|
Finnish Grammar
The Finnish language is spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns elsewhere. Unlike the languages spoken in neighbouring countries, such as Swedish and Norwegian, which are North Germanic languages, or Russian, which is a Slavic language, Finnish is a Uralic language of the Finnic languages group. Typologically, Finnish is agglutinative. As in some other Uralic languages, Finnish has vowel harmony, and like other Finnic languages, it has consonant gradation. Pronouns The pronouns are inflected in the Finnish language much in the same way that their referent nouns are. Personal pronouns The personal pronouns are used to refer to human beings only. The personal pronouns in Finnish in the nominative case are listed in the following table: : Because Finnish verbs are inflected for person and number, in the Finnish standard language subject pronouns are not required, and the first and second-person pronouns are usually omitted except when used for em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Finnish orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T–V Distinction
The T–V distinction is the contextual use of different pronouns that exists in some languages and serves to convey formality or familiarity. Its name comes from the Latin pronouns '' tu'' and '' vos''. The distinction takes a number of forms and indicates varying levels of politeness, familiarity, courtesy, age or even insult toward the addressee. The field that studies and describes this phenomenon is sociolinguistics. Many languages lack this type of distinction, instead relying on other morphological or discourse features to convey formality. English historically contained the distinction, using the pronouns ''thou'' and ''you'', but the familiar ''thou'' largely disappeared from the era of Early Modern English onward, with the exception of a few dialects. Additionally, British commoners historically spoke to nobility and royalty using the third person rather than the second person, a practice that has fallen out of favour. English speakers today often employ semantic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence, by way of some inflection. Declensions may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and article (grammar), articles to indicate grammatical number, number (e.g. singular, dual, plural), grammatical case, case (e.g. nominative case, accusative case, genitive case, dative case), grammatical gender, gender (e.g. masculine, neuter, feminine), and a number of other grammatical categories. Meanwhile, the inflectional change of verbs is called Grammatical conjugation, ''conjugation''. Declension occurs in many of the world's languages. It is an important aspect of language families like Quechuan languages, Quechuan (i.e., languages native to the Andes), Indo-European languages, Indo-European (e.g. German language, German, Baltic language, Lithuanian, Latvian, Slavic languages, Slavic, Sanskrit, Latin, Ancient Greek, Modern Greek, Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Nelson Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Grand Canyon, utopia'', etc. * Actions: ''swimming, exercises, diffusions, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Qualities: ''colors, lengths, deafness, weights, roundness, symmetry, warp speed,'' etc. * Mental or physical states of existence: ''jealousy, sleep, heat, joy, stomachache, confusion, mind meld,'' etc. Lexical categories (parts of speech) are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. The syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic (, backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a word, but depends phonologically on another word or phrase. In this sense, it is syntactically independent but phonologically dependent—always attached to a host.SIL International (2003). SIL Glossary of Linguistic Terms: What is a clitic? "This page is an extract from the LinguaLinks Library, Version 5.0 published on CD-ROM by SIL International, 2003." Retrieved from . A clitic is pronounced like an affix, but plays a syntactic role at the phrase level. In other words, clitics have the ''form'' of affixes, but the distribution of function words. For example, the contracted forms of the auxiliary verbs in ''I'm'' and ''we've'' are clitics. Clitics can belong to any grammatical category, although they are commonly pronouns, determiners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indefinite Pronoun
An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun which does not have a specific familiar referent. Indefinite pronouns are in contrast to definite pronouns. Indefinite pronouns can represent either count nouns or noncount nouns. They often have related forms across these categories: universal (such as ''everyone'', ''everything''), assertive existential (such as ''somebody'', ''something''), elective existential (such as ''anyone'', ''anything''), and negative (such as ''nobody'', ''nothing''). Many languages distinguish forms of indefinites used in affirmative contexts from those used in non-affirmative contexts. For instance, English "something" can be used only in affirmative contexts while "anything" is used otherwise. Indefinite pronouns are associated with indefinite determiners of a similar or identical form (such as ''every'', ''any'', ''all'', ''some''). A pronoun can be thought of as ''replacing'' a noun phrase, while a determiner ''introduces'' a noun phrase and precedes any a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to another noun or pronoun (its antecedent) within the same sentence. In the English language specifically, a reflexive pronoun will end in ''-self'' or ''-selves'', and refer to a previously named noun or pronoun (''myself'', ''yourself'', ''ourselves'', ''themselves'', etc.). English intensive pronouns, used for emphasis, take the same form. In generative grammar, a reflexive pronoun is an anaphor that must be bound by its antecedent (see binding). In a general sense, it is a noun phrase that obligatorily gets its meaning from another noun phrase in the sentence. Different languages have different binding domains for reflexive pronouns, according to their structure. Origins and usage In Indo-European languages, the reflexive pronoun has its origins in Proto-Indo-European. In some languages, some distinction exists between normal object and reflexive pronouns, mainly in the third person: whether one says "I like me" or "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
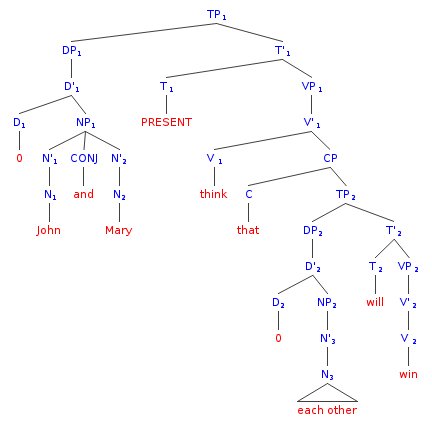
Reciprocal Pronoun
A reciprocal pronoun is a pronoun that indicates a reciprocal relationship. A reciprocal pronoun can be used for one of the participants of a reciprocal construction, i.e. a clause in which two participants are in a mutual relationship. The reciprocal pronouns of English are ''one another'' and ''each other'', and they form the category of anaphors along with reflexive pronouns (''myself'', ''yourselves'', ''themselves,'' etc.). Defining properties Semantics of reciprocal relation Reflexive pronouns are used similarly to reciprocal pronouns in the sense that they typically refer back to the subject of the sentence. (1) ''John and Mary like themselves.'' (2) ''John and Mary like each other.'' The main difference between reflexives, as in example (1), and reciprocal pronouns, as in example (2), is that reflexives are used when the subject acts upon itself, while reciprocals are used when members of a group perform the same action relative to one another. Reciprocal pronouns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause. It serves the purpose of conjoining modifying information about an antecedent referent. An example is the word ''which'' in the sentence "This is the house which Jack built." Here the relative pronoun ''which'' conjoins the relative clause "Jack built," which modifies the noun ''house'' in the main sentence. ''Which'' has an anaphoric relationship to its antecedent "house" in the main clause. In the English language, the following are the most common relative pronouns: ''which'', ''that'', ''whose'', ''whoever'', ''whomever'', ''who'' and ''whom''. According to some dependency grammar theories, a relative pronoun does not simply mark the subordinate (relative) clause but also may be considered to play the role of a noun within that clause. For example, in the relative clause "that Jack built," "that" is deemed a pronoun functioning as the object of the verb "built." Compare this with "Jack built the house after he m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative Pronoun
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', ''who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of them start with '' wh-'' (compare Five Ws). They may be used in both direct questions (''Where is he going?'') and in indirect questions (''I wonder where he is going''). In English and various other languages the same forms are also used as relative pronouns in certain relative clauses (''The country where he was born'') and certain adverb clauses (''I go where he goes''). It can also be used as a modal, since question words are more likely to appear in modal sentences, like (''Why was he walking?'') A particular type of interrogative word is the interrogative particle, which serves to convert a statement into a yes–no question, without having any other meaning. Examples include ''est-ce que'' in French, ли ''li'' in Russian, ''cz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antecedent (grammar)
In grammar, an antecedent is an expression (word, phrase, clause, sentence, etc.) that gives its meaning to a proform (pronoun, pro-verb, pro-adverb, etc.). A proform takes its meaning from its antecedent; e.g., "John arrived late because traffic held him up." The pronoun ''him'' refers to and takes its meaning from ''John'', so ''John'' is the antecedent of ''him''. Proforms usually follow their antecedents, but sometimes they precede them, in which case one is, technically, dealing with postcedents instead of antecedents. The prefix ''ante-'' means "before" or "in front of", and ''post-'' means "after" or "behind". The term ''antecedent'' stems from traditional grammar. The linguistic term that is closely related to ''antecedent'' and ''proform'' is '' anaphora''. Theories of syntax explore the distinction between antecedents and postcedents in terms of binding. Examples Almost any syntactic category can serve as the antecedent to a proform. The following examples illustrate a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercorrect
In sociolinguistics, hypercorrection is non-standard use of language that results from the over-application of a perceived rule of language-usage prescription. A speaker or writer who produces a hypercorrection generally believes through a misunderstanding of such rules that the form is more "correct", standard, or otherwise preferable, often combined with a desire to appear formal or educated. Linguistic hypercorrection occurs when a real or imagined grammatical rule is applied in an inappropriate context, so that an attempt to be "correct" leads to an incorrect result. It does not occur when a speaker follows "a natural speech instinct", according to Otto Jespersen and Robert J. Menner. Hypercorrection can be found among speakers of less prestigious language varieties who attempt to produce forms associated with high-prestige varieties, even in situations where speakers of those varieties would not. Some commentators call such production ''hyperurbanism''. Hypercorrection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |