|
Final-obstruent Devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Quebec French, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voiced obstruents in final position (at the end of a word) become voiceless before voiceless consonants and in pausa. The process can be written as *C obstruent, +voice/sub> → Cvoice/sub>/__#. Languages with final-obstruent devoicing Germanic languages Most modern continental West Germanic languages developed final devoicing, the earliest evidence appearing in Old Dutch around the 9th or 10th century. * Afrikaans * Central Franconian (Luxembourgish and Ripuarian) * Dutch, also Old and Middle Dutch * (High) German, also Middle High German * Gothic (for fricatives) * Limburgish * Low German language, Low German, also Middle Low German * Old English language, Old English (for fricatives, inconsistently for ) * West Frisian language, West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonological Process
A phonological rule is a formal way of expressing a systematic phonological or morphophonological process in linguistics. Phonological rules are commonly used in generative phonology as a notation to capture sound-related operations and computations the human brain performs when producing or comprehending spoken language. They may use phonetic notation or distinctive features or both. John Goldsmith (1995) defines phonological rules as mappings between two different levels of sounds representation—in this case, the abstract or underlying level and the surface level—and Bruce Hayes (2009) describes them as "generalizations" about the different ways a sound can be pronounced in different environments. That is to say, phonological rules describe how a speaker goes from the abstract representation stored in their brain, to the actual sound they articulate when they speak. In general, phonological rules start with the ''underlying representation'' of a sound (the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourgish Language
Luxembourgish ( ; also ''Luxemburgish'', ''Luxembourgian'', ''Letzebu(e)rgesch''; ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 400,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide. The language is standardized and officially the national language of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. As such, Luxembourgish is different from the German language also used in the Grand Duchy. The German language exists in a national standard variety of Luxembourg, which is slightly different from the standard varieties in Germany, Austria or Switzerland. Another important language of Luxembourg is French, which had a certain influence on both the national language, Luxembourgish, and the Luxembourg national variety of German. Luxembourgish, German and French are the three official languages ''(Amtssprachen)'' of Luxembourg. As a standard form of the Moselle Franconian language, Luxembourgish has similarities with other High German dialects and the wider group of West Germanic lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Language
North Frisian is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group. North Frisian is closely related to the Saterland Frisian language of Northwest Germany and West Frisian which is spoken in the Netherlands. All of these are also closely related to the English language forming the Anglo-Frisian group. The phonological system of the North Frisian dialects is strongly being influenced by Standard German and is slowly adapting to that of the German language. With a number of native speakers probably even less than 10,000 and decreasing use in mainland North Frisia, the North Frisian language is endangered. It is protected as a minority language and has become an official language in the Nordfriesland district and on Heligoland island. Classification The closest relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Frisian Language
West Frisian (; ), or simply Frisian ( ; ), is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland () in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisians, Frisian ancestry. It is the most widely spoken of the Frisian languages. In the study of the evolution of English language, English, West Frisian is notable as being the most closely related foreign tongue to the various dialects of Old English spoken across the Heptarchy, these being part of the Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian branch of the West Germanic family. Name The name "West Frisian" is only used outside the Netherlands, to distinguish this language from the closely related Frisian languages of East Frisian language, East Frisian, including Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian, and North Frisian language, North Frisian spoken in Germany. Within the Netherlands, however, "West Frisian" refers to the West Frisian Dutch, West Frisian dialect of the Dutch language while the We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English Language
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman (a type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers became dominant in England, their language re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Low German
Middle Low German is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225–34 (). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Middle Low German was the leading written language in the north of Central Europe and served as a lingua franca in the northern half of Europe. It was used parallel to medieval Latin also for purposes of diplomacy and for deeds. Terminology While ''Middle Low German'' (MLG) is a scholarly term developed in hindsight, speakers in their time referred to the language mainly as (Saxon) or (the Saxon language). In contrast to Latin as the primary written language, speakers also referred to discourse in Saxon as speaking/writing , i.e. 'clearly, intelligibly'. This contains the same root as 'German' (cf., High German: , Dutch ( archaically ''N(i)ederduytsche'' to mean the contemporary version of the Dutch language) both from Proto-Germanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
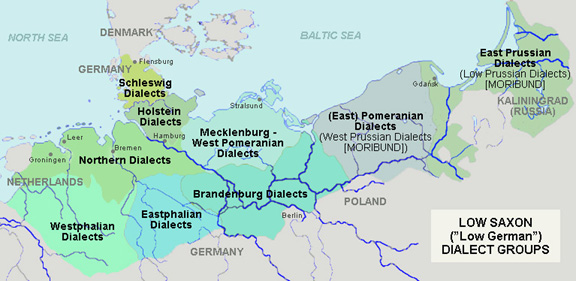
Low German Language
Low German is a West Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian and English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard High German, which is based on High German dialects. Low German evolved from Old Saxon (Old Low German), which is most closely related to Old Frisian and Old English (Anglo-Saxon). The Low German diale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limburgish
Limburgish ( or ; ; also Limburgian, Limburgic or Limburgan) refers to a group of South Low Franconian Variety (linguistics), varieties spoken in Belgium and the Netherlands, characterized by their distance to, and limited participation in the formation of, Standard Dutch. In the Limburg (Netherlands), Dutch province of Limburg, all dialects, despite their differences, have been given collectively a regional language status, including those comprising "Limburgish" as used in this article. Limburgish shares many vocabulary and grammatical characteristics with both German language, German and Dutch language, Dutch. A characteristic feature of many dialects of Limburgish is the occurrence of a Lexical rule, lexical Pitch accent (intonation), pitch accent (Franconian tone accent), which is shared with the adjacent Central Franconian dialects of German. Etymology The name ''Limburgish'' (and variants of it) derives only indirectly from the now Belgian town of Limbourg (''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Language
Gothic is an extinct language, extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the ''Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian language (Germanic), Burgundian and Vandalic language, Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other, mainly Romance languages, Romance, languages. As a Germanic language, Gothic is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is the earliest Germanic language that is attested in any sizable texts, but it lacks any modern descendants. The oldest documents in Gothic date back to the fourth century. The language was in decline by the mid-sixth century, partly because of the military defeat of the Goths at the hands of the Franks, the elimination of the Goths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Standard German
Swiss Standard German (SSG; ), or Swiss High German ( or ; ), referred to by the Swiss as , or , is the written form of one (German language, German) of four languages of Switzerland, national languages in Switzerland, besides French language, French, Italian language, Italian, and Romansh language, Romansh. It is a variety of Standard German, used in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland and in Liechtenstein. It is mainly written and rather less often spoken. Swiss Standard German differs from Swiss German, an umbrella term for the various Alemannic German dialects (in the sense of "traditional regional varieties") that are the default everyday languages in German-speaking Switzerland. Standard German is a pluricentric language. In contrast with other local Variety (linguistics), varieties of Standard German, Swiss Standard German has distinctive features in all linguistic domains: not only in phonology, but also in vocabulary, syntax, morphology ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian German
Austrian German (), Austrian Standard German (ASG), Standard Austrian German (), Austrian High German (), or simply just Austrian (), is the variety of Standard German written and spoken in Austria and South Tyrol. It has the highest prestige (sociolinguistics), sociolinguistic prestige locally, as it is the variation used in the media and for other formal situations. In less formal situations, Austrians use Bavarian language, Bavarian and Alemannic German, Alemannic dialects, which are traditionally spoken but rarely written in Austria. It has been standardized with the publishing of the ''Österreichisches Wörterbuch'' in 1951. History Austrian German has its beginning in the mid-18th century, when Empress Maria Theresa and her son Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II introduced compulsory education, compulsory schooling in 1774, and several reforms of administration in their multilingual Habsburg Empire. At the time, the written standard was ''Oberdeutsche Schreibsprache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; or ; , shortened as ''Mhdt.'' or ''Mhd.'') is the term for the form of High German, High German language, German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German (OHG) into Early New High German (ENHG). High German is defined as those varieties of German which were affected by the High German consonant shift, Second Sound Shift; the Middle Low German (MLG) and Middle Dutch languages spoken to the North and North West, which did not participate in this sound change, are not part of MHG. While there is no ''standard'' MHG, the prestige of the Hohenstaufen court gave rise in the late 12th century to a supra-regional literary language () based on Swabian dialect, Swabian, an Alemannic German, Alemannic dialect. This historical interpretation is complicated by the tendency of modern editions of MHG texts to use ''normalised'' spellings based on this variety (usually called "Classical MHG"), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |