|
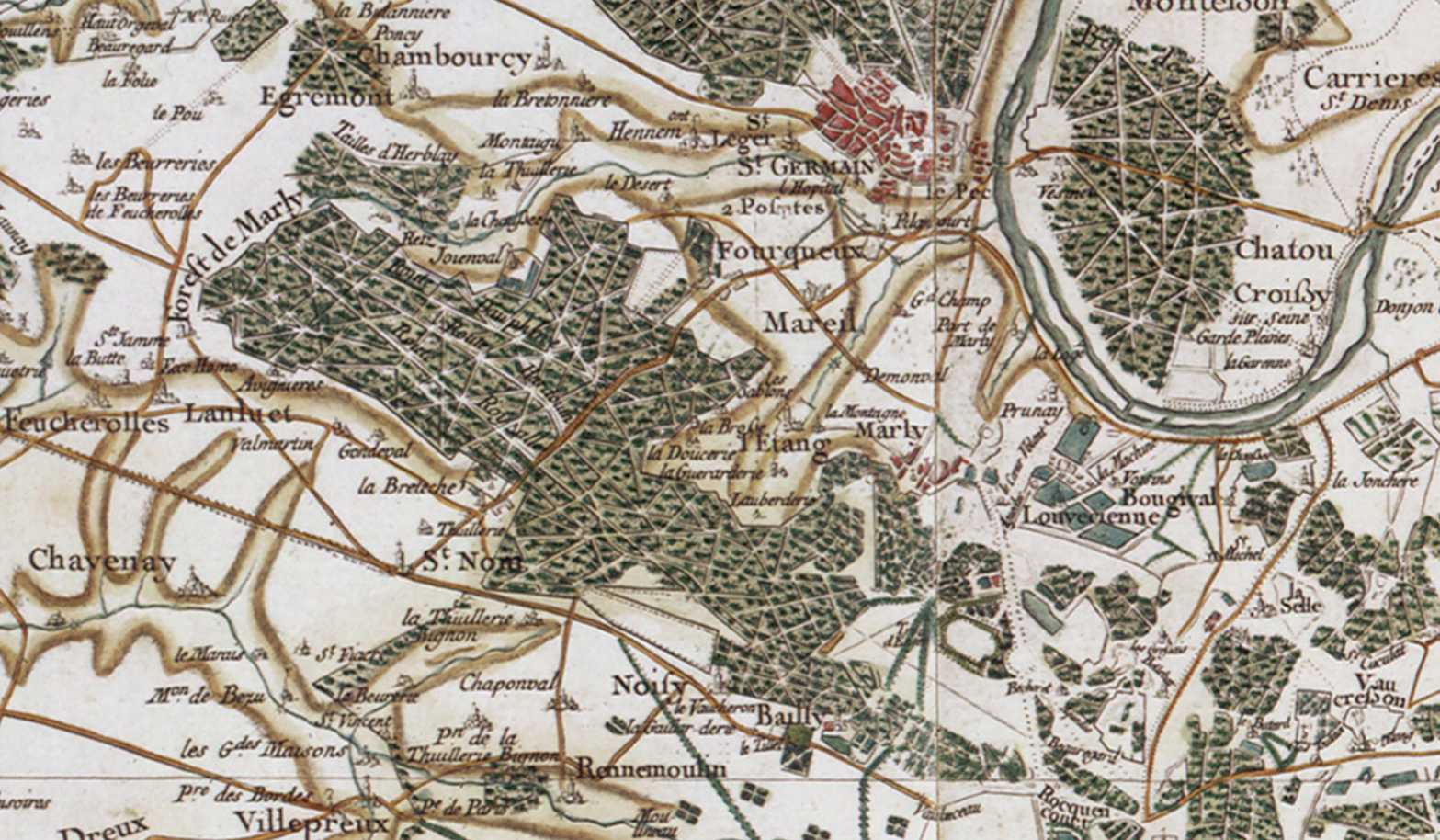
Forêt De Marly
The Forêt de Marly (known as the forêt de Cruye until the 18th century) is a 2000 hectare forest estate in Yvelines, between Saint-Germain-en-Laye and Versailles about 15 km to the west of Paris. It is about 12 km long east to west, over the communes of Louveciennes, Marly-le-Roi, Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche, Feucherolles and others. Historically, it was a hunting estate of the kings of France, then of the presidents of the Republic, but (since 1935) is now divided along its whole length by the A13 autoroute. See also * Désert de Retz * National Forest (France) Travaux Image:Camille Pissarro - Allée dans le parc de Marly.jpg, ''Bois de Marly'', 1871, Camille Pissarro Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( , ; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). H .... Colección Thyssen Bornemisza. Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yvelines
Yvelines () is a department in the western part of the Île-de-France region in Northern France. In 2019, it had a population of 1,448,207.Populations légales 2019: 78 Yvelines INSEE Its prefecture is , home to the , the principal residence of the King of France from 1682 until 1789, a |
Saint-Germain-en-Laye
Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the centre of Paris. Inhabitants are called ''Saint-Germanois'' or ''Saint-Germinois''. With its elegant tree-lined streets it is one of the more affluent suburbs of Paris, combining both high-end leisure spots and exclusive residential neighborhoods (see the Golden Triangle of the Yvelines). Saint-Germain-en-Laye is a sub-prefecture of the department. Because it includes the National Forest of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, it covers approximately , making it the largest commune in the Yvelines. It occupies a large loop of the Seine. Saint-Germain-en-Laye lies at one of the western termini of Line A of the RER. History Saint-Germain-en-Laye was founded in 1020 when King Robert the Pious (ruled 996–1031) founded a convent on the site of the present Church of Saint-Germain. In 1688, James II of England exile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Versailles (city)
Versailles () is a commune in the department of the Yvelines, Île-de-France, renowned worldwide for the Château de Versailles and the gardens of Versailles, designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Located in the western suburbs of the French capital, from the centre of Paris, Versailles is a wealthy suburb of Paris with a service-based economy and is a major tourist destination. According to the 2017 census, the population of the city is 85,862 inhabitants, down from a peak of 94,145 in 1975.Population en historique depuis 1968 INSEE A founded at the will of King |
Louveciennes
Louveciennes () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, between Versailles and Saint-Germain-en-Laye, and adjacent to Marly-le-Roi. Population Sights * Many castles from the 17th and 18th century (Chateau des Voisins, Chateau de Madame Du Barry, Chateau du Pont, Chateau du Parc, Chateau des Sources). *The Château de Louveciennes, built in 1700 by Louis XIV and given to Madame du Barry by Louis XV. *The Louveciennes Aqueduct of the Machine de Marly Image:Louveciennes Château de Voisins.JPG, Chateau of Voisins Image:Louveciennes Château du Pont.JPG, Chateau of Pont Culture Louveciennes was frequented by impressionist painters in the 19th century; according to the official site, there are over 120 paintings by Renoir, Pissarro, Sisley, and Monet depicting Louveciennes. The composer Camille Saint-Saëns lived in Louveciennes from 1865 to 1870. Marie Louise Élisab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marly-le-Roi
Marly-le-Roi () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yvelines Departments of France, department in the Regions of France, administrative region of Île-de-France, France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the Kilometre Zero, centre of Paris. Marly-le-Roi was the location of the Château de Marly, the famous leisure residence of the Sun King Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV which was destroyed after the French Revolution. The Marly-le-Roi National Estate and Park now occupies much of the grounds of the former château, including restored waterways and lawns. Demographics The inhabitants are called ''Marlychois'' or less commonly ''Marlésiens''. Transport Marly-le-Roi is served by Marly-le-Roi station on the Transilien Paris-Saint-Lazare suburban rail line. International relations Marly-le-Roi is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Kita, Mali, Kita, Mali * Leichlingen, Germany * Marlow, Buckinghamshire, Marlow, England, United Kingdom * Viseu, Por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche
Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche () is a wealthy commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. History Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche was built around 4 core hamlets near the Forest of Marly. The village takes its name from a 9th-century co-bishop, saint Nonne, who re-evangelized the country after the Norman invasions, and from La Bretesche, a wooden stronghold (from ''breit eiche'': big oak tree) consisting of a hamlet at the edge of the forest of Cruye, now the forest of Marly. The hamlet was originally called "Saint-Nonne au Val de Galie", the name of the parish, then "Saint-Nom près de la Bretesche" and since the Revolution, "Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche". During the French Revolution the district was called "La Montagne Fromentale" and then "l'Union la Bretesche". The hamlets of Avinières, Val-Martin, La Tuilerie-Bignon were the responsibility of numerous lords, as well as of the Dames de Poissy and the Vaux-de-Cernay Abbey. The north of the villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feucherolles
Feucherolles () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France in north-central France. Twin towns Along with Crespières, Chavenay and Saint-Nom-la-Bretèche Feucherolles is twinned with Rösrath, Germany. See also *Communes of the Yvelines department An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious, ... References Communes of Yvelines {{Yvelines-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A13 Autoroute
Autoroute 13, or ''L'Autoroute de Normandie'' links Paris to Caen, Calvados. The motorway starts in Paris at the Porte d'Auteuil, a former gate of the Paris walls, and ends at Mondeville's Mondeville 2 (Porte de Paris) exchange junction on the Boulevard Périphérique (Caen). The A13 is France's oldest motorway (opening in 1946) and is intensively used between Paris and Normandy for both commuting and holiday makers. The A13 is operated by the Société des Autoroutes de Paris Normandie from Buchelay toll onwards, whilst the Parisian stretch of motorway is operated by the Île-de-France The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ... Council. Its total length is . The A13 is toll-free within the Île-de-France region and between junctions 21 and 24 to the south of Rouen. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forêt De Marly - Cassini
The Chablis region of Burgundy is classified according to four tiers of ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designation. The top two are the crus of Chablis and include the 7 Grand cru vineyards followed by the lower Premier crus. Wines made entirely from fruit from these vineyards are entitled to list their wines as ''cru classé'' Chablis on the wine label. Below these tiers are the lower designations of basic Chablis AOC and Petit Chablis. Soil quality and hill slope play a major role in delineating the differences. Many of the Premier Crus, and all the Grand Crus vineyards, are planted along valley of the Serein river as it flows into the Yonne with the best sites located on a southwest facing slope that receives the maximum amount of sun exposure. All of Chablis' Grand Cru vineyards and many of their better Premier Cru vineyards are planted on primarily Kimmeridgean soil (a composition of limestone, clay and tiny fossilized oyster shells) which is believed to impart m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Désert De Retz
The Désert de Retz is a garden on the edge of the forêt de Marly in the commune of Chambourcy, in north-central France. It was created at the end of the 18th century by the aristocrat François Racine de Monville on his estate. The architect Boullée was involved in the creation of both Monville's town houses; it is less likely he had much do with the Désert de Retz, although Monville did, for a while, engage him as assistant to the architect Francois Barbier until 1780. Monville probably designed many of the features and structures himself, or had a strong supervisory role. The garden included between 17 and 20 structures, of which ten still survive, mostly referring to classical antiquity. Those buildings included a summer house (the "colonne brisée", or ruined column), in the form of the base of a shattered column from an imaginary gigantic temple, an ice house in the form of an Egyptian pyramid, an obelisk, a colonnaded temple dedicated to Pan, an open-air theatre, a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Forest (France)
A national forest (french: forêt domaniale) is a forest owned by the French state. This status originates with the Edict of Moulins of 1566. French national forests are managed by the National Board of Forestry (NFB) under the national forestry law, the successor of ordinances and regulations that have taken place since the time of Charlemagne "at the discretion of political, economic and demographic context of France, making the first state-owned natural forest areas whose management is rigorously controlled". Legal status National forests have existed in some form since ancient times: in fact state ownership is a legal system distinct from inheritance and private property that dates back to the Edict of Moulins (1566). Thus, a number of royal forests are the "property" of the state, which has delegated the management of the Ministry of Agriculture who has himself told NFB and sometimes about national parks. or the abusus, the public domain is inalienable. Dispositio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Pissarro
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( , ; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and Post-Impressionism. Pissarro studied from great forerunners, including Gustave Courbet and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot. He later studied and worked alongside Georges Seurat and Paul Signac when he took on the Neo-Impressionist style at the age of 54. In 1873 he helped establish a collective society of fifteen aspiring artists, becoming the "pivotal" figure in holding the group together and encouraging the other members. Art historian John Rewald called Pissarro the "dean of the Impressionist painters", not only because he was the oldest of the group, but also "by virtue of his wisdom and his balanced, kind, and warmhearted personality". Paul Cézanne said "he was a father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |