|
Flame Safety Lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp that provides illumination in coal mines and is designed to operate in air that may contain coal dust or gases, both of which are potentially flammable or explosive. Until the development of effective electric lamps in the early 1900s, miners used flame lamps to provide illumination. Open flame lamps could ignite flammable gases which collected in mines, causing explosions; safety lamps were developed to enclose the flame and prevent it from igniting the surrounding atmosphere. Flame safety lamps have been replaced in mining with sealed explosion-proof electric lights. Background Damps or gases Miners have traditionally referred to the various gases encountered during mining as damps, from the Middle Low German word ''dampf'' (meaning " vapour"). Damps are variable mixtures and are historic terms. * '' Firedamp'' Naturally occurring flammable mixtures, principally methane. * '' Blackdamp'' or ''Chokedamp'' Nitrogen and carbon d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mine Safety Lamp
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines * Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimdon Grange
Trimdon Grange is a village in County Durham, in England. It is situated ten miles to the west of Hartlepool, and a short distance to the north of Trimdon. Colliery disaster At 14:40 on 16 February 1882 the Trimdon Grange colliery suffered a major explosion causing the deaths of 69 men and boys. The coroner (TW Snagge) reported to both houses of Parliament: * The mine was a dusty mine and watering should have been daily but it was done "not in all places, but where it was absolutely necessary." * The mine was not "more than ordinarily gassy", but there is some evidence that the identified points of leakage might have been points of accumulation from leaks elsewhere. * The lamps in use were Davy pattern and naked lights called "midgies" in some areas. The coroner found no evidence that the midgies were connected with the explosion. * Good order and discipline prevailed in Trimdon Grange Colliery. * The air pressure had been exceptionally low, the lowest it had been that month, fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for the first time: potassium and sodium in 1807 and calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium and boron the following year, as well as for discovering the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine. Davy also studied the forces involved in these separations, inventing the new field of electrochemistry. Davy is also credited to have been the first to discover clathrate hydrates in his lab. In 1799 he experimented with nitrous oxide and was astonished at how it made him laugh, so he nicknamed it "laughing gas" and wrote about its potential anaesthetic properties in relieving pain during surgery. Davy was a baronet, President of the Royal Society (PRS), Member of the Royal Irish Academy (MRIA), Fellow of the Geological Society (FGS), and a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
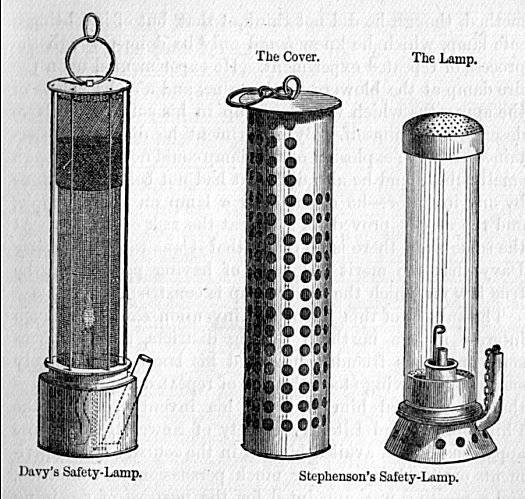
Davy Lamp
The Davy lamp is a safety lamp for use in flammable atmospheres, invented in 1815 by Sir Humphry Davy.Brief History of the Miner's Flame Safety Lamp at minerslamps.net. Accessed 7 July 20121 It consists of a lamp with the flame enclosed inside a mesh screen. It was created for use in s, to reduce the danger of explosions due to the presence of and other flammable gases, called '' |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. Self-help advocate Samuel Smiles particularly praised his achievements. His chosen rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway line in the world to use locomotives, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geordie Lamp
The Geordie lamp was a safety lamp for use in flammable atmospheres, invented by George Stephenson in 1815 as a miner's lamp to prevent explosions due to firedamp in coal mines. Origin In 1815, Stephenson was the engine-wright at the Killingworth Colliery in Northumberland and had been experimenting for several years with candles close to firedamp emissions in the mine. In August he ordered an oil lamp which was delivered on 21 October and tested by him in the mine in the presence of explosive gases. He improved this over several weeks with the addition of capillary tubes at the base so that it gave more light and tried new versions on 4 and 30 November. This was presented to the Literary and Philosophical Society (Lit & Phil) of Newcastle upon Tyne on 5 December 1815. Although controversy arose between Stephenson's design and the Davy lamp (invented by Humphry Davy in the same year), Stephenson's original design worked on significantly different principles from Davy's final d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Triangle
The fire triangle or combustion triangle is a simple model for understanding the necessary ingredients for most fires. The triangle illustrates the three elements a fire needs to ignite: heat, fuel, and an oxidizing agent (usually oxygen). A fire naturally occurs when the elements are present and combined in the right mixture. A fire can be prevented or extinguished by removing any one of the elements in the fire triangle. For example, covering a fire with a fire blanket blocks oxygen and can extinguish a fire. In large fires where firefighters are called in, decreasing the amount of oxygen is not usually an option because there is no effective way to make that happen in an extended area. Fire tetrahedron The fire tetrahedron represents the addition of a component in the chemical chain reaction, to the three already present in the fire triangle. Once a fire has started, the resulting exothermic chain reaction sustains the fire and allows it to continue until or unless at leas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Reid Clanny
William Reid Clanny FRSE (1776 – 10 January 1850) was an Irish physician and inventor of a safety lamp. Life Clanny was born in Bangor, County Down, Kingdom of Ireland. He trained as a physician at Edinburgh, and served as an assistant surgeon in the Royal Navy. He was present at the Battle of Copenhagen in 1801. He left the Navy and graduated in 1803 before settling for a while in Durham. He moved to Bishopwearmouth, near Sunderland, England and practised there for 45 years. While in Durham, on 4th February, 1806, he was initiated into Freemasonry at the Marquis of Granby Lodge. Then after moving to Sunderland, he joined The Sea Captain's Lodge, later to be renamed Palatine Lodge No 97. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1825, his proposers being Sir George Ballingall, Robert Kaye Greville, and Sir William Newbigging. Clanny died on 10 January 1850 and was buried at Galleys Gill Cemetery in Sunderland. The entry in the Dictionary of National Bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallsend
Wallsend is a town in North Tyneside, England, at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall. It has a population of 43,842 and lies east of Newcastle upon Tyne. History Roman Wallsend In Roman times, this was the site of the fort of Segedunum. This fort protected the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall, which did not terminate at the western wall of the fort, but continued from its south-eastern corner down to the shore of the River Tyne. As David Breeze writes, "In the early nineteenth century, as recorded by Bruce, John Buddle the Younger had often seen the Wall foundations extending far into the river when swimming there as a boy." Pre-Conquest The withdrawal of the Romans from the Wall immediately brought the Picts from the north and shortly afterwards the Angles, sailing from near the mouth of the River Elbe with frequent raids both from sea and from land. Ida the Saxon laid waste to the whole of the north in 547 and Wallsend doubtless suffered in the general devastation. It was not un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |
Sir James Lowther, 4th Baronet
Sir James Lowther, 4th Baronet, FRS (1673 – 2 January 1755) was an English landowner, industrialist and Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons for 54 years between 1694 and 1755. His ownership and development of coal mines around Whitehaven in Cumberland gave him substantial revenues, and he was reputed the richest commoner in England. Early life Lowther was baptised on 5 August 1673 at St Giles in the Fields, London, the second son of Sir John Lowther, 2nd Baronet and Jane Leigh. Educated privately in London, he attended Queen's College, Oxford and the Middle Temple. On the death of his father in 1706, the baronetcy was inherited by James's elder brother Christopher, but Christopher (whose drinking and gambling had led his father to disinherit him) was cut off with an annuity of about £100 a year and the family properties passed to James, who subsequently inherited the baronetcy in 1731, when his brother died without children. Politics In 1694, Lowther was returne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and port on the English north west coast and near to the Lake District National Park in Cumbria, England. Historically in Cumberland, it lies by road south-west of Carlisle and to the north of Barrow-in-Furness. It is the administrative seat of the Borough of Copeland, and has a town council for the parish of Whitehaven. The population of the town was 23,986 at the 2011 census. The town's growth was largely due to the exploitation of the extensive coal measures by the Lowther family, driving a growing export of coal through the harbour from the 17th century onwards. It was also a major port for trading with the American colonies, and was, after London, the second busiest port of England by tonnage from 1750 to 1772. This prosperity led to the creation of a Georgian planned town in the 18th century which has left an architectural legacy of over 170 listed buildings. Whitehaven has been designated a "gem town" by the Council for British Archaeology due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |