|
Fort Meade Radar Station
The Fort Meade radar station was a Cold War military site with several sets of radar equipment in various Army and USAF radar networks. The site operated c. 1950 until 1979 and had a Project Nike command post and radar network. Lashup site L-14 Site L-14 of the temporary Lashup Radar Network was the ground-controlled interception radar station established at Fort George G. Meade until the radar's surveillance area was covered by a Quantico AFS radar in 1955. The Fort Meade radar station also had the first experimental AN/GSG-2 Antiaircraft Defense System in 1955. ARAACOM site W-13DC In 1957 the Fort Meade station was designated an Army Air-Defense Command Post (AADCP) for the Washington-Baltimore Defense Area. The site had the first operational Martin AN/FSG-I Antiaircraft Defense System, a fire distribution center for Nike Missiles and which was operated by the 35th Antiaircraft Artillery Brigade. Designated W-13DC, the site had an AN/FPS-67 search radar and later a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nike Missile
The United States Army's Nike Ajax was the world's first operational guided surface-to-air missile (SAM), entering service in 1954. Nike Ajax was designed to attack conventional bomber aircraft flying at high subsonic speeds and altitudes above . Nike was initially deployed in the US to provide defense against Soviet bomber attacks, and was later deployed overseas to protect US bases, as well as being sold to various allied forces. Some examples remained in use until the 1970s. Originally known simply as Nike, it gained the Ajax as part of a 1956 renaming effort that resulted from the introduction of Hercules. It was initially given the identifier SAM-A-7 (Surface-to-air, Army, design 7) as part of an early tri-service identification system, but later changed to MIM-3 (Mobile Interceptor Missile, design 3) in 1962.Nike was initially designated SAM-G-7, and later changed to SAM-A-7. Originally the Air Force used A while the Army used G, but the Air Force abandoned the 1947 tri-se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bendix AN/FPS-65 Radar
The AN/FPS-20 was a widely used L band early warning and ground-controlled interception radar system employed by the United States Air Force Air Defense Command, the NORAD Pinetree Line in Canada, the USAF CONAD in the continental United States, and a variety of other users. The design started life as the Bendix AN/FPS-3 in 1950, was upgraded to the FPS-20, then spawned over a dozen different variants as additional upgrades were applied. The FPS-20 formed the backbone of the US air defense network through the early Cold War with over 200 units deployed. Most FPS-20 sites were replaced by modern equipment in the late 1960s, although a number were turned over to the FAA, modified for air traffic control use, and became ARSR-60s. The first AN/FPS-3 arrived in December 1950, slated for installation at Eniwetok Atoll to control aircraft involved in the atomic bomb tests of early 1951. Over the next few years, 48 FPS-3s were installed to replace older systems in the Lashup Radar Network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/FPS-14
The AN/FPS-14 was a medium-range search Radar used by the United States Air Force Air Defense Command. This medium-range search radar was designed and built by Bendix as a SAGE system gap-filler radar to provide low-altitude coverage. Operating in the S-band at a frequency between 2700 and 2900 MHz, the AN/FPS-14 could detect at a range of 65 miles. The system was deployed in the late 1950s and 1960s at unmanned radar facilities (called "Gap Fillers") designed to fill the low-altitude gaps between manned long-range radar stations. Gaps in coverage existed due to the curvature of the earth, mountains, hills, valleys, rivers, and so forth. The typical unmanned gap-filler radar annex consisted of a small L-shaped cinder-block building, with the radar equipment and the data-transmission equipment in one section and one or more diesel generators in the other section. These unmanned gap-filler sites generally had a three-legged radar tower about 85 feet tall where the AN/FP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterson Air Force Base
Peterson Space Force Base, previously Peterson Air Force Base, Peterson Field, and Army Air Base, Colorado Springs, is a U.S. Space Force Base that shares an airfield with the adjacent Colorado Springs Municipal Airport and is home to the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD), the Space Force's 21st Space Wing, elements of the Space Force's Space Systems Command, and United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) headquarters. Developed as a World War II air support base for Camp Carson, the facility conducted Army Air Forces training and supported Cold War air defense centers at the nearby Ent Air Force Base, Chidlaw Building, and Cheyenne Mountain Complex. The base was the location of the Air Force Space Command headquarters from 1987 to 20 December 2019 and has had NORAD/NORTHCOM command center operations since the 2006 Cheyenne Mountain Realignment placed the nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex centers on standby. On 26 July 2021, the installation was renamed Peterson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/FPS-90
The AN/FPS-6 Radar was a long-range height finding radar used by the United States Air Force's Air Defense Command. The AN/FPS-6 radar was introduced into service in the late 1950s and served as the principal height-finder radar for the United States for several decades thereafter. It was also used by the Royal Air Force alongside their AMES Type 80s. Built by General Electric, the S-band radar operated on a frequency of 2700 to 2900 MHz. Between 1953 and 1960, about 450 units of the AN/FPS-6 and the mobile AN/MPS-14 version were produced. The AN/FPS-90 and AN/FPS-116 radars were identical to the AN/FPS-6 except for receiver modifications. Operation The radar consisted of an antenna group, a transmitter group, a receiver group, and an ancillary group. Most fixed sites had a remote group, which allowed the control of the radar from inside the operations center. Also located in operations, was the anti-jam receivers. These receivers were fed with raw video from the tower receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric AN/FPS-6 Radar
The AN/FPS-6 Radar was a long-range height finding radar used by the United States Air Force's Air Defense Command. The AN/FPS-6 radar was introduced into service in the late 1950s and served as the principal height-finder radar for the United States for several decades thereafter. It was also used by the Royal Air Force alongside their AMES Type 80s. Built by General Electric, the S-band radar operated on a frequency of 2700 to 2900 MHz. Between 1953 and 1960, about 450 units of the AN/FPS-6 and the mobile AN/MPS-14 version were produced. The AN/FPS-90 and AN/FPS-116 radars were identical to the AN/FPS-6 except for receiver modifications. Operation The radar consisted of an antenna group, a transmitter group, a receiver group, and an ancillary group. Most fixed sites had a remote group, which allowed the control of the radar from inside the operations center. Also located in operations, was the anti-jam receivers. These receivers were fed with raw video from the tower receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Lee Air Force Station
Fort Lee Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force station. It is located northwest of Prince George, Virginia. It was closed in 1983 due to budget cuts. History Fort Lee Air Force Station, located on the United States Army Fort Lee installation, was selected in 1956 for a Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) system direction center (DC) site, designated DC-04. The SAGE system was a network linking Air Force (and later FAA) General Surveillance Radar stations into a centralized center for Air Defense, intended to provide early warning and response for a Soviet nuclear attack. This automated control system was used by NORAD for tracking and intercepting enemy bomber aircraft. In the later versions the system could automatically direct aircraft to an interception by sending instructions directly to the aircraft's autopilot. The 4625th Air Defense Wing was activated at the site under the 85th Air Division on 1 December 1956 to supervise the construction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-Automatic Ground Environment
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of mainframe computer, large computers and associated computer network, networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. SAGE directed and controlled the NORAD response to a possible Soviet air attack, operating in this role from the late 1950s into the 1980s. Its enormous computers and huge displays remain a part of cold war lore, and after decommissioning were common props in movies such as ''Dr. Strangelove'' and Colossus: The Forbin Project, ''Colossus'', and on science fiction TV series such as ''The Time Tunnel''. The processing power behind SAGE was supplied by the largest discrete component-based computer ever built, the IBM-manufactured AN/FSQ-7 Combat Direction Central, AN/FSQ-7. Each SAGE Direction Center (DC) housed an FSQ-7 which occupied an entire floor, approximately not including supporting equipment. The F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Air Defense Sector
The Washington Air Defense Sector (WaADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command (ADC) 26th Air Division, being stationed at Fort Lee Air Force Station (AFS), Virginia. It was inactivated on 1 April 1966. History WaADS was established in December 1956 as the 4625th Air Defense Wing. It was not assigned any units until 1958 when it assumed control of former ADC Eastern Air Defense Force units primarily in Maryland, Delaware, and Virginia. Units of the 32d Air Division in North and South Carolina were transferred to WaADS in 1961 as the 26th Air Division area of responsibility expanded southward. The organization provided command and control over several aircraft, missile and radar squadrons. On 1 February 1959 the new Semi Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) Direction Center (DC-04) became operational. DC-04 was equipped with dual AN/FSQ-7 Computers. The day-to-day operations of the command were to tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo Air Force Station
Palermo Air Force Station (ADC ID: P-54, NORAD ID: Z-54) is a closed United States Air Force (USAF) General Surveillance Radar station. It was located in Palermo, New Jersey, north of Sea Isle City, in Cape May County, New Jersey, United States. It was closed in 1970. History In 1948 USAF directed Air Defense Command (ADC) to take radar sets out of storage for operation in the Northeastern United States. By August. a radar had been placed in operation at Palermo, NJ. This hasty program was appropriately named "Lashup."Winkler & Webster, p.3 The AN/TPS-1B long-range search radar at Palermo (Lashup Site L-14) fed into a primitive control center established at Roslyn Air Warning Station, New York. Prompted by the start of the Korean War, on July 11, 1950, the Secretary of the Air Force asked the Secretary of Defense for approval to expedite construction of additional stations, and it received the Defense Secretary's approval on July 21, the Air Force directed the Army Corps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
770th Radar Squadron
77 may refer to: * 77 (number) * one of the years 77 BC, AD 77, 1977, 2077 Music * 77 (band), a Spanish hard rock band * 77 (Matt Kennon album), ''77'' (Matt Kennon album) * ''Talking Heads: 77'', debut album by Talking Heads * 77 (Nude Beach album), ''77'' (Nude Beach album), an album by the band Nude Beach See also * '77 (other) * 7/7, the 7 July 2005 London bombings * * List of highways numbered {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
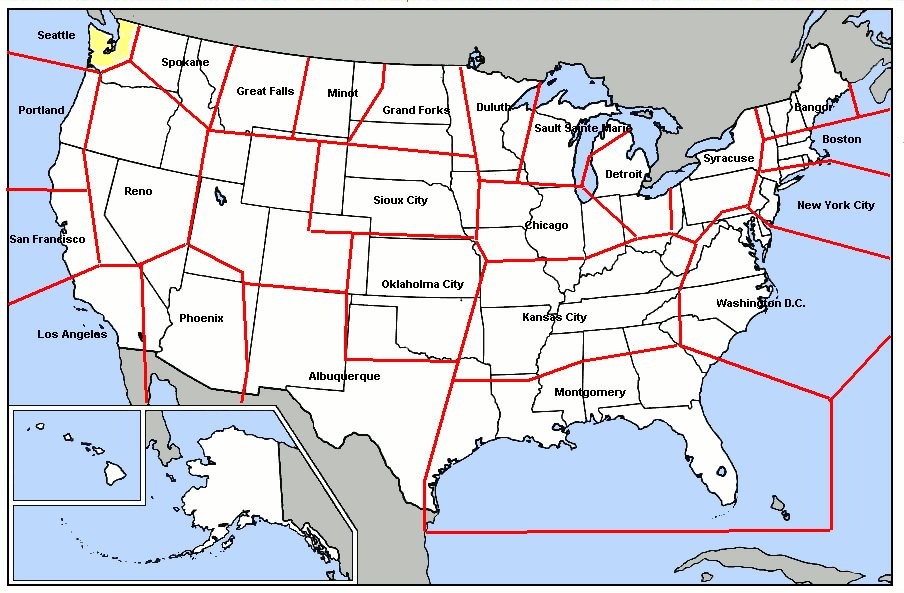
List Of USAF Aerospace Defense Command General Surveillance Radar Stations
United States general surveillance radar stations include Army and USAF stations of various US air defense networks (in reverse chronological order): *Joint Surveillance System (JSS), with radar stations controlled by joint FAA/USAF ROCCs beginning in 1980 *SAGE radar stations, for the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment network prior to the JSS (the 1st SAGE squadrons were designated in 1958) *Alaska Ring radar net, the radar stations of Alaskan Air Command *Permanent System radar stations, the Air Defense Command manual network of radar stations prior to deployment of SAGE *Lashup Radar Network radar stations, the radar stations deployed 1950-2 when the "Radar Fence" Plan was not approved * Temporary radar net, the "five-station radar net" established in 1948 *Army Radar Stations, World War II installations of the Aircraft Warning Service with radars (cf. filter centers, Ground Observer Corps stations, etc.) By usage: *RBS Express sites, temporary stations for Radar Bomb Scoring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |