|
Fort Of Alqueidão
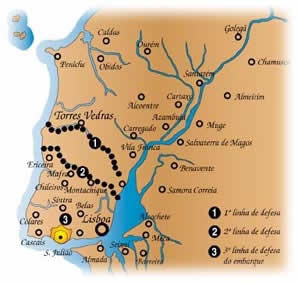
The Fort of Alqueidão, also known as ''Forte Grande'' (Big Fort), is located about 2 kilometres south of the parish of Sobral de Monte Agraço, in the municipality of Sobral de Monte Agraço, in the Lisbon District of Portugal. It was one of the first and one of the largest of 152 military works known as the Lines of Torres Vedras that were built in 1809-10 to defend Lisbon during the Peninsular War (1807–14). The fort played a major role in stopping the advance of Napoleonic troops. History Following the Treaty of Fontainebleau signed between France and Spain in October 1807, which provided for the invasion and subsequent division of Portuguese territory into three kingdoms, French troops under the command of General Junot entered Portugal, which requested support from the British. In July 1808 troops commanded by the Duke of Wellington, at the time known as Arthur Wellesley, landed in Portugal and defeated French troops at the Battles of Roliça and Vimeiro. This forced Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Richard Fletcher, 1st Baronet
Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Richard Fletcher, 1st Baronet (1768 – 31 August 1813) was an engineer in the British Army known for his work on the Lines of Torres Vedras. He fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and Peninsular Wars, and was mentioned in dispatches a number of times, most notably for his actions at Talavera, Busaco, Badajoz and Vitoria. Fletcher was twice wounded in the line of duty before being killed in action at the Siege of San Sebastian. Personal life Little is known of Richard Fletcher's early life, even his exact date of birth is obscure. It is known however that the year was 1768 and his father was a clergyman.Heathcote (p.50) On 27 November 1796, at Plymouth, he married Elizabeth Mudge the daughter of a doctor. Fletcher and his wife went on to have five children together; two sons and three daughters. Though Fletcher was buried near to where he was killed at San Sebastián, a monument to his memory, purchased by the Royal Engineers, stands at the west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenal
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly regarded as synonyms, although subtle differences in usage exist. A sub-armory is a place of temporary storage or carrying of weapons and ammunition, such as any temporary post or patrol vehicle that is only operational in certain times of the day. Etymology The term in English entered the language in the 16th century as a loanword from french: arsenal, itself deriving from the it, arsenale, which in turn is thought to be a corruption of ar, دار الصناعة, , meaning "manufacturing shop". Types A lower-class arsenal, which can furnish the materiel and equipment of a small army, may contain a laboratory, gun and carriage factories, small-arms ammunition, small-arms, harness, saddlery tent and powder factories; in addition, it mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEA And Norway Grants
The EEA Grants and Norway Grants represent the contributions of Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway to reducing social and economic disparities in the European Economic Area (EEA) and strengthening bilateral relations with 15 EU countries in Central and Southern Europe. Through the Grants, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway are also contributing to strengthening fundamental European values such as democracy, tolerance and the rule of law. Background The EEA and Norway Grants have their basis in the EEA Agreement. Under this agreement, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway are part of the European Single Market (ESM), which enables the free movement of goods, services, capital and people in the internal market. The EEA Agreement sets out the common goals involved in working together to reduce social and economic disparities in Europe and strengthen cooperation between European countries. Ever since the EEA Agreement entered into force, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway have contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Beresford, 1st Viscount Beresford
General William Carr Beresford, 1st Viscount Beresford, 1st Marquis of Campo Maior, (; 2 October 1768 – 8 January 1854) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and politician. A general in the British Army and a Marshal in the Portuguese Army, he fought alongside The Duke of Wellington in the Peninsular War and held the office of Master-General of the Ordnance in 1828 in Wellington's first ministry. He led the 1806 failed British invasion of Buenos Aires. Background Beresford was the illegitimate son of the 1st Marquess of Waterford. He was the brother of Admiral Sir John Beresford, 1st Baronet (who was also illegitimate), and the half-brother of the 2nd Marquess of Waterford, Archbishop Lord John Beresford and General Lord George Beresford. Peninsular War Commander in Chief of the Portuguese Army In that same year Beresford was sent to Madeira, which he occupied in name of the Queen of Portugal, remaining there for six months as Governor and Commander in Chief. The exiled Portu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Pack
Major-General Sir Denis Pack (7 October 1775–24 July 1823) was an Anglo-Irish military officer during the Napoleonic Wars. Background A descendant of Sir Christopher Packe, Pack was the son of the Very Reverend Thomas Pack, Dean of Ossory in the east of Ireland. His mother was Catherine, daughter and heiress of Denis Sullivan of Berehaven, Ireland. His tomb is in St. Canice's Cathedral in Kilkenny, Ireland near Kilkenny Castle. Military career He saw service in Flanders in 1794, was on the Quiberon expedition of 1795, and in Ireland of the suppression of the 1798 rebellion. He commanded the 71st Foot during the capture of the Cape of Good Hope in 1806. His regiment was incorporated to the forces of General William Beresford when he led the first British invasion to Buenos Aires in June of that year. Their regiment contributed more than half of the invading troops, and with them Beresford occupied Buenos Aires without greater resistance. However, in the second week ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Of Archeira
The Fort of Archeira is located in the municipality of Torres Vedras, in the Lisbon District of Portugal. It is also today known as the Furadouro Redoubt and was called the “Cheira” at the time of construction. Construction began in 1810 as part of the first of the three Lines of Torres Vedras, which were defensive lines to protect the Portuguese capital Lisbon from invasion by the French during the Peninsular War (1807–14) or, in the event of defeat, to protect the embarkation of a retreating British Army. Background Despite the defeat of French forces in earlier invasions of Portugal during the Peninsular War, the threat of further invasions led the commander of the British troops in Portugal, Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, to order on October 20, 1809 the construction of three defensive lines to the north of the capital, between the Atlantic Ocean and the River Tagus. The Lines of Torres Vedras, consisting of 152 forts, redoubts and other military works, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
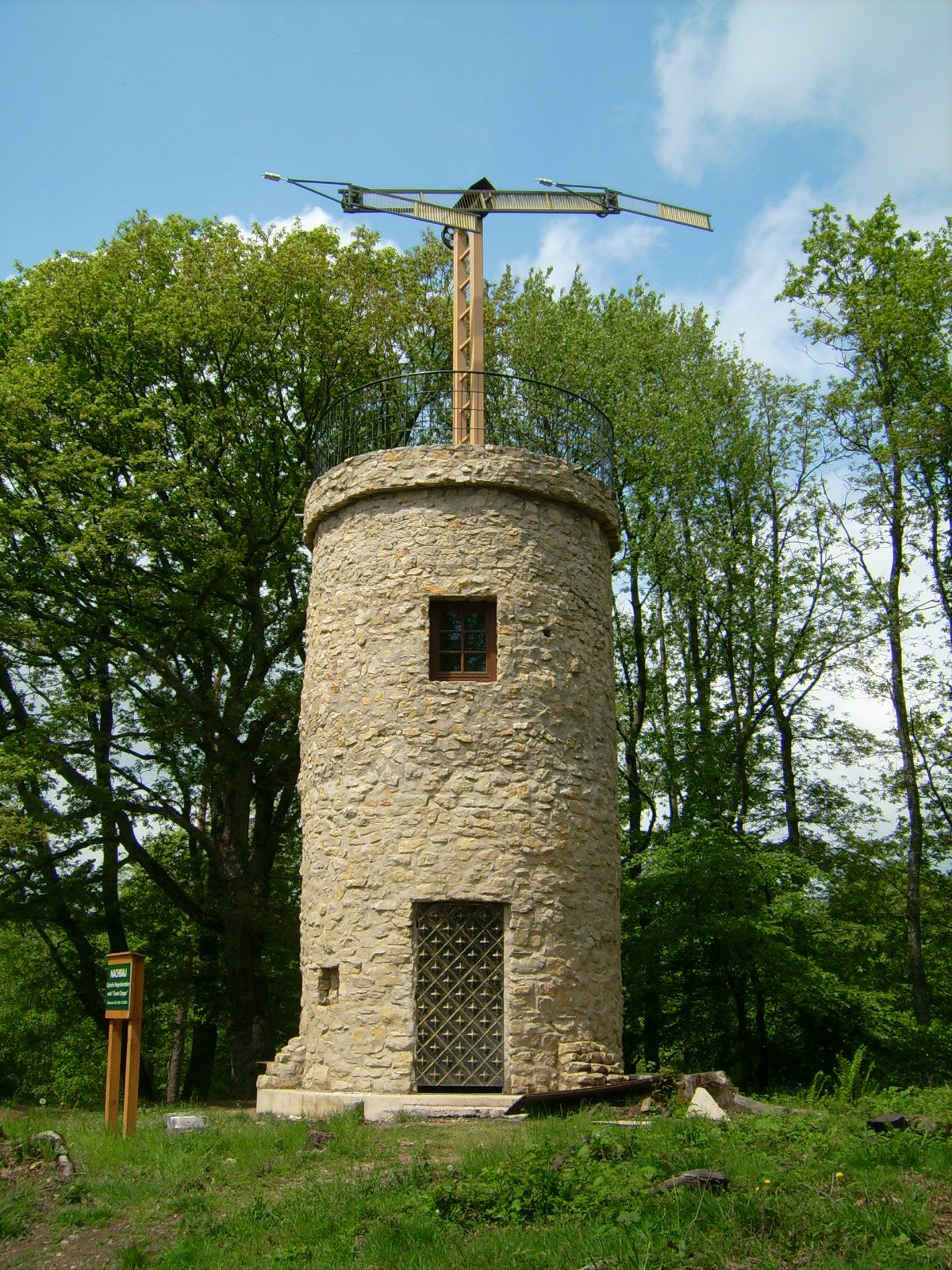
Optical Telegraph
An optical telegraph is a line of stations, typically towers, for the purpose of conveying textual information by means of visual signals. There are two main types of such systems; the semaphore telegraph which uses pivoted indicator arms and conveys information according to the direction the indicators point, and the shutter telegraph which uses panels that can be rotated to block or pass the light from the sky behind to convey information. The most widely used system was invented in 1792 in France by Claude Chappe, and was popular in the late eighteenth to early nineteenth centuries. This system is often referred to as ''semaphore'' without qualification. Lines of relay towers with a semaphore rig at the top were built within line of sight of each other, at separations of . Operators at each tower would watch the neighboring tower through a telescope, and when the semaphore arms began to move spelling out a message, they would pass the message on to the next tower. This sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redoubt
A redoubt (historically redout) is a fort or fort system usually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying on earthworks, although some are constructed of stone or brick. It is meant to protect soldiers outside the main defensive line and can be a permanent structure or a hastily constructed temporary fortification. The word means "a place of retreat". Redoubts were a component of the military strategies of most European empires during the colonial era, especially in the outer works of Vauban-style fortresses made popular during the 17th century, although the concept of redoubts has existed since medieval times. A redoubt differs from a redan in that the redan is open in the rear, whereas the redoubt was considered an enclosed work. The advent of mobile warfare in the 20th century diminished the importance of stationary defence positions and siege warfare. Historically important redoubts English Civil War During the English Civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.png)