|
First Images Of Earth From Space
This is a timeline of first images of Earth from space. The initial photographs and digital images of planet Earth taken from outer space were preceded by aerial photography and continue in the form of satellite imagery. For the purpose of this list, a spaceflight is defined as any flight that crosses the Kármán line, the FAI-recognized edge of space, which is above mean sea level (AMSL). Images See also * List of notable images of Earth from space ** ** ** * * * * * * * * * * View of Earth from Mars In astronomy, an extraterrestrial sky is a view of outer space from the surface of an astronomical body other than Earth. The only extraterrestrial sky that has been directly observed and photographed by astronauts is that of the Moon. The ski ... References {{Earth Lists of firsts in space Photography and videography of Earth from space Spaceflight timelines Image galleries Astronomy image articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Image
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as ''pixels'', each with '' finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions fed as input by its spatial coordinates denoted with ''x'', ''y'' on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. Raster Raster images have a finite set of digital values, called ''picture elements'' or pixels. The digital image contains a fixed number of rows and columns of pixels. Pixels are the smallest individual element in an image, holding antiquated values that represent the brightness of a given color at any specific point. Typically, the pixels are stored in computer memory as a raster image or raster map, a two-dimensional array of small integers. These values are often transmitted or stored in a compressed form. Raster images can be created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
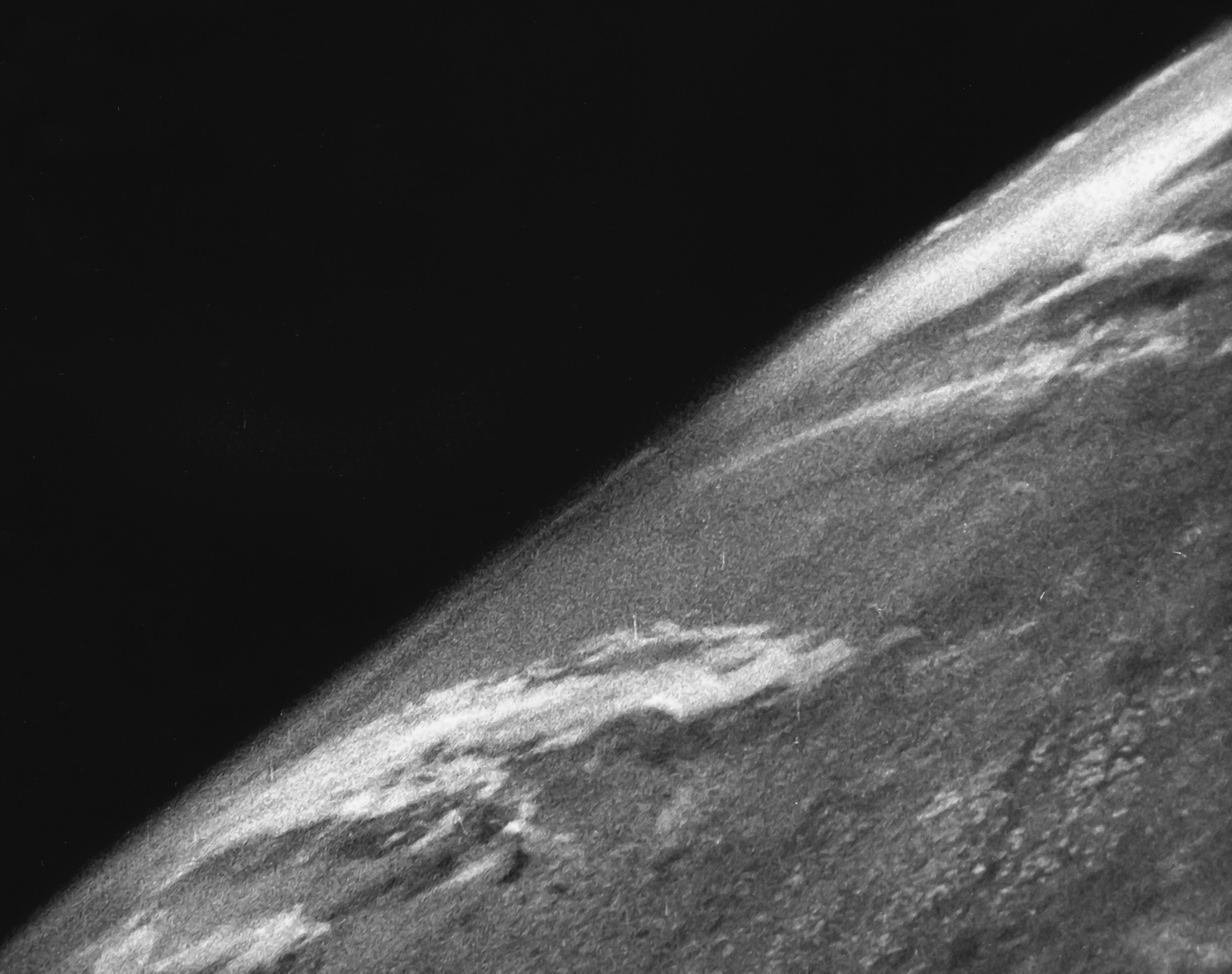
Radar Image
Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and digital computer storage to record its images. In a radar image, one can see only the energy that was reflected back towards the radar antenna. The radar moves along a flight path and the area illuminated by the radar, or footprint, is moved along the surface in a swath, building the image as it does so. Digital radar images are composed of many dots. Each pixel in the radar image represents the radar backscatter for that area on the ground: brighter areas represent high backscatter, darker areas represents low backscatter. The traditional application of radar is to display the position and motion of typically highly reflective objects (such as aircraft or ships) by sending out a radiowave signal, and then detecting the direction and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quill (satellite)
Quill was an experimental United States National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) program of the 1960s, which provided the first images of Earth from space using a synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Radar-imaging spacecraft of this design were not intended to be deployed operationally, since it was known that this system's resolution, inferior to that of concurrent experimental airborne systems, would not serve that purpose. Instead, the program's predominant goal was to show whether the propagation of radar waves through a large volume of the atmosphere and ionosphere would dangerously degrade the performance of the synthetic aperture feature. A detailed description of the program has been made available on-line by NRO. Objectives Initially, the primary benefit seen to be offered by radar imaging was its capability for operating at night and also for imaging through clouds or other atmospheric obstructions which absorbed or scattered waves not only in the visible spectrum but also in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resolution is directly connected to angular resolution, other instruments, like synthetic aperture radar or a network of weather stations, produce data whose spatial sampling layout is more related to the Earth's surface, such as in remote sensing and satellite imagery. See also * Image resolution Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how cl ... * Ground sample distance * Level of detail * Resel References Accuracy and precision {{physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KH-7 Gambit
BYEMAN codenamed GAMBIT, the KH-7 (Air Force Program 206) was a reconnaissance satellite used by the United States from July 1963 to June 1967. Like the older CORONA system, it acquired imagery intelligence by taking photographs and returning the undeveloped film to earth. It achieved a typical ground-resolution of to . Though most of the imagery from the KH-7 satellites was declassified in 2002, details of the satellite program (and the satellite's construction) remained classified until 2011. In its summary report following the conclusion of the program, the National Reconnaissance Office concluded that the GAMBIT program was considered highly successful in that it produced the first high-resolution satellite photography, 69.4% of the images having a resolution under ; its record of successful launches, orbits, and recoveries far surpassed the records of earlier systems; and it advanced the state of the art to the point where follow-on larger systems could be developed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gherman Titov
Gherman Stepanovich Titov (russian: Герман Степанович Титов; 11 September 1935 – 20 September 2000) was a Soviet cosmonaut who, on 6 August 1961, became the second human to orbit the Earth, aboard Vostok 2, preceded by Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1. He was the fourth person in space, counting suborbital voyages of US astronauts Alan Shepard and Gus Grissom. A month short of 26 years old at launch, he was the youngest person to fly in space until 2021 when Oliver Daemen flew on Blue Origin NS-16 at the age of 18. Since Daemen flew a suborbital mission, Titov remains the youngest man to fly in Earth orbit. Titov's flight finally proved that humans could live and work in space. He was the first person to orbit the Earth multiple times (a total of 17), the first to pilot a spaceship and to spend more than a day in space. He was also the first to sleep in orbit and to suffer from space sickness (becoming the first person to vomit in space). Titov was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok 2
Vostok 2 (russian: Восток-2, ''Orient 2'' or ''East 2'') was a Soviet space mission which carried cosmonaut Gherman Titov into orbit for a full day on August 6, 1961, to study the effects of a more prolonged period of weightlessness on the human body. Titov orbited the Earth over 17 times, exceeding the single orbit of Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1 − as well as the suborbital spaceflights of American astronauts Alan Shepard and Gus Grissom aboard their respective Mercury-Redstone 3 and 4 missions. Titov's number of orbits and flight time would not be surpassed by an American astronaut until Gordon Cooper's Mercury-Atlas 9 spaceflight in May 1963. After the flight of Vostok 1, Sergei Korolev took a short vacation in Crimea where he began working out the flight plan for the next mission. There were considerable arguments over the duration of the mission as flight doctors argued for no more than three orbits. The flight of Korabl-Sputnik 2 nine months earlier had carried t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast, and resolution of the film. The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can be chemically developed into a visible photograph. In addition to visible light, all films are sensitive to ultraviolet light, X-rays, gamma rays, and high-energy particles. Unmodified silver halide crystals are sensitive only to the blue part of the visible spectrum, producing unnatural-looking rendit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoverer 14
Discoverer 14, also known as Corona 9009, was a spy satellite used in the Corona program managed by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the Department of Defense and the United States Air Force. On 19 August 1960, usable photographic film images of the Soviet Union taken by the satellite were recovered by a C-119 recovery aircraft. This was the first successful recovery of film from an orbiting satellite and the first mid-air recovery of an object returning from Earth orbit. Background "Discoverer" was the civilian designation and cover for the Corona satellite photo-reconnaissance series of satellites managed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the Department of Defense and the U.S. Air Force. The primary goal of the satellites was to replace the U-2 spyplane in surveilling the Sino-Soviet Bloc, determining the disposition and speed of production of Soviet missiles and long-range bombers assets. The Corona program was also used to produce maps and charts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CORONA (satellite)
The CORONA program was a series of American strategic reconnaissance satellites produced and operated by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Directorate of Science & Technology with substantial assistance from the U.S. Air Force. The CORONA satellites were used for photographic surveillance of the Soviet Union (USSR), China, and other areas beginning in June 1959 and ending in May 1972. History In 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial Earth satellite. Officially, Sputnik was launched to correspond with the International Geophysical Year, a solar period that the International Council of Scientific Unions declared would be ideal for the launching of artificial satellites to study Earth and the solar system. However, the launch led to public concern about the perceived technological gap between the West and the Soviet Union. The unanticipated success of the mission precipitated the Sputnik Crisis, and prompted President Dwight D. Eisenhower t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |