|
Form Factor (other)
Form factor or form-factor may refer to: Manufacturing * Form factor (design), an aspect of design which defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of hardware components, particularly in electronics and electronic packaging ** Form factor (mobile phones) ** Motherboard form factor ** Hard disk drive form factor * FormFactor (company), a semiconductor test and measurement company, acquired Cascade Microtech in 2016 Scattering theory * Form factor (quantum field theory), a semi-empirical formula used in effective quantum field theories * Atomic form factor, or atomic scattering factor, a measure of the amplitude of a wave scattered from an isolated atom * Electric form factor, the Fourier transform of electric charge distribution in space * Magnetic form factor, the Fourier transform of an electric current distribution in space Other sciences * Form factor (electronics), characterizing the functional form of oscillating signals * Form factor ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (design)
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically evolved slower than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for hardware compatibility between different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of transportat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (mobile Phones)
The form factor of a mobile phone is its size, shape, and style, as well as the layout and position of its major components. With one non-movable section Bar A bar (also known as a slab, block, candybar) phone takes the shape of a cuboid, usually with rounded corners and/or edges. The name is derived from the rough resemblance to a chocolate bar in size and shape. This form factor is widely used by a variety of manufacturers, such as Nokia and Sony Ericsson. Bar-type smartphones commonly have the screen and keypad on a single face. Sony had a well-known ' Mars Bar' phone model CM-H333 in 1993 that was longer and thinner than the typical bar phone. Bar phones without a full keyboard tend to have a 3×4 numerical keypad; text is often generated on such systems using the Text on 9 keys algorithm. Keyboard bars These are variants of bars that have a full QWERTY keyboard on the front. While they are technically the same as a regular bar phone, the keyboard and all the buttons ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
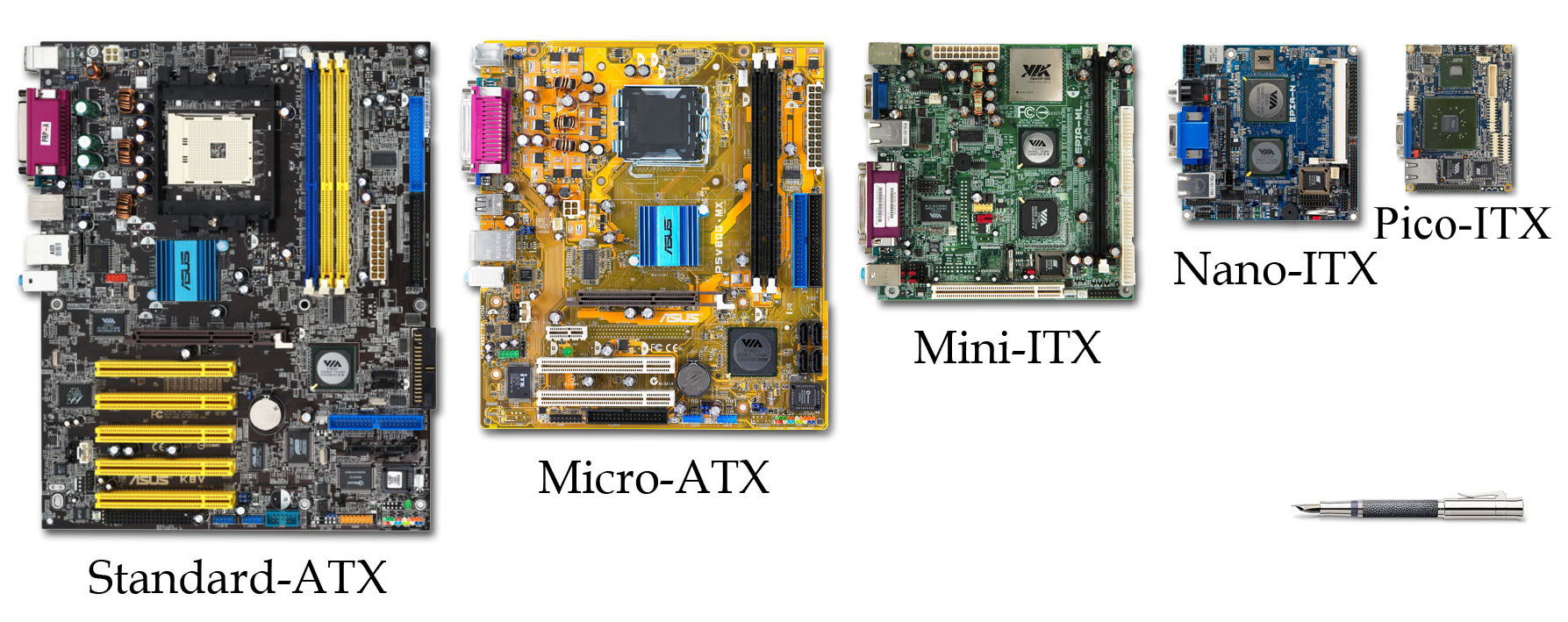
Motherboard Form Factor
In computing, the motherboard form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented. Overview of form factors A PC motherboard is the main circuit board within a typical desktop computer A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive Form Factor
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like mobile phones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FormFactor (company)
Formfactor, Inc. is a provider of test and measurement technologies for integrated circuits, with its headquarters in Livermore, California. It provides semiconductor companies with products to improve device performance and provide test and measurement technologies for integrated circuits. History FormFactor was founded in Elmsford, NY in 1993, and set up its first headquarters in Livermore, California in 1995. The company completed an initial public offering (IPO) on the Nasdaq as FORM, in June 2003 with 6 million shares priced at $14. FormFactor released the first x64 DRAM probe card in 2000, followed by the x128 DRAM probe card in 2002. The company shipped the first SmartMatrix full- wafer probe cards in February 2009. In October 2012, FormFactor signed an agreement with Astria Semiconductors Holdings, Inc. for the acquisition of MicroProbe, Inc. for $100 million in cash and $16.8 million in stocks. In June 2016, FormFactor acquired Cascade Microtech for $352 million. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Microtech
Cascade Microtech is a semiconductor test equipment manufacturer based in Beaverton in the Portland metropolitan area of the United States. Founded in 1983, the Oregon Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...-based company employs nearly 400 people. Formerly publicly traded company as CSCD on the NASDAQ, the company is now fully merged with FormFactor, Inc. History In the early 1980s, Eric W. Strid and K. Reed Gleason, employees at Tektronix (Tek), attempted to get their bosses to make a microwave wafer probe for testing microchips. Management declined, but did license the technology to the two, leading to the formation of Cascade Microtech in 1982 on a part-time basis. Dale E. Carlton joined the company as well, and in 1983 they produced their first product. The founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (quantum Field Theory)
In elementary particle physics and mathematical physics, in particular in effective field theory, a form factor is a function that encapsulates the properties of a certain particle interaction without including all of the underlying physics, but instead, providing the momentum dependence of suitable matrix elements. It is further measured experimentally in confirmation or specification of a theory—see experimental particle physics. Photon–nucleon example For example, at low energies the interaction of a photon with a nucleon is a very complicated calculation involving interactions between the photon and a sea of quarks and gluons, and often the calculation cannot be fully performed from first principles. Often in this context, form factors are also called " structure functions", since they can be used to describe the structure of the nucleon. However, the generic Lorentz-invariant form of the matrix element for the electromagnetic current interaction is known, : \varepsilon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Form Factor
In physics, the atomic form factor, or atomic scattering factor, is a measure of the scattering amplitude of a wave by an isolated atom. The atomic form factor depends on the type of scattering, which in turn depends on the nature of the incident radiation, typically X-ray diffraction, X-ray, Electron diffraction, electron or Neutron diffraction, neutron. The common feature of all form factors is that they involve a Fourier transform of a spatial density distribution of the scattering object from space, real space to momentum space (also known as reciprocal space). For an object with spatial density distribution, \rho(\mathbf), the form factor, f(\mathbf), is defined as :f(\mathbf)=\int \rho(\mathbf) e^\mathrm^3\mathbf, where \rho(\mathbf) is the spatial density of the scatterer about its center of mass (\mathbf=0), and \mathbf is the momentum transfer. As a result of the nature of the Fourier transform, the broader the distribution of the scatterer \rho in real space \mathbf, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Form Factor
The electric form factor is the Fourier transform of electric charge distribution in a nucleon. Nucleons (protons and neutrons) are made of up and down quarks which have charges associated with them (2/3 & -1/3, respectively). The study of Form Factors falls within the regime of Perturbative QCD. The idea originated from young William Thomson. See also * Form factor (other) Form factor or form-factor may refer to: Manufacturing * Form factor (design), an aspect of design which defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of hardware components, particularly in electronics and electroni ... References Electrodynamics {{particle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Form Factor
In electromagnetism, a magnetic form factor is the Fourier transform of an electric charge distribution in space. See also * Atomic form factor, for the form factor relevant to magnetic diffraction of free neutrons by unpaired outer electrons of an atom. * Electric form factor * Form factor (quantum field theory) In elementary particle physics and mathematical physics, in particular in effective field theory, a form factor is a function that encapsulates the properties of a certain particle interaction without including all of the underlying physics, but ... External links Magnetic form factors Andrey Zheludev, HFIR Center for Neutron Scattering, Oak Ridge National Laboratory"The magnetic form factor of the neutron" E.E.W. Bruins, November 1996 Electromagnetism {{math-physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (electronics)
In electronics and electrical engineering, the form factor of an alternating current waveform (signal) is the ratio of the RMS (root mean square) value to the average value (mathematical mean of absolute values of all points on the waveform). It identifies the ratio of the direct current of equal power relative to the given alternating current. The former can also be defined as the direct current that will produce equivalent heat. Calculating the form factor For an ideal, continuous wave function over time T, the RMS can be calculated in integral form: X_\mathrm = \sqrt The rectified average is then the mean of the integral of the function's absolute value: X_\mathrm = The quotient of these two values is the form factor, k_\mathrm, or in unambiguous situations, k. k_\mathrm = \frac \mathrm \mathrm = \frac = \frac X_\mathrm reflects the variation in the function's distance from the average, and is disproportionately impacted by large deviations from the unrectified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (radiative Transfer)
Form factor or form-factor may refer to: Manufacturing * Form factor (design), an aspect of design which defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of hardware components, particularly in electronics and electronic packaging ** Form factor (mobile phones) ** Motherboard form factor ** Hard disk drive form factor * FormFactor (company), a semiconductor test and measurement company, acquired Cascade Microtech in 2016 Scattering theory * Form factor (quantum field theory), a semi-empirical formula used in effective quantum field theories * Atomic form factor, or atomic scattering factor, a measure of the amplitude of a wave scattered from an isolated atom * Electric form factor, the Fourier transform of electric charge distribution in space * Magnetic form factor, the Fourier transform of an electric current distribution in space Other sciences * Form factor (electronics), characterizing the functional form of oscillating signals * Form factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |