|
Fire Walking
Firewalking is the act of walking barefoot over a bed of hot embers or stones. It has been practiced by many people and cultures in many parts of the world, with the earliest known reference dating from Iron Age India . It is often used as a rite of passage, as a test of strength and courage, and in religion as a test of faith. Modern physics has explained the phenomenon, concluding that the foot does not touch the hot surface long enough to burn and that embers are poor conductors of heat. History Walking on fire has existed for several thousand years, with records dating back to 1200 BCE. (livescience.com) Cultures across the globe use firewalking for rites of healing, initiation, and faith. Firewalking is also practiced by: * The Sawau clan on the island of Beqa, to the south of Viti Levu in the Fijian Islands. The phenomenon was examined in 1902 when it was already a tourist attraction, with a "Probable Explanation of the Mystery" arrived at. * San Pedro Manrique, a vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Walking (1234969885)
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The ''flame'' is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water contamination. If fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Willey (physicist)
David G. Willey (born 4 November 1947), known as the Mad Scientist, is a former physics instructor at the University of Pittsburgh at Johnstown in Johnstown, Pennsylvania. Physics has been a major interest in his life since he attended The Coleshill School and the John Port School in Etwall, Derbyshire. He has been presenting physics shows since the early 1980s. Willey is a scientific consultant for the skeptics group, C.S.I. (Committee for Skeptical Inquiry). He also designs physics apparatus/equipment for the Science Kit Boreal Labs. In his spare time he enjoys hunting, woodworking, working with stained glass, and playing golf. Education and career Willey studied at Aston University and Birmingham University from 1966 to 1971. Then he taught at Saltley Grammar School, in Birmingham from 1971 to 1972. Next, Willey moved from his home country of England to the United States and enrolled at the Ohio State University. He was in Columbus, Ohio until he obtained his masters in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Effusivity
In thermodynamics, a material's thermal effusivity, thermal inertia or thermal responsivity is a measure of its ability to exchange thermal energy with its surroundings. It is defined as the square root of the product of the material's thermal conductivity (\lambda) and its volumetric heat capacity (\rho c_p). :e = \sqrt The SI units for thermal effusivity are \sqrt / (), or, equivalently, / ( \sqrt). Thermal effusivity is a parameter that emerges upon applying solutions of the heat equation to heat flow through a thin surface-like region. It becomes particularly useful when the region is selected adjacent to a material's actual surface. Knowing the effusivity and equilibrium temperature of each of two material bodies then enables an estimate of their interface temperature T_m when placed into thermal contact. :T_m = \frac Specialty sensors have also been developed based on this relationship to measure effusivity. Thermal effusivity and thermal diffusivity are related quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials like Rockwool or Styrofoam. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla T is the temperature gradient. This is known as Fourier's Law for heat conduction. Although commonly expressed as a scalar, the most general form of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Heat Capacity
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature. The SI unit of specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram, J⋅kg−1⋅K−1. For example, the heat required to raise the temperature of of water by is , so the specific heat capacity of water is . Specific heat capacity often varies with temperature, and is different for each state of matter. Liquid water has one of the highest specific heat capacities among common substances, about at 20 °C; but that of ice, just below 0 °C, is only . The specific heat capacities of iron, granite, and hydrogen gas are about 449 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1, 790 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1, and 14300 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Straight Dope
"The Straight Dope" was a question-and-answer newspaper column written under the pseudonym Cecil Adams. Contributions were made by multiple authors, and it was illustrated (also pseudonymously) by Slug Signorino. It was first published in 1973 in the ''Chicago Reader'' as well as in print syndication nationally in the United States, and on a website with the same name. On more than one occasion, the authors (i.e. Cecil Adams) were forced to retract or modify an answer when confronted by the readers. Following the column of June 27, 2018, the "Straight Dope" column was placed on hiatus, with no decision made regarding its future. The website and associated forum continue to be active. Chicago's public radio station, WBEZ, has purchased Sun-Times Media (STM), which owns the Straight Dope, including the SDMB. Name and tagline The column derives its name from the American idiom meaning roughly "the true information; the full story" and covers many subjects, including history, scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
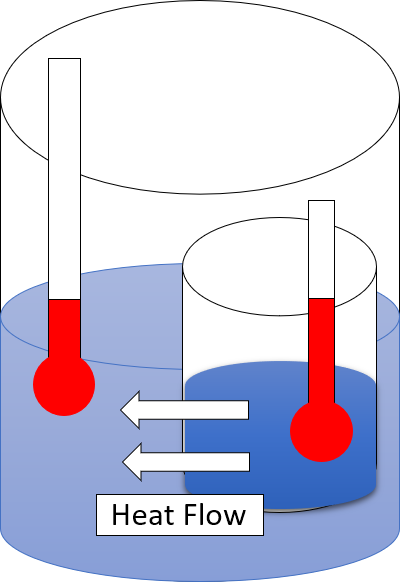
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Durkheim
David Émile Durkheim ( or ; 15 April 1858 – 15 November 1917) was a French sociologist. Durkheim formally established the academic discipline of sociology and is commonly cited as one of the principal architects of modern social science, along with both Karl Marx and Max Weber. Much of Durkheim's work was concerned with how societies can maintain their integrity and coherence in modernity, an era in which traditional social and religious ties are much less universal, and in which new social institutions have come into being. Durkheim's conception of the scientific study of society laid the groundwork for modern sociology, and he used such scientific tools as statistics, surveys, and historical observation in his analysis of suicides in Catholic and Protestant groups. His first major sociological work was (1893; ''The Division of Labour in Society''), followed in 1895 by (''The Rules of Sociological Method''), the same year in which Durkheim set up the first European dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including language relatedness, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Geographical Society of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the southern Pacific have also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)