|
Finnish Conquest Of East Karelia (1941)
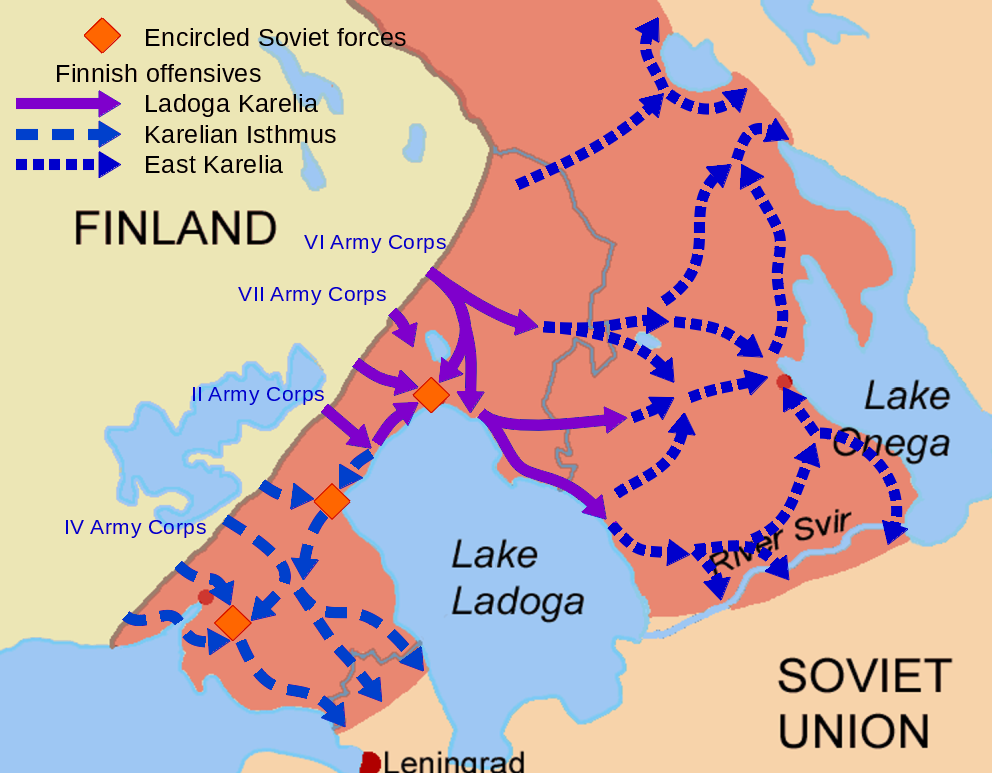
The Finnish invasion of East Karelia was a military campaign in 1941. It was part of the Continuation War. Finnish troops occupied East Karelia and held it until 1944. For over a month after the outbreak of the Continuation War, the Karelian Army reinforced and prepared to resume its earlier offensive while waiting for the recapture of the Karelian Isthmus. The Soviets had prepared fortifications and brought troops to the front. When encirclements on the western shore of Lake Ladoga were resolved, the Finnish 7th Division was transferred to the junction of VI and VII Corps. Preparations and plans The Finnish 14th Division, commanded by Colonel Erkki Raappana (who in turn operated under the direct command of the Finnish HQ), started its advance on July 4. It was the northernmost Finnish unit south of the demarcation line between Finnish and German forces. It was opposed by elements of the Soviet 54th Rifle Division. It encircled and mauled the defending Soviet 337th Rifle Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944, as part of World War II.; sv, fortsättningskriget; german: Fortsetzungskrieg. According to Finnish historian Olli Vehviläinen, the term 'Continuation War' was created at the start of the conflict by the Finnish government, to justify the invasion to the population as a continuation of the defensive Winter War and separate from the German war effort. He titled the chapter addressing the issue in his book as "Finland's War of Retaliation". Vehviläinen asserted that the reality of that claim changed when the Finnish forces crossed the 1939 frontier and started annexation operations. The US Library of Congress catalogue also lists the variants War of Retribution and War of Continuation (see authority control)., group="Note" In Soviet historiography, the war was called the Finnish Front of the Great Patriotic War.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Finnish Operations In Karelia In 1941
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woldemar Oinonen
Voldemar Oinonen (1891–1963) was a Finnish military commander. Ranks * 1939–1940 Assistant Chief General Staff * 1940 General Officer Commanding 23rd Division * 1940 General Officer Commanding 11th Separate Division * 1940–1941 Acting General Officer Commanding III Corps * 1941–1942 General Officer Commanding Group Oinonen * 1942–1944 Chief of Staff The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supporti ... of the Home Troops * 1944 Acting Commander in Chief of the Home Troops {{DEFAULTSORT:Oinonen, Voldemar 1891 births 1963 deaths People from Lappeenranta People from Viipuri Province (Grand Duchy of Finland) Finnish military personnel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruben Lagus
Ernst Ruben Lagus (12 October 1896 – 15 July 1959), better known as Ruben Lagus, was a Finnish major general, a member of the Jäger Movement and the recipient of the first Mannerheim Cross. He participated in the Eastern Front of World War I as a volunteer of the 27th Royal Prussian Jäger Battalion, in the Finnish Civil War as battalion commander and as a supply officer in the Winter War. During the Continuation War, he commanded an armoured brigade, later division, which had a significant role in the influential Battle of Tali-Ihantala. Early life Ernst Ruben Lagus was born on 12 October 1896 in Koski Hl, Grand Duchy of Finland to parents Aleksander Gabriel Lagus and Emma Matilda Bellman. He became involved in the Jäger Movement, where Finnish volunteers received military training in Germany, and followed his brother to Germany in 1915. While in Germany, the Finnish volunteers formed the 27th Royal Prussian Jäger Battalion, fighting for the Imperial German Army on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (russian: Петрозаводск, p=pʲɪtrəzɐˈvotsk; Karelian, Vepsian and fi, Petroskoi) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city was 280,890 as of 2022. Etymology The name of the city is a combination of words Peter (Peter the Great) and ''zavod'' (meaning factory). It was previously known as ''Shuysky Zavod'' (1703–1704) and ''Petrovskaya Sloboda'' (1704–1777), which was the first name of the city related to Peter the Great. It was renamed to Petrozavodsk after Catherine the Great granted the settlement the status of a city. An ancient Swedish name was ''Onegaborg'', known from a map from 1592 of the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, and hence translated to Finnish as ''Äänislinna'', a name used during the occupation of Eastern Karelia by Finnish forces during the Continuation War (1941–1944) in the context of World War II. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pryazha
Pryazha (russian: Пря́жа; krl, Priäžä; fi, Prääsä) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) and the administrative center of Pryazhinsky District of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, located from the Shuya River and west of Petrozavodsk, the capital of the republic. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 3,675. History It was first mentioned in the 17th century as the village of Pryazha or Padlovo (). It was granted urban-type settlement status in 1962. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Pryazha serves as the administrative center of Pryazhinsky District, of which it is a part.Law #871-ZRK As a municipal division, Pryazha, together with three rural localities, is incorporated within Pryazhinsky Municipal District as Pryazhinskoye Urban Settlement.Law #813-ZRK Tourism The Blue Highway, an international tourist route, starts in Mo i Rana, Norway, goes through Sweden Sweden, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Syamozero
Lake Syamozero (, , Karelian: ''Seämärvi'') is a large freshwater lake in the Republic of Karelia, northwestern part of Russia. It is located west of Petrozavodsk, the capital of the Republic, and has an area of 265–270 km². Maximum depth is about 24 m. There are a few islands on the lake. Syamozero is used for fishery, water transport Maritime transport (or ocean transport) and hydraulic effluvial transport, or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people (passengers) or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used throu ... and timber rafting. The lake is part of the basin of the Shuya River, which flows into Lake Onega. 2016 Boat Disaster On June 18, 2016, 14 children died when a storm caught a tour group on the lake. Four people have been arrested on suspicion of safety violations as there had been repeated warnings days prior of an impending storm and advising against boating on the lake. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erkki Raappana
Major General Erkki Johannes Raappana (June 2, 1893 – September 14, 1962) was the commander of the 14th Division of the Finnish Army during the Second World War. Raappana was born in Oulujoki. From 1916 to 1918, he served in the 27th Jäger Battalion, a light infantry unit of the Imperial German Army. In 1918 he took part in the Finnish Civil War as a lieutenant of the White side. Among many of his known accomplishments, General Raappana was chosen to command the Finnish detachment - nicknamed "Group Raappana" ("Ryhmä Raappana" in Finnish) - that was to stop the enemy in the very final Finnish-Soviet battle during World War II. It was the Battle of Ilomantsi The Battle of Ilomantsi was a part of the Svir–Petrozavodsk Offensive of the Continuation War (1941–1944). It was fought from 26 July to 13 August 1944, between Finland and the Soviet Union in an area roughly 40 kilometers wide and 30 ..., fought during the Continuation War (1941–1944). The ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish 7th Division (Continuation War)
7th Division (, also known as Sword division) was a Finnish Army division in the Continuation War. The division was formed Savo-Karjala military province from the men in Pohjois-Savo (Northern Savonia) and Pohjois-Karjala (North Karelia) civil guard districts. History As a component of the VII Corps, the 7th Division took part in the Army of Karelia's 1941 conquest of East Karelia. At the start of the war the 7th Division was the westernmost division of the VII Corps, the westernmost division of the Army of Karelia, intended to operate between Lake Ladoga and Lake Opega as part of the Finnish invasion of East Karelia. By July 1941 the division was commanded by Colonel Antero Svensson and had advanced to the Matkaselkä Railway and pushed the Soviets back towards Lake Ladoga. The 7th Division captured Sortavala, a Russian town since 1917 but which had previously been part of Finland, on 8 August 1941 after a fierce battle. The division advanced between Ladoga and Ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Reconquest Of The Karelian Isthmus (1941)
The Finnish invasion of the Karelian Isthmus refers to a military campaign carried out by Finland in 1941. It was part of what is commonly referred to as the Continuation War. Early in the war Finnish forces liberated the Karelian Isthmus. It had been ceded to the Soviet Union on 13 March 1940, in the Moscow Peace Treaty, which marked the end of the Winter War. Later, in the summer of 1944, the Soviet Union reconquered the southern part of the isthmus in the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive. Initial setup of the forces The Finnish forces facing the Karelian Isthmus consisted of two Finnish army corps. The Finnish II Corps was north of the river Vuoksi and the Finnish IV Corps south of it. The Finnish II Corps was commanded by Major-General Taavetti Laatikainen and it consisted of three divisions (the 10th, 15th and 18th divisions) as the 10th Division had been added to it after the II Corps had been forced to give the 2nd Division over to operations in Ladoga Karelia. Neny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Reconquest Of Ladoga Karelia (1941)
The Finnish invasion of Ladoga Karelia was a military campaign carried out by Finland in 1941. Initial layout of forces At the start of the Continuation War the Finnish army was deployed in a defensive posture, but on June 29 Mannerheim created the Army of Karelia, commanded by Lt. Gen. Erik Heinrichs, and ordered it to prepare to attack Ladoga Karelia. The Army of Karelia consisted of VI Corps (the 5th and 11th Divisions), VII Corps (the 7th and 19th divisions) and Group Oinonen (also known as Group O, the Cavalry Brigade, and the 1st Jaeger Brigade and 2nd Jaeger Brigade). The Finnish 1st Division was kept in reserve. Lunde (2011) p. 158 The Finns planned to separate the defending Soviet forces by reaching the shore of Lake Ladoga and then to advance along the shores of the lake. Nenye (2016) p. 68 Opposing them were the Soviet 7th Army with the 168th Rifle Division near Sortavala and the 71st Rifle Division north of Jänisjärvi ("Hare Lake"). The Soviets had prepared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |