|
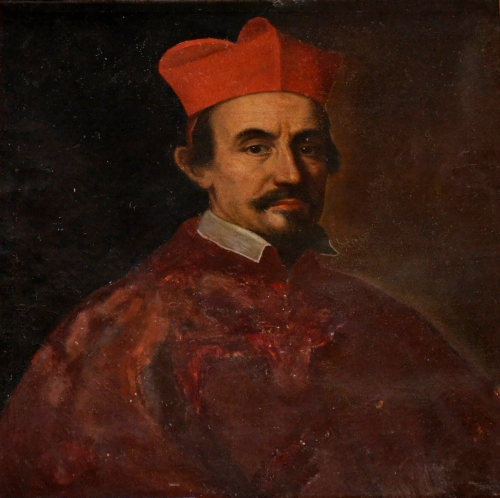
François Guillaume De Castelnau-Clermont-Ludève
François Guillaume de Castelnau de Clermont-Lodève (1480–1541) was a French diplomat and Cardinal (Catholicism), Cardinal. He was the son of Pierre-Tristan, Seigneur de Clermont et de Clermont-Lodève and Vicomte de Nébouzan, and Catherine d'Amboise. His father was a member of the Order of Saint Michael. François' grandmother had been heiress of Dieudonné Guillaume de Clermont. He had an elder brother, Pierre de Castelnau, who was heir to the family estates. François was also the nephew of Cardinal Georges d'Amboise (1498-1510), who was largely responsible for François' swift rise to prominence in the Church. Cardinal d'Amboise had been Archbishop of Narbonne from 1491 to 1494. Education and early career Francois de Castelnau was appointed Major Archdeacon of the Church of Narbonne, before 1501, when he was appointed to the diocese of Saint-Pons. He already was Bachelor in Theology. He was appointed Administrator of the diocese of Saint-Pons-de-Thomières on 17 Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal (Catholicism)
A cardinal ( la, Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae cardinalis, literally 'cardinal of the Holy Roman Church') is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church. Cardinals are created by the ruling pope and typically hold the title for life. Collectively, they constitute the College of Cardinals. Their most solemn responsibility is to elect a new pope in a conclave, almost always from among themselves (with a few historical exceptions), when the Holy See is vacant. During the period between a pope's death or resignation and the election of his successor, the day-to-day governance of the Holy See is in the hands of the College of Cardinals. The right to participate in a conclave is limited to cardinals who have not reached the age of 80 years by the day the vacancy occurs. In addition, cardinals collectively participate in papal consistories (which generally take place annually), in which matters of importance to the Church are considered and new cardinals may be created. Cardina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The League Of Cambrai
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice; they were joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and the Swiss. The war started with the ''Italienzug'' of Maximilian I, King of the Romans, crossing into Venetian territory in February 1508 with his army on the way to be crowned Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope in Rome. Meanwhile, Pope Julius II, intending to curb Venetian influence in northern Italy, brought together the League of Cambrai — an anti-Venetian alliance consisting of him, Maximilian I, Louis XII of France, and Ferdinand II of Aragon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Clement VII
Pope Clement VII ( la, Clemens VII; it, Clemente VII; born Giulio de' Medici; 26 May 1478 – 25 September 1534) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 November 1523 to his death on 25 September 1534. Deemed "the most unfortunate of the popes", Clement VII's reign was marked by a rapid succession of political, military, and religious struggles—many long in the making—which had far-reaching consequences for Christianity and world politics. Elected in 1523 at the end of the Italian Renaissance, Clement came to the papacy with a high reputation as a statesman. He had served with distinction as chief advisor to Pope Leo X (1513–1521), Pope Adrian VI (1522–1523), and commendably as gran maestro of Florence (1519–1523). Assuming leadership at a time of crisis, with the Protestant Reformation spreading; the Church nearing bankruptcy; and large, foreign armies invading Italy, Clement initially tried to unite Christendom by making peace among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciotto Orsini
Franciotto Orsini (1473–1534) was an Italian Roman Catholic cardinal. Biography A member of the Orsini family, Franciotto Orsini was born in Rome in 1473, the son of Orso Orsini di Monteredondo and Costanza Savelli. He was a nephew of Pope Leo X on his father's side. Orsini was educated in Florence by Lorenzo de' Medici. Early in his life, he participated in several military exercises, fighting against the forces of Cesare Borgia. Moving to Rome, he became a protonotary apostolic. His uncle Pope Leo X made him a cardinal deacon in the consistory of July 1, 1517. He received the red hat and the deaconry of San Giorgio in Velabro on July 6, 1517. He was administrator of the see of Nicastro from September 15, 1517 to May 5, 1518. He became archpriest of St. Peter's Basilica. On January 18, 1519, he was named administrator of the see of Boiano, holding this post until July 24, 1523. He was deposed from the cardinalate on August 8, 1519, though later reinstated. Sometime af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeo Colonna
Pompeo Colonna (12 May 1479 – 28 June 1532) was an Italian noble, ''condottiero'', politician, and cardinal. At the culmination of his career he was Viceroy of the Kingdom of Naples (1530–1532) for the Emperor Charles V. Born in Rome, he was the son of Girolamo Colonna, whose father Antonio was second Prince of Salerno; and Vittoria Conti, of the Conti de Poli. His family belonged to the highest rank of nobility both of the City of Rome and of the Kingdom of Naples. Pompeo and his family were hereditary supporters of the Holy Roman Empire (Ghibbelines), and they spent their careers fighting their hereditary enemies, the Orsini family, and defending and expanding their family territories and interests. He played a significant, if sometimes disruptive, role in the Conclaves of 1521 and 1523 on behalf of the Imperial interest. His family commitments and his conclave activities brought Pompeo into conflict with the second Medici pope, Clement VII, whose election he vigorously opp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conclave Capitulation
A conclave capitulation was a compact or unilateral contract drawn up by the College of Cardinals during a papal conclave to constrain the actions of the pope elected by the conclave. The legal term '' capitulation'' more frequently refers to the commitment of a sovereign state to relinquish jurisdiction within its borders over the subjects of a foreign state. Before balloting began, all cardinals present at the conclave would swear to be bound by its provisions if elected pope. Capitulations were used by the College of Cardinals to assert its collective authority and limit papal supremacy, to "make the Church an oligarchy instead of a monarchy." Similar electoral capitulations were used on occasion from the 14th to the 17th centuries in Northern and Central Europe to constrain an elected king, emperor, prince, or bishop. History The College had made informal attempts to influence the actions of popes before drafting formal capitulations. The first capitulation was drafted in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Adrian VI
Pope Adrian VI ( la, Hadrianus VI; it, Adriano VI; nl, Adrianus/Adriaan VI), born Adriaan Florensz Boeyens (2 March 1459 – 14 September 1523), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 January 1522 until his death on 14 September 1523. The only Dutchman to become pope, he was the last non-Italian pope until the Polish John Paul II 455 years later. Born in the Episcopal principality of Utrecht, Adrian studied at the University of Leuven in the Low Countries, where he rose to the position of professor of theology, also serving as its rector (the equivalent of president or vice-chancellor). In 1507, he became the tutor of the future Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, who later trusted him as both his emissary and his regent. In 1516, Charles, now King of Castile and Aragon, appointed Adrian bishop of Tortosa, Spain, and soon thereafter Grand Inquisitor of the kingdoms of Aragon and Castile. Pope Leo X made him a cardinal in 1517 and after Leo's dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De Lorraine
Jean de Lorraine (9 April 1498 – c. 18 May 1550) was the third son of the ruling Duke of Lorraine, and a French cardinal, who was (at one time or another) archbishop of Reims (1532–1538), Lyon (1537–1539), and Narbonne (1524–1550), bishop of Metz, and Administrator of the dioceses of Toul, Verdun, Thérouanne, Luçon, Albi, Valence, Nantes and Agen (1538–1550). He was a personal friend, companion, and advisor of King Francis I of France. Jean de Lorraine was the richest prelate in the reign of Francis I, as well as the most flagrant pluralist. He is one of several cardinals known as the ''Cardinal de Lorraine''. Biography Born in Bar-le-Duc, Jean was the sixth child of twelve, of René II, Duke of Lorraine and his wife Philippa of Guelders, sister of Charles, Duke of Guelders. He was a younger brother of Antoine, Duke of Lorraine and Claude, Duke of Guise. His younger brother, François, Comte de Lambesc, died in the Battle of Pavia in 1525. In 1520 his mother retired t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Bourbon De Vendome , names sometimes translated to English as "Louis"
{{disambiguation ...
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish-Israeli Olympic soccer player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Conclave, 1523
The 1523 papal conclave elected Cardinal Giulio de' Medici as Pope Clement VII to succeed Pope Adrian VI. According to conclave historian Baumgartner, the conclave was the "last conclave of the Renaissance".Baumgartner, 2003, p. 101. Background Adrian VI experienced ill health during the final months of his life, inspiring the cardinals to begin politicking.Baumgartner, 2003, p. 98. Francis I of France had just dispatched a large army into northern Italy in 1522, and expecting to leverage this force to effect the election of French cardinal Jean de Lorraine, or more likely a pro-French Italian cardinal such as Niccolò Fieschi. However, his army experienced a major defeat at the Battle of Bicocca prior to the conclave. In any case, the three French cardinals were ordered by Francis I to rush to Rome. Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, strengthened by the Battle of Bicocca, supported Giulio de' Medici, an advocate for imperial policy within the College. Henry VIII of England would ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Agde
The former France, French Roman Catholic diocese of Agde existed from about the 6th century to the Concordat of 1801 between First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte and Pope Pius VII. Agde is in the south of France, in what is now the department of Hérault. The last bishop, Charles François de Rouvroy de Saint Simon Sandricourt, was guillotined in Paris on July 25, 1794. The diocesan seat was Agde Cathedral, the Cathedral of Saint-Étienne, originally dedicated to Saint Andrew. The cathedral was served by a Chapter, consisting of twelve Canon regular, Canons, including the Archdeacon, the Sacristan, the Precentor and the Treasurer. There were twelve Chaplain, chaplains (''hebdomidarii''), eight for daily services and four for requiems. There were thirty-two Prebendary, prebendaries. The diocese had only twenty-six parishes. The territory of the former diocese is now part of the diocese of Montpellier. Bishops To 1000 *Venustus (Venuste, in French) ca. 405 *Beticus ca. 450? *So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Valence
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Valence (–Die–Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux) (Latin: ''Dioecesis Valentinensis (–Diensis–Sancti Pauli Tricastinorum)''; French: ''Diocèse de Valence (–Die–Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux'') is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Roman Catholic Church in southern France. The contemporary diocese is co-extensive with the department of Drôme. The Cathedral of Valence was originally dedicated to Saints Cornelius and Cyprianus (Bishops of Rome and of Carthage, both mid-third century martyrs), but in 1095, during his visit to France to rouse up the aristocracy for a Crusade to liberate the Holy Land, Pope Urban II rededicated the cathedral to Saint Apollinaris, one of Valence's sixth century bishops. The Cathedral had fourteen Canons, including a Dean, a Provost, the Archdeacon, a Theologian, and the Abbot of S. Felix. In the Great Western Schism (1378–1417), the Bishops of Valence-et-Die were all appointed by and were loyal to the Popes of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |