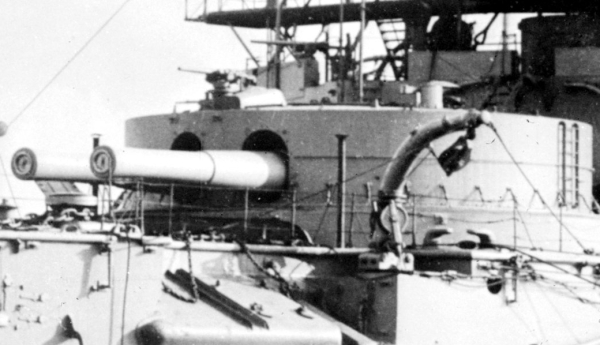
Frederic Dreyer
Admiral Sir Frederic Charles Dreyer, (8 January 1878 – 11 December 1956) was an officer of the Royal Navy. A gunnery expert, he developed a fire control system for British warships, and served as flag captain to Admiral Sir John Jellicoe at the Battle of Jutland. He retired with the rank of admiral in 1943, having served through two world wars and having already retired once. Background and early life Frederic Dreyer was born on 8 January 1878 in the Irish town of Parsonstown (now Birr) in King's County (now County Offaly), the second son of the Danish-born astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer who was director of the Armagh Observatory. Educated at The Royal School, Armagh, in 1891 Dreyer joined the Royal Navy and entered the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth. Royal Navy career Early years At Dartmouth Dreyer performed well in his examinations and was placed fifth in his term. He then served as a midshipman in HMS ''Anson'' (1893–1896) and HMS ''Barfleur'' (1896–1897). In ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birr, County Offaly
Birr (; ga, Biorra, meaning "plain of water") is a town in County Offaly, Ireland. Between 1620 and 1899 it was called Parsonstown, after the Parsons family who were local landowners and hereditary Earls of Rosse. Birr is a designated Irish ''Heritage Town'' with a carefully preserved Georgian heritage. Birr itself has graceful wide streets and elegant buildings. Many of the houses in John's Place and Oxmantown Mall have exquisite fanlight windows of the Georgian period. The town is known for Birr Castle and gardens, home of the Parsons family, and also site of the Leviathan of Parsonstown, the largest telescope in the world for over 70 years, and a large modern radio telescope. Access and transport The town is situated near the meeting of the Camcor and Little Brosna rivers, the latter flowing on into the River Shannon near Victoria Lock. The Ormond Flying Club has been in operation at Birr Airfield for over 30 years. The area has been linked with aviation for some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armagh Observatory
Armagh Observatory is an astronomical research institute in Armagh, Northern Ireland. Around 25 astronomers are based at the observatory, studying stellar astrophysics, the Sun, Solar System astronomy and Earth's climate. In 2018, Armagh Observatory was recognized for having 224 years of unbroken weather records. History The Observatory is located close to the centre of the city of Armagh, adjacent to the Armagh Planetarium in approximately of landscaped grounds known as the Armagh Astropark. It was founded in 1789 by The Most Rev. and Rt Hon. The 1st Baron Rokeby, Church of Ireland Lord Primate of All Ireland and Lord Archbishop of Armagh. In 1795 through 1797 Solar observations were made at Armagh, including measurements of sunspots. Ernst Julius Öpik (grandfather of Lembit Öpik MP) was based here for over 30 years and among his many contributions to astrophysics he wrote of the dangers of an asteroid impacting on the Earth. One of the observatory's directors, Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Excellent (shore Establishment)
HMS ''Excellent'' is a Royal Navy "stone frigate" (shore establishment) sited on Whale Island near Portsmouth in Hampshire. HMS ''Excellent'' is itself part of the Maritime Warfare School, with a headquarters at HMS ''Collingwood'', although a number of lodger units are resident within the site, the principal of which is the headquarters of Fleet Commander (Navy Command Headquarters). History RN Gunnery School afloat In the 1829 a Commander George Smith advocated the establishment of a Naval School of Gunnery; accordingly, the following year, the third-rate HMS ''Excellent'' was converted into a training ship and moored just north of Portsmouth Dockyard, opposite Fareham Creek. Smith was given oversight and set up ''Excellent'' not only as a training establishment but also as a platform for experimental firing of new weapons (the creek was used as a firing range). In 1832 Smith was replaced in command by Captain Thomas Hastings, under whom the school grew both numerically a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies south of Sicily (Italy), east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The official languages are Maltese and English, and 66% of the current Maltese population is at least conversational in the Italian language. Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC. Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Normans, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British, amongst others. With a population of about 516,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country in area and fourth most densely populated sovereign cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Hood (1891)
HMS ''Hood'' was a modified pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Royal Navy in the early 1890s. She differed from the other ships of the class in that she had cylindrical gun turrets instead of barbettes and a lower freeboard. She served most of her active career in the Mediterranean Sea, where her low freeboard was less of a disadvantage. The ship was placed in reserve in 1907 and later became the receiving ship at Queenstown, Ireland. ''Hood'' was used in the development of anti-torpedo bulges in 1913 and was scuttled in late 1914 to act as a blockship across the southern entrance of Portland Harbour after the start of World War I. Design ''Hood'', the last of the eight ''Royal Sovereign''-class battleships to be built, differed significantly from the other ships of her class in that she had a forward freeboard of only compared to of the other ships. The ''Royal Sovereign''s had reverted to a higher freeboard after several classes of low-freeboard vessel had been cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Hawke (1891)
HMS ''Hawke'', launched in 1891, was the seventh British warship to be named ''Hawke''. She was an protected cruiser. In September 1911 the ''Hawke'' collided with the ocean liner RMS ''Olympic''. The damage smashed the ''Hawke''s bow and damaged the stern of the ''Olympic''. Construction ''Hawke'' was laid down at Chatham Dockyard on 17 June 1889, one of nine ''Edgar''-class cruisers ordered for the Royal Navy under the Naval Defence Act 1889, and launched on 11 March 1891. Sea trials in March 1892 were satisfactory, with her engines reaching the required power, and the ship was completed on 16 May 1893. ''Hawke'' was long overall and between perpendiculars, with a beam of and a draught of . She displaced . Armament consisted of two 9.2 inch guns, on the ships centreline, backed up by ten six-inch guns, of which four were in casemates on the main deck and the remainder behind open shields. Twelve 6-pounder and four 3-pounder guns provided anti-torpedo-boat defences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Scylla (1891)
Five vessels of the British Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Scylla'', after the sea monster Scylla of Greek mythology. * was an 18-gun brig-sloop launched in 1809 and broken up 1846. * was a wooden screw corvette launched in 1856 and sold for breakup in 1882. * was an second class cruiser in service from 1891 to 1914. * was a light cruiser launched in 1940, seriously damaged by a mine in 1944, and sold in 1950. * was a in service from 1970 to 1993, and sunk as an artificial reef An artificial reef is a human-created underwater structure, typically built to promote marine life in areas with a generally featureless bottom, to control erosion, block ship passage, block the use of trawling nets, or improve surfing. Many re ... in 2004. {{DEFAULTSORT:Scylla, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheerness
Sheerness () is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby town of Minster which has a population of 21,319. Sheerness began as a fort built in the 16th century to protect the River Medway from naval invasion. In 1665 plans were first laid by the Navy Board for Sheerness Dockyard, a facility where warships might be provisioned and repaired. The site was favoured by Samuel Pepys, then Clerk of the Acts of the navy, for shipbuilding over Chatham inland. After the raid on the Medway in 1667, the older fortification was strengthened; in 1669 a Royal Navy dockyard was established in the town, where warships were stocked and repaired until its closure in 1960. Beginning with the construction of a pier and a promenade in the 19th century, Sheerness acquired the added attractions of a seaside resort. Indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval College, Greenwich
The Royal Naval College, Greenwich, was a Royal Navy training establishment between 1873 and 1998, providing courses for naval officers. It was the home of the Royal Navy's staff college, which provided advanced training for officers. The equivalent in the British Army was the Staff College, Camberley, and the equivalent in the Royal Air Force was the RAF Staff College, Bracknell. History The Royal Naval College, Greenwich, was founded by an Order in Council dated 16 January 1873. The establishment of its officers consisted of a President, who was always a Flag Officer; a Captain, Royal Navy; a Director of Studies; and Professors of Mathematics, Physical Science, Chemistry, Applied Mechanics, and Fortification. It was to take in officers who were already Sub-Lieutenants and to operate as "the university of the Navy". The Director of Studies, a civilian, was in charge of an Academic Board, while the Captain of the College was a naval officer who acted as chief of staff. The Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Repulse (1892)
HMS ''Repulse'' was one of seven ''Royal Sovereign''-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Royal Navy in the 1890s. Assigned to the Channel Fleet, where she often served as a flagship, after commissioning in 1894, the ship participated in a series of annual manoeuvres, and the Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee Fleet Review during the rest of the decade. ''Repulse'' was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1902 and remained there until December 1903, when she returned home for an extensive refit. After its completion in 1905, ''Repulse'' was assigned to the Reserve Fleet until she was sold for scrap in 1911. Design and description The design of the ''Royal Sovereign''-class ships was derived from that of the battleships, greatly enlarged to improve seakeeping and to provide space for a secondary armament as in the preceding battleships. The ships displaced at normal load and at deep load. They had a length between perpendiculars of and were long overall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Barfleur (1892)
HMS ''Barfleur'' was the second and last of the pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Royal Navy in the 1890s. Intended for service abroad, they exchanged heavy armour and a powerful armament for high speed and long range to counter the foreign armoured cruisers then being built as commerce raiders and were rated as second-class battleships. ''Barfleur'' was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1895 and participated in the International Squadron (Cretan intervention, 1897–1898), blockade of Crete imposed by the Great Powers after a Greek rebellion began on Crete against their Ottoman Empire, Ottoman overlords in February 1897. She joined her sister ship on the China Station the following year and became the flagship of the station's second-in-command. During the Boxer Rebellion in 1900, both ships contributed Landing party, landing parties to participate in the Battle of Taku Forts (1900), Battles of the Taku Forts and Battle of Tientsin, of Tientsin. Already made ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Anson (1886)
HMS ''Anson'' was the last of six ironclad battleships built for the Royal Navy during the 1880s. The ship was completed, except for her armament, in 1887, but had to wait two years for her guns to be installed. She was assigned to the Channel Fleet in mid-1889 as a flagship for the fleet's second-in-command. Two years later, the passenger ship sank with the loss of 562 lives after colliding with ''Anson'' in the Bay of Gibraltar. In mid-1893, ''Anson'' was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet, subsequently returning home in 1900 when she was assigned to the Reserve Fleet. She recommissioned for the Home Fleet in early 1901. ''Anson'' was paid off three years later and then sold for scrap in 1909. Design and description The Admiral class was built in response to French ironclad battleships of the and es. ''Anson'' and her sister ship, , were enlarged and improved versions of the previous pair of Admirals, and . The sisters had a length between perpendiculars of , a beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |