|
FOXP3
FOXP3 ( forkhead box P3), also known as scurfin, is a protein involved in immune system responses. A member of the FOX protein family, FOXP3 appears to function as a master regulator of the regulatory pathway in the development and function of regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells generally turn the immune response down. In cancer, an excess of regulatory T cell activity can prevent the immune system from destroying cancer cells. In autoimmune disease, a deficiency of regulatory T cell activity can allow other autoimmune cells to attack the body's own tissues. While the precise control mechanism has not yet been established, FOX proteins belong to the forkhead/ winged-helix family of transcriptional regulators and are presumed to exert control via similar DNA binding interactions during transcription. In regulatory T cell model systems, the FOXP3 transcription factor occupies the promoters for genes involved in regulatory T-cell function, and may inhibit transcription of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cells
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
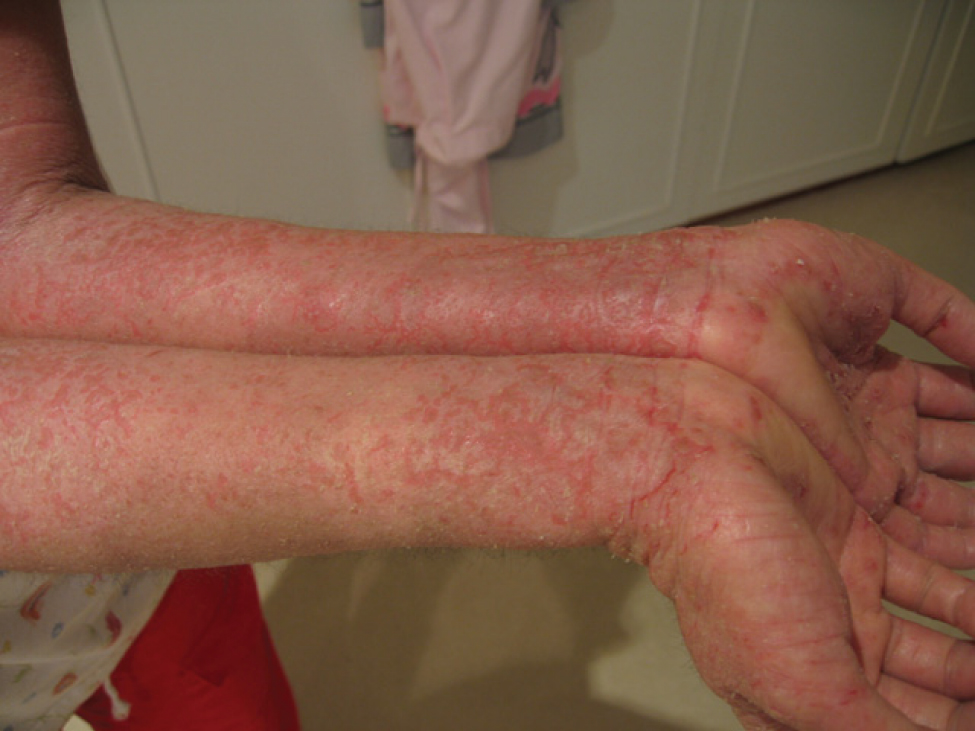
IPEX Syndrome
Immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked (or IPEX) syndrome is a rare disease linked to the dysfunction of the gene encoding transcription factor forkhead box P3 ( FOXP3), widely considered to be the master regulator of the regulatory T cell lineage. It leads to the dysfunction of CD4+ regulatory T-cells and the subsequent autoimmunity. The disorder is one of the autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes and manifests with autoimmune enteropathy, psoriasiform or eczematous dermatitis, nail dystrophy, autoimmune endocrinopathies, and autoimmune skin conditions such as alopecia universalis and bullous pemphigoid. Management for IPEX has seen limited success in treating the syndrome by bone marrow transplantation. Presentation The most representative criterion for diagnose of IPEX syndrome is autoimmune enteropathy. First symptoms of enteropathy begin in first day of life and they are characterized by diarrhea, vomiting, gastritis, ileus and colitis. The second hallmark i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Tolerance
Immune tolerance, or immunological tolerance, or immunotolerance, is a state of unresponsiveness of the immune system to substances or tissue that would otherwise have the capacity to elicit an immune response in a given organism. It is induced by prior exposure to that specific antigen and contrasts with conventional immune-mediated elimination of foreign antigens (see Immune response). Tolerance is classified into central tolerance or peripheral tolerance depending on where the state is originally induced—in the thymus and bone marrow (central) or in other tissues and lymph nodes (peripheral). The mechanisms by which these forms of tolerance are established are distinct, but the resulting effect is similar. Immune tolerance is important for normal physiology. Central tolerance is the main way the immune system learns to discriminate self from non-self. Peripheral tolerance is key to preventing over-reactivity of the immune system to various environmental entities (allergens, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD25
Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain (also called CD25) is the human protein encoded by the ''IL2RA'' gene. The interleukin 2 (IL2) receptor alpha (IL2RA) and beta (IL2RB) chains, together with the common gamma chain (IL2RG), constitute the high-affinity IL2 receptor. Homodimeric alpha chains (IL2RA) result in low-affinity receptor, while homodimeric beta (IL2RB) chains produce a medium-affinity receptor. Normally an integral-membrane protein, soluble IL2RA has been isolated and determined to result from extracellular proteolysis. Alternately-spliced IL2RA mRNAs have been isolated, but the significance of each is currently unknown. Description It is a type I transmembrane protein present on activated T cells, activated B cells, some thymocytes, myeloid precursors, and oligodendrocytes. Though IL2RA has been used as a marker to identify CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in mice, it has been found that a large proportion of resting memory T cells constitutively express IL2RA in human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOX Proteins
FOX (forkhead box) proteins are a family of transcription factors that play important roles in regulating the expression of genes involved in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and longevity. Many FOX proteins are important to embryonic development. FOX proteins also have pioneering transcription activity by being able to bind condensed chromatin during cell differentiation processes. The defining feature of FOX proteins is the forkhead box, a sequence of 80 to 100 amino acids forming a motif that binds to DNA. This forkhead motif is also known as the winged helix, due to the butterfly-like appearance of the loops in the protein structure of the domain. Forkhead proteins are a subgroup of the helix-turn-helix class of proteins. Biological roles Many genes encoding FOX proteins have been identified. For example, the FOXF2 gene encodes forkhead box F2, one of many human homologues of the ''Drosophila melanogaster'' transcription factor forkhead. FOXF2 is expressed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suppressor-inducer T Cell
Suppressor-inducer T cells are a specific subset of CD4+ T helper cells that "induce" CD8+ cytotoxic T cells to become "suppressor" cells. Suppressor T cells are also known as CD25+–Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (nTregs), and reduce inflammation Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im .... References T cells {{Immunology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fork Head Domain
The fork head domain is a type of protein domain that is often found in transcription factors and whose purpose is to bind DNA. Function The fork head protein of ''Drosophila melanogaster'', a transcription factor that promotes terminal rather than segmental development, contains neither homeodomains nor zinc-fingers characteristic of other transcription factors. Instead, it contains a distinct type of DNA-binding region, containing around 100 amino acids, which has since been identified in a number of transcription factors (including ''D. melanogaster'' FD1-5, mammalian HNF3, human HTLF, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' HCM1, etc.). This is referred to as the fork head domain but is also known as a "winged helix". The fork head domain binds B-DNA as a monomer, but shows no similarity to previously identified DNA-binding motifs. Although the domain is found in several different transcription factors, a common function is their involvement in early developmental decisions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum. IBD also occurs in dogs and is thought to arise from a combination of host genetics, intestinal microenvironment, environmental components and the immune system. There is an ongoing discussion, however, that the term "chronic enteropathy" might be better to use than "inflammatory bowel disease" in dogs because it differs from IBD in humans in how the dogs respond to treatment. For example, many dogs respond to only dietary changes compared to humans with IBD, who often need immunosuppressive treatment. Some dogs may also need immunosuppressant or antibiotic treatment when dietary changes are not enough. After having excl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |