|
Formyl Peptide Receptor 3
N-formyl peptide receptor 3 (FPR3) is a receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FPR3'' gene. Nomenclature note Confusingly, there are two nomenclatures for FPR receptors and their genes, the first one used, FPR, FPR1, and FPR2 and its replacement (which corresponds directly to these three respective receptors and their genes), FPR1, FPR2, and FPR3. The latter nomenclature is recommended by the International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and is used here. Other previously used names for FPR1 are NFPR, and FMLPR; for FPR2 are FPRH1, FPRL1, RFP, LXA4R, ALXR, FPR2/ALX, HM63, FMLPX, and FPR2A; and for FPR3 are FPRH2, FPRL2, and FMLPY. FPR3 function The overall function of FPR3 is quite unclear. Compared to FPR1 and FPR2, FPR3 is highly phosphorylated (a signal for receptor inactivation and internalization) and more localized to small intracellular vesicles. This suggests that FPR3 rapidly internalizes after binding its ligands and thereby may serve as a "d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
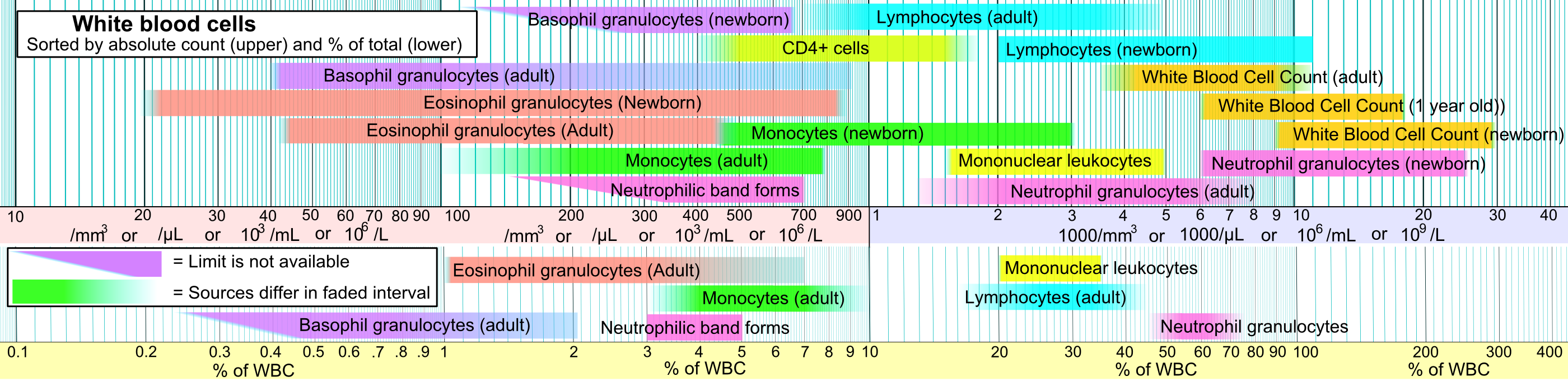
Basophils
Basophils are a type of white blood cell. Basophils are the least common type of granulocyte, representing about 0.5% to 1% of circulating white blood cells. However, they are the largest type of granulocyte. They are responsible for inflammatory reactions during immune response, as well as in the formation of acute and chronic allergic diseases, including anaphylaxis, asthma, atopic dermatitis and hay fever. They also produce compounds that coordinate immune responses, including histamine and serotonin that induce inflammation, heparin that prevents blood clotting, although there are less than that found in mast cell granules. Mast cells were once thought to be basophils that migrated from blood into their resident tissues ( connective tissue), but they are now known to be different types of cells. Basophils were discovered in 1879 by German physician Paul Ehrlich, who one year earlier had found a cell type present in tissues that he termed ''mastzellen'' (now mast cells). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine
''N''-Formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLF, fMLP or ''N''-formyl-met-leu-phe) is an ''N''- formylated tripeptide and sometimes simply referred to as chemotactic peptide is a potent polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) chemotactic factor and is also a macrophage activator. fMLF is the prototypical representative of the ''N''-formylated oligopeptide family of chemotactic factors. These oligopeptides are known to be, or mimic the actions of, the ''N''-formyl oligopeptides that are (a) released by tissue bacteria, (b) attract and activate circulating blood leukocytes by binding to specific G protein coupled receptors on these cells, and (c) thereby direct the inflammatory response to sites of bacterial invasion. fMLF is involved in the innate immunity mechanism for host defense against pathogens. fMLF led to the first discovery of a leukocyte receptor for a chemotactic factor, defined three different types of fMLF receptors that have complementary and/or opposing effects on i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formyl Peptide Receptor 2
N-formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) located on the surface of many cell types of various animal species. The human receptor protein is encoded by the ''FPR2'' gene and is activated to regulate cell function by binding any one of a wide variety of ligands including not only certain N-Formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides such as N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) but also the polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolite of arachidonic acid, lipoxin A4 (LXA4). Because of its interaction with lipoxin A4, FPR2 is also commonly named the ALX/FPR2 or just ALX receptor. Expression The FPR2 receptor is expressed on human neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, T cells, synovial fibroblasts, and intestinal and airway epithelium. Function Many oligopeptides that possess an N-Formylmethionine ''N''-terminal residue such as the prototypical tripeptide N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (i.e. FMLP), are products of the prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formyl Peptide Receptor 1
Formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1, FPR1 receptor, fMet-Leu-Phe receptor 1, FMLP receptor 1, or N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine receptor 1) is a cell surface receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''formyl peptide receptor 1'' (''FPR1'') gene. This gene encodes a G protein-coupled receptor cell surface protein that binds and is activated by N-Formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides, particularly N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP). FPR1 is prominently expressed by mammalian phagocytic and blood leukocyte cells where it functions to mediate these cells' responses to the N-formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides which are released by invading microorganisms and injured tissues. FPR1 directs these cells to sites of invading pathogens or disrupted tissues and then stimulates these cells to kill the pathogens or to remove tissue debris; as such, it is an important component of the innate immune system that operates in host defense and damage control. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanin
Humanin is a micropeptide encoded in the mitochondrial genome by the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, MT-RNR2. Its structure contains a three-turn α-helix, and no symmetry. In ''in vitro'' and animal models, it appears to have cytoprotective effects. Gene Humanin is encoded in the mitochondrial genome by the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, MT-RNR2. Multiple isoforms are found in the nuclear genome and are named MTRNR2L followed by a number. Protein The expressed peptide contains a three-turn α-helix, and has no symmetry. The length of the peptide depends on where it is produced. If it is produced inside the mitochondria it will be 21 amino acids long. If it is produced outside the mitochondria, in the cytosol, it will be 24 amino acids long. Both peptides have been shown to have biological activity. Other species The rat, ''Rattus norvegicus'', has a gene, ''rattin'', that encodes a 38 amino acid peptide homologous to humanin. The two genes produce cDNAs that show 88% sequence identity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathepsin D
Cathepsin D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTSD'' gene. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a protein dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Cathepsin D is an aspartic endo-protease that is ubiquitously distributed in lysosomes. The main function of cathepsin D is to degrade proteins and activate precursors of bioactive proteins in pre-lysosomal compartments. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase A1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of the ''CTSD'' gene is initiated from several sites, including one that is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Homozygous deletion of the ''CTSD'' gene leads to early lethality in the postnatal phase. Deficiency of ''CTSD'' gene has been repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEBP1
Heme binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HEBP1 gene. Function The full-length protein encoded by this gene is an intracellular tetrapyrrole-binding protein. This protein includes a natural chemoattractant peptide of 21 amino acids at the N-terminus, which is a natural ligand for formyl peptide receptor-like receptor 2 ( FPRL2) and promotes calcium mobilization and chemotaxis in monocytes and dendritic cell Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...s. References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADH Dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) from its reduced form (NADH) to its oxidized form (NAD+). Members of the NADH dehydrogenase family and analogues are commonly systematically named using the format ''NADH:acceptor oxidoreductase''. The chemical reaction these enzymes catalyze are generally represented with the follow equation; : NADH + H+ + acceptor NAD+ + reduced acceptor NADH dehydrogenase is a flavoprotein that contains iron-sulfur centers. NADH dehydrogenase is used in the electron transport chain for generation of ATP. The EC term NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.11) is defined for NADH dehydrogenases that use a quinone (excluding ubiquinone) as the acceptor. The EC term NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Respiratory complex I, (also known as NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, Type I NADH dehydrogenase and mitochondrial complex I) is the first large protein complex of the respiratory chains of many organisms from bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |