|
Ford 9-inch Axle
The Ford 9-inch is an automobile axle manufactured by Ford Motor Company. It is known as one of the most popular axles in automotive history. It was introduced in 1957 model year cars and ended production in 1986, having been phased out in favor of the Ford 8.8 inch axle. However, aftermarket companies still produce the 9-inch design. It is a semi-floating drop-out axle and had a GAWR up to . One of the features which distinguishes this axle from other high-performance or heavy-duty domestic solid axles is that unlike other axle designs, access to the differential gears is not through the rear center cover; rather, in the Ford 9 inch, the rear cover is welded to the axle housing, and access to internals is obtained by removing the center cover on the pinion (front) side of the axle through which the driveshaft yoke connects, with the differential assembly coming out of the axle as a unit attached to the cover. Although this requires disconnecting the driveshaft to access the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobiles and commercial vehicles under the Ford brand, and luxury cars under its Lincoln luxury brand. Ford also owns Brazilian SUV manufacturer Troller, an 8% stake in Aston Martin of the United Kingdom and a 32% stake in China's Jiangling Motors. It also has joint ventures in China (Changan Ford), Taiwan (Ford Lio Ho), Thailand ( AutoAlliance Thailand), and Turkey ( Ford Otosan). The company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and is controlled by the Ford family; they have minority ownership but the majority of the voting power. Ford introduced methods for large-scale manufacturing of cars and large-scale management of an industrial workforce using elaborately engineered manufacturing sequences typified by moving assembly lines; by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford 8
Ford 7Y is a car built by Ford UK from 1938 until 1939. During that time 65,098 cars were produced. The car was officially marketed as a Ford Eight, and was a rebodied and slightly larger version of the Model Y. The car was powered by a 8hp (RAC horsepower) Ford sidevalve engine. A minor facelift, unveiled in September 1939, resulted in the first Anglia. The car sported some unusual features such as openable rear windows that were located in the main body work as this was only a two-door vehicle. A rear wheel cover was available on the de-luxe models with the standard version also having a recess in the rear bodywork to accept the spare wheel, albeit not covered. The storage of the spare wheel in this manner mimics the styling of the V8 Pilot An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
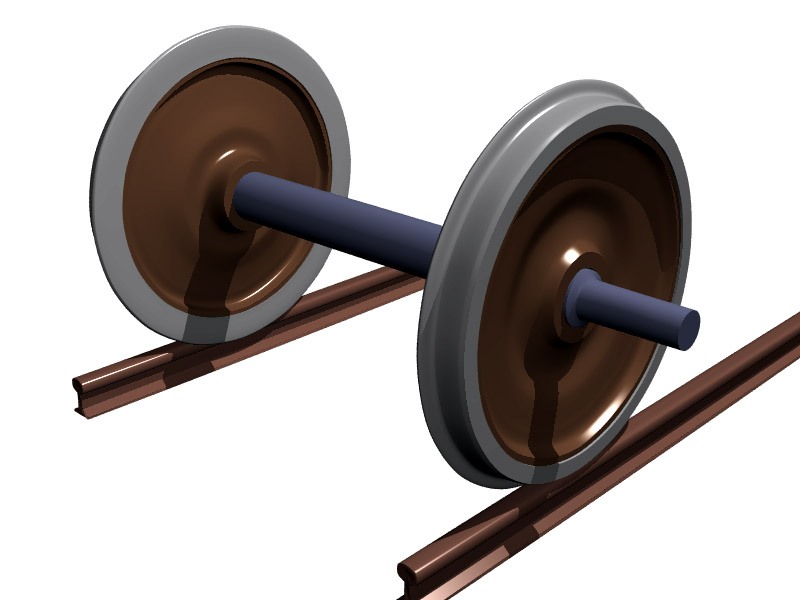
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a ''spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft which rotates with the wheel, being either bolted or splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft''. However, in looser usage, an entire assembly including the surrounding axle housing (typically a casting) is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Axle Weight Rating
Vehicle weight is a measurement of wheeled motor vehicles; either an actual measured weight of the vehicle under defined conditions or a gross weight rating for its weight carrying capacity. Curb or kerb weight Curb weight (U.S. English) or kerb weight (British English) is the total mass of a vehicle with standard equipment and all necessary operating consumables such as motor oil, transmission oil, brake fluid, coolant, air conditioning refrigerant, and sometimes a full tank of fuel, while not loaded with either passengers or cargo. The gross vehicle weight is larger and includes the maximum payload of passengers and cargo. This definition may differ from definitions used by governmental regulatory agencies or other organizations. For example, many European Union manufacturers include the weight of a driver and luggage to follow European Directive 95/48/EC. Organizations may also define curb weight with fixed levels of fuel and other variables to equalize the value for the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Axle
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice), or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential (mechanical Device)
A differential is a gear train with three drive shafts that has the property that the rotational speed of one shaft is the average of the speeds of the others, or a fixed multiple of that average. Functional description The following description of a differential applies to a traditional rear-wheel-drive car or truck with an open or limited slip differential combined with a reduction gearset using bevel gears (these are not strictly necessary; see spur-gear differential): Thus, for example, if the car is making a turn to the right, the main ring gear may make 10 full rotations. During that time, the left wheel will make more rotations because it has farther to travel, and the right wheel will make fewer rotations as it has less distance to travel. The sun gears (which drive the axle half-shafts) will rotate at different speeds relative to the ring gear (one faster, one slower) by, say, 2 full turns each (4 full turns relative to each other), resulting in the left wheel mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinion
A pinion is a round gear—usually the smaller of two meshed gears—used in several applications, including drivetrain and rack and pinion systems. Applications Drivetrain Drivetrains usually feature a gear known as the pinion, which may vary in different systems, including * the typically smaller gear in a gear drive train (although in the first commercially successful steam locomotive—the ''Salamanca''—the ''pinion'' was rather large). In many cases, such as remote controlled toys, the pinion is also the drive gear for a reduction in speed, since electric motors operate at higher speed and lower torque than desirable at the wheels. However the reverse is true in watches, where gear trains commence with a high-torque, low-speed spring and terminate in the fast-and-weak escapement. * the smaller gear that drives in a 90-degree angle towards a crown gear in a differential drive. * the small front sprocket on a chain driven motorcycle. *the clutch bell gear when pair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Falcon (Australia)
The Ford Falcon is a full-size car, full-sized car that was manufactured by Ford Australia from 1960 to 2016. From the XA series of 1972 onward, each Falcon and range of derivates have been designed, developed, and built in Australia, following the phasing out of the American-influenced Ford Falcon (North America), Falcon of 1960 to 1971, which had been re-engineered locally as the XK to XY series for the harsher Australian conditions. The luxury-oriented Ford Fairmont model joined the range from 1965. Luxury long-wheelbase derivative versions called the Ford Fairlane (Australia), Ford Fairlane and LTD arrived in 1967 and 1973 respectively with production ending in 2007. Over 3,000,000 Ford Falcon and its derivatives were made in seven generations to 2016, almost exclusively in Australia and New Zealand, but also South Africa and some RHD Asian markets. Along with its closest Australian-made rival, the Holden Commodore, the Falcon once dominated the fleets of taxis in Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Falcon (North America)
The Ford Falcon is a model line of cars that was produced by Ford from the 1960 to 1970 model years. The first compact car marketed by the American Big Three automobile manufacturers (though antedated by the Rambler American), the Falcon was the third car line introduced by Ford, following the full-sized Ford and the Ford Thunderbird. In contrast to its competitors, the Falcon was developed as a scaled-down version of the full-size Ford Galaxie sedan. Through its production, the Falcon was offered in the same body styles as its full-sized Galaxie counterpart, including two-door and four-door sedans, two-door hardtops and convertibles, two-door and four-door station wagons (the former, serving as a basis of the final Ford sedan delivery), and coupe utility pickups (serving as the basis of the Ford Ranchero). During its production, the Falcon served as the basis for multiple Ford vehicle lines, including the first generations of the Ford Mustang pony car and the Ford Econoline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dana 60
The Dana/Spicer Model 60 is an automotive axle manufactured by Dana Holding Corporation and used in OEM pickup and limited passenger car applications by Chevrolet, Dodge, Chrysler, Jeep, Ford and Land Rover. There are front and rear versions of the Dana 60. It can be readily identified by its straight axle tubes, 10 bolt asymmetrical cover, and a "60" cast into the housing. Gross axle weight ratings are often lowered by the vehicle manufacturer for safety and tire reasons. They are also lowered to reduce loads on other powertrain components such as transmissions and transfer cases. Dana 60 Axles are also increasingly swapped into many custom offroad applications to accommodate larger tires and deep compound gearing with locking differentials. __TOC__ General specifications Every Dana 60 that was originally manufactured by Dana Corp (i.e. not aftermarket) is stamped with a build date and bill of materials on the back of the right hand axle tube. * Gross Axle Weight Rating ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software, and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles, and trucks and their respective engineering subsystems. It also includes modification of vehicles. Manufacturing domain deals with the creation and assembling the whole parts of automobiles is also included in it. The automotive engineering field is research intensive and involves direct application of mathematical models and formulas. The study of automotive engineering is to design, develop, fabricate, and test vehicles or vehicle components from the concept stage to production stage. Production, development, and manufacturing are the three major functions in this field. Disciplines Automobile engineering Automobile engineering is a branch study of engineering which teaches manufacturing, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)

