|
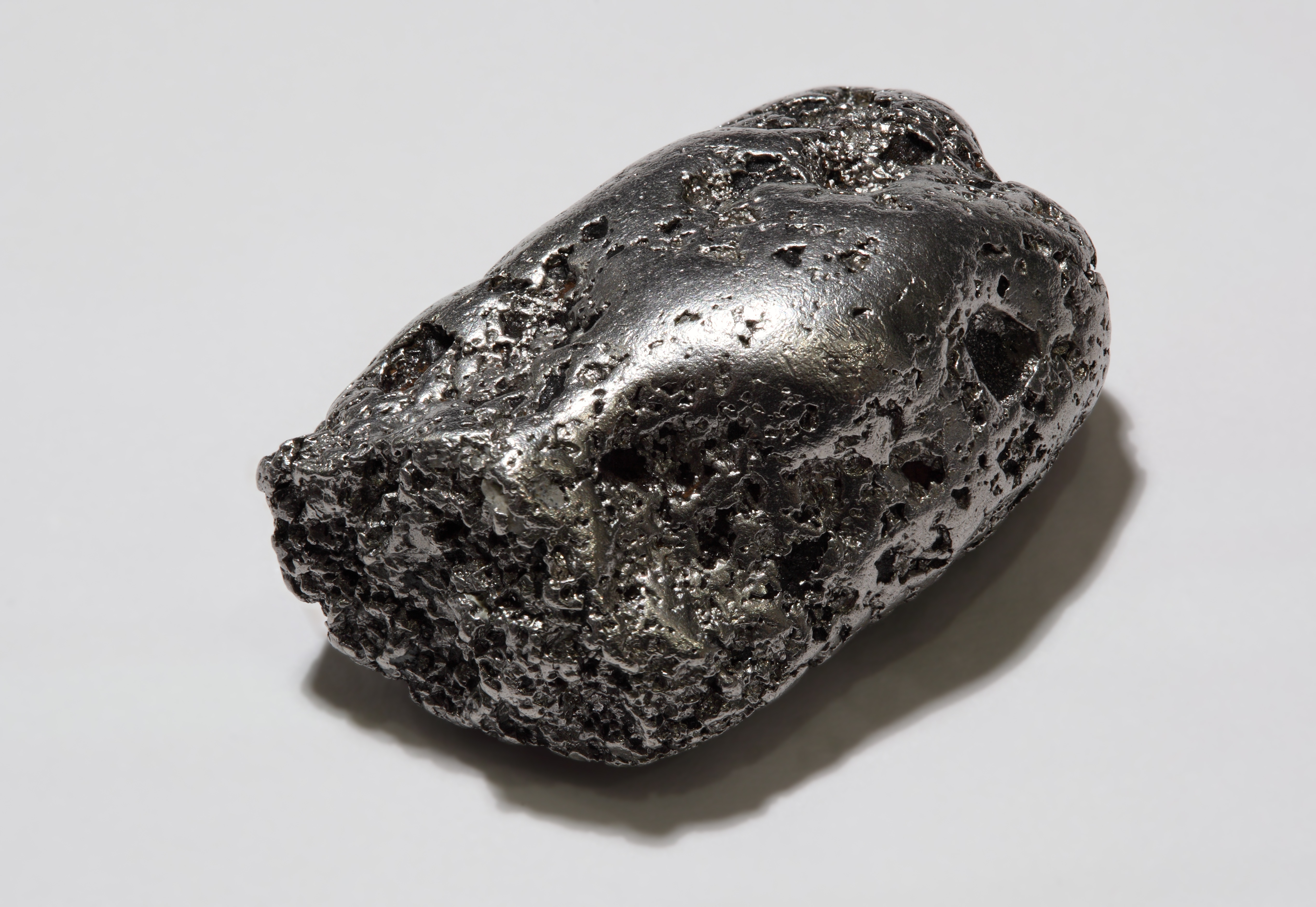
Fracture (mineralogy)
In the field of mineralogy, fracture is the texture and shape of a rock's surface formed when a mineral is fractured. Minerals often have a highly distinctive fracture, making it a principal feature used in their identification. Fracture differs from cleavage in that the latter involves clean splitting along the cleavage planes of the mineral's crystal structure, as opposed to more general breakage. All minerals exhibit fracture, but when very strong cleavage is present, it can be difficult to see. Terminology Five types of fractures are recognized in mineralogy: conchoidal, earthy, hackly, splintery (or fibrous), and uneven factures. Conchoidal fracture Conchoidal fracture breakage that resembles the concentric ripples of a mussel shell. It often occurs in amorphous or fine-grained minerals such as flint, opal or obsidian, but may also occur in crystalline minerals such as quartz. Subconchoidal fracture is similar to conchoidal fracture, but with less significant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval China, and Sanskrit texts from ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the '' Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola wrote works such as '' De re metallica'' (''On Metals'', 1556) and '' De Natura Fossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
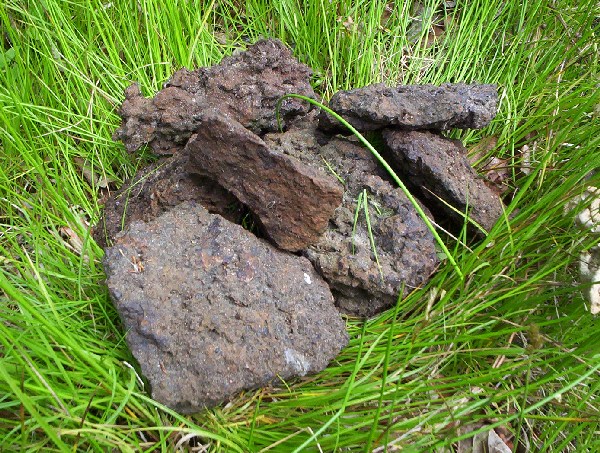
Limonite Bog Iron Cm02
Limonite () is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as FeO(OH)·H2O, although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxide can vary quite widely. Limonite is one of the three principal iron ores, the others being hematite and magnetite, and has been mined for the production of iron since at least 2500 BP. Names Limonite is named for the Greek word λειμών (/leː.mɔ̌ːn/), meaning "wet meadow", or λίμνη (/lím.nɛː/), meaning “marshy lake” as an allusion to its occurrence as '' bog iron ore'' in meadows and marshes. In its brown form it is sometimes called brown hematite or brown iron ore. Characteristics Limonite is relatively dense with a specific gravity varying from 2.7 to 4.3.Northrop, Stuart A. (1959) "Limonite" ''Minerals of New Mexico'' (revised edition) University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp. 329–333, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenopyrite
Arsenopyrite (International Mineralogical Association, IMA List of mineral symbols, symbol: Apy) is an iron arsenic sulfide (FeAsS). It is a hard (Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs 5.5-6) metallic, opaque, steel grey to silver white mineral with a relatively high specific gravity of 6.1. When dissolved in nitric acid, it releases elemental sulfur. When arsenopyrite is heated, it produces sulfur and arsenic vapor. With 46% arsenic content, arsenopyrite, along with orpiment, is a principal ore of arsenic. When deposits of arsenopyrite become exposed to the atmosphere, the mineral slowly converts into iron arsenates. Arsenopyrite is generally an acid-consuming sulfide mineral, unlike pyrite, iron pyrite which can lead to acid mine drainage. The crystal habit, hardness, density, and garlic odour when struck are diagnostic. Arsenopyrite in older literature may be referred to as ''mispickel'', a name of German origin. Arsenopyrite also can be associated with significant amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyanite
Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates metamorphism deep in the Earth's crust. Kyanite is also known as disthene or cyanite. Kyanite is strongly anisotropic, in that its hardness varies depending on its crystallographic direction. In kyanite, this anisotropism can be considered an identifying characteristic, along with its characteristic blue color. Its name comes from the same origin as that of the color cyan, being derived from the Ancient Greek word κύανος. This is generally rendered into English as ''kyanos'' or ''kuanos'' and means "dark blue". Kyanite is used as a raw material in the manufacture of ceramics and abrasives, and it is an important index mineral used by geologists to trace metamorphic zones. Properties Kyanite is an aluminum silicate mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
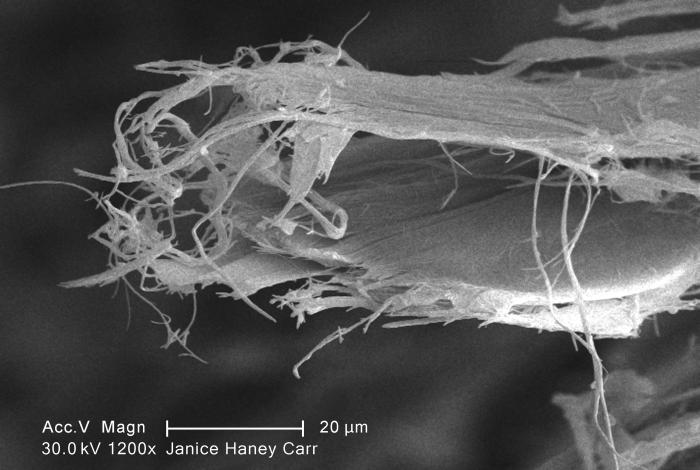
Chrysotile
Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor (2007)29 C.F.R. 1910.1001 Appendix J. and a similar proportion in other countries.Institut national de recherche sur la sécurité (1997).Amiante." ''Fiches toxicologiques.'' n° 167. (in French) It is a soft, fibrous silicate mineral in the serpentine subgroup of phyllosilicates; as such, it is distinct from other asbestiform minerals in the amphibole group. Its idealized chemical formula is Mg( Si O)( OH). The material has physical properties which make it desirable for inclusion in building materials, but poses serious health risks when dispersed into air and inhaled. Polytypes Three polytypes of chrysotile are known. These are very difficult to distinguish in hand specimens, and polarized light microscopy must normally be used. Some older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysotile 1
Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United StatesOccupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor (2007)29 C.F.R. 1910.1001 Appendix J. and a similar proportion in other countries.Institut national de recherche sur la sécurité (1997).Amiante." ''Fiches toxicologiques.'' n° 167. (in French) It is a soft, fibrous silicate mineral in the serpentine subgroup of phyllosilicates; as such, it is distinct from other asbestiform minerals in the amphibole group. Its idealized chemical formula is Mg( Si O)( OH). The material has physical properties which make it desirable for inclusion in building materials, but poses serious health risks when dispersed into air and inhaled. Polytypes Three polytypes of chrysotile are known. These are very difficult to distinguish in hand specimens, and polarized light microscopy must normally be used. Some older publica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Copper
Native copper is an uncombined form of copper that occurs as a natural mineral. Copper is one of the few metallic elements to occur in native form, although it most commonly occurs in oxidized states and mixed with other elements. Native copper was an important ore of copper in historic times and was used by pre-historic peoples. Native copper occurs rarely as isometric cubic and octahedral crystals, but more typically as irregular masses and fracture fillings. It has a reddish, orangish, and/or brownish color on fresh surfaces, but typically is weathered and coated with a green tarnish of copper(II) carbonate (also known as patina or verdigris). Its specific gravity is 8.9 and its hardness is 2.5–3. The mines of the Keweenaw native copper deposits of Upper Michigan were major copper producers in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and are the largest deposits of native copper in the world. (Web archive; click cancel when it asks for authentication.) Native Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Metal
A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native deposits singly or in alloys include aluminium, antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, rhenium, selenium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zinc, as well as the gold group (gold, copper, lead, aluminium, mercury, silver) and the platinum group (platinum, iridium, osmium, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium). Among the alloys found in native state have been brass, bronze, pewter, German silver, osmiridium, electrum, white gold, silver-mercury amalgam, and gold-mercury amalgam. Only gold, silver, copper and the platinum group occur native in large amounts. Over geological time scales, very few metals can resist natural weathering processes like oxidation, so mainly the less reactive metals such as gold and platinum are found as native metals. The others usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminite
Aluminite is a hydrous aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Al2SO4(OH)4·7H2O. It is an earthy white to gray-white monoclinic mineral which almost never exhibits crystal form. It forms botryoidal to mammillary clay-like masses. It has a very soft Mohs hardness of 1–2 and a specific gravity of 1.66–1.82. It forms in clay and lignite deposits as an oxidation product of pyrite and marcasite along with aluminium silicates. It also occurs in volcanic sublimates, in native sulfur deposits and rarely in caves. It occurs in association with basaluminite, gibbsite, epsomite, gypsum, celestine, dolomite and goethite. It was first described in 1807 from Halle, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named for its aluminium content. It is also known as ''alley stone'', ''halite'' and ''websterite'' (named after Orcadian Orcadians, also known as Orkneymen, are an ethnic group native to the Orkney Islands, who speak an Orcadian dialect of the Scots language, a West Germanic language, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

