|
Ferry Flying
Ferry flying is the flying of aircraft for the purpose of returning to base, delivery to a customer, moving from one base of operations to another or moving to or from a maintenance facility for maintenance, repair, and operations. A commercial airliner may need to be moved from one airport to another to satisfy the next day's timetable or facilitate routine maintenance; this is commonly known as a positioning flight or repositioning flight, and may carry revenue freight or passengers as local aviation regulations and airline policies allow. They may also be necessary following a major weather event or other similar disruption which causes multiple cancellations across an airline's network resulting in many aircraft and crew being 'out of position' for normal operations; the 2010 eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull or the mass evacuation of US airspace following the 9/11 attacks being significant examples of this. Ferry permit A ferry permit is a written authorization issued by a Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Mollison
James Allan Mollison MBE (19 April 1905 – 30 October 1959) was a Scottish pioneer aviator who, flying solo or with his wife, Amy Johnson, set many records during the rapid development of aviation in the 1930s. Early years Born on 19 April 1905 in Glasgow, the only child of Hector Alexander Mollison, a consultant engineer, and Thomasina Macnee Addie (''d''. 1965). He was educated at The Glasgow Academy and Edinburgh Academy. He was attracted at an early age to flying. Obtaining his Royal Air Force (RAF) Short Service Commission at 18, he was the youngest officer in the service, and upon completion of training was posted to India, flying on active service in Waziristan.Aitken 1991, p. 343. Aviation career At the age of 22, Mollison became a flying instructor at Central Flying School (CFS), again setting the record for being the youngest in this role. Shortly after, he transferred to the RAF Reserve and devoted his time to civil aviation. In 1928–29, he worked as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Airforce Service Pilots
The Women Airforce Service Pilots (WASP) (also Women's Army Service Pilots or Women's Auxiliary Service Pilots) was a civilian women pilots' organization, whose members were United States federal civil service employees. Members of WASP became trained pilots who tested aircraft, ferried aircraft, and trained other pilots. Their purpose was to free male pilots for combat roles during World War II. Despite various members of the armed forces being involved in the creation of the program, the WASP and its members had no military standing. WASP was preceded by the Women's Flying Training Detachment (WFTD) and the Women's Auxiliary Ferrying Squadron (WAFS). Both were organized separately in September 1942. They were pioneering organizations of civilian women pilots, who were attached to the United States Army Air Forces to fly military aircraft during World War II. On August 5, 1943, the WFTD and WAFS merged to create the WASP organization. The WASP arrangement with the US Army Air F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Aircraft Test Serials
United Kingdom aircraft test serials are used to externally identify aircraft flown within the United Kingdom without a full Certificate of Airworthiness. They can be used for testing experimental and prototype aircraft or modifications, pre-delivery flights for foreign customers and are sometimes referred to as "B" class markings. 1930s An initial set of markings was introduced in 1929, each company was allocated a letter to which would follow a number, sometimes with a hyphen or a gap between. For example, A was allocated to the Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft and ''A 1'' was used in March 1930 on an Armstrong Whitworth Starling. Sometimes Hawker and Vickers would also add the letters PV to the markings to indicate a private venture (that is a type in development not paid for by the Air Ministry). 1940s The presentation was changed to look like a military serial for security reasons during the Second World War. For example, the prototype de Havilland Mosquito was allocated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Ferry Command
RAF Ferry Command was the secretive Royal Air Force command formed on 20 July 1941 to ferry urgently needed aircraft from their place of manufacture in the United States and Canada, to the front line operational units in Britain, Europe, North Africa and the Middle East during the Second World War. It was later subsumed into the new Transport Command on 25 March 1943 by being reduced to Group status. History The practice of ferrying aircraft from US manufacturers to the UK was begun by the Ministry of Aircraft Production. Its minister, Lord Beaverbrook, a Canadian by origin, reached an agreement with Sir Edward Beatty, a friend and chairman of the Canadian Pacific Railway Company, to provide ground facilities and support. MAP would discretely provide civilian crews and management. Previously, aircraft were being assembled then disassembled and then transported by ship across the Atlantic, and were subject to long delays and frequent attacks by German U-Boats. Former RAF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
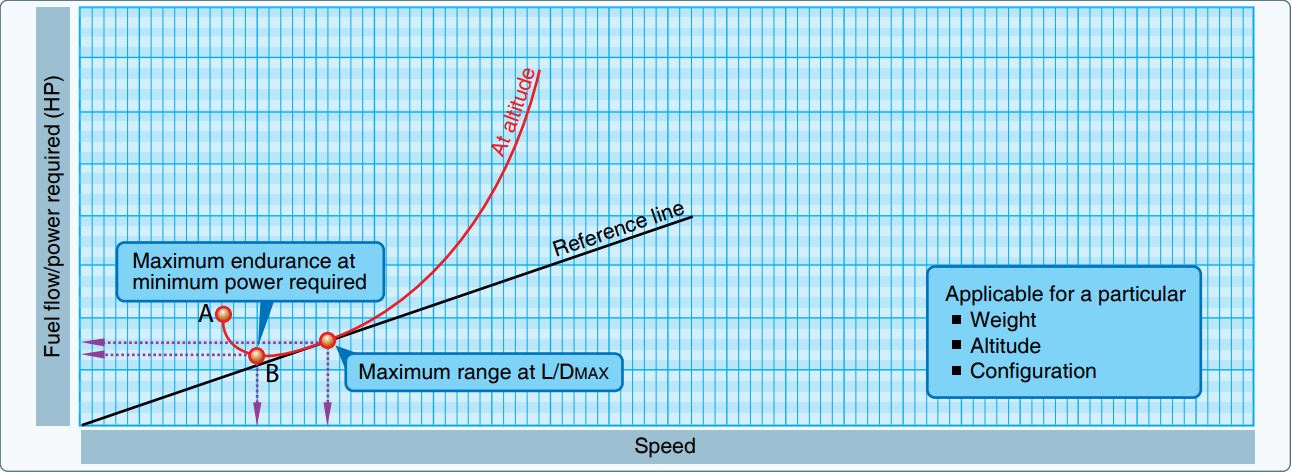
Ferry Range
The maximal total range is the maximum distance an aircraft can fly between takeoff and landing. Powered aircraft range is limited by the aviation fuel energy storage capacity (chemical or electrical) considering both weight and volume limits. Unpowered aircraft range depends on factors such as cross-country speed and environmental conditions. The range can be seen as the cross-country ground speed multiplied by the maximum time in the air. The fuel time limit for powered aircraft is fixed by the available fuel (considering reserve fuel requirements) and rate of consumption. Some aircraft can gain energy while airborne through the environment (e.g. collecting solar energy or through rising air currents from mechanical or thermal lifting) or from in-flight refueling. These aircraft could theoretically have an infinite range. Ferry range means the maximum range that an aircraft engaged in ferry flying can achieve. This usually means maximum fuel load, optionally with extra fuel tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Mileage
Dead mileage, dead running, light running, empty cars or deadheading in public transport and empty leg in air charter is when a revenue-gaining vehicle operates without carrying or accepting passengers, such as when coming from a garage to begin its first trip of the day. Similar terms in the UK include empty coaching stock (ECS) move and dead in tow (DIT). The term '' deadheading'' also applies to the practice of allowing employees of a common carrier to use a vehicle as a non-revenue passenger. For example, an airline might assign a pilot living in New York to a flight from Denver to Los Angeles, and the pilot would simply catch any flight going to Denver, either wearing their uniform or showing ID, in lieu of buying a ticket. Also, some transport companies will allow employees to use the service when off duty, such as a city bus line allowing an off-duty driver to commute to and from work, free. Additionally, inspectors from a regulatory agency may use transport on a dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Transport Auxiliary
The Air Transport Auxiliary (ATA) was a British civilian organisation set up at the start of World War II, the Second World War with headquarters at White Waltham Airfield in Berkshire. The ATA Ferry flying, ferried new, repaired and damaged military aircraft between factories, assembly plants, transatlantic delivery points, maintenance units (MUs), scrapyards, and active service squadrons and airfields, but not to naval aircraft carriers. It also flew service personnel on urgent duty from one place to another and performed some air ambulance work. Notably, around 10% of its pilots were women, and from 1943 they received equal pay to their male colleagues, a first for the British government. Mission The initial plan was that the ATA would carry personnel, mail and medical supplies, but the pilots were immediately needed to work with the Royal Air Force (RAF) ferry pools transporting aircraft. By 1 May 1940 the ATA had taken over transporting all military aircraft from factories to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana Barnato Walker
Diana Barnato Walker MBE FRAeS (15 January 1918 – 28 April 2008) was a pioneering British aviator. In World War II, she became one of the first women pilots of the Air Transport Auxiliary, flying 80 types of aircraft and delivering 260 Spitfires. In 1963, she became the first British woman to break the sound barrier, flying at Mach 1.6, which also represented a world air speed record for women. Early life Diana Barnato was born on 15 January 1918 in London, the younger daughter of Woolf Joel Barnato (1895–1948), a financier and racing driver, and Dorothy Maitland, ''née'' Falk (1892/3–1961). In 1936, at the age of 18, she was a debutante and was presented to King Edward VIII at Buckingham Palace. She attended Queen's College, London. From an early age, she became interested in aircraft and at age 20 she decided to become a pilot. Her initial training was in Tiger Moths at the Brooklands Flying Club, the aerodrome being located within the famous motor racing circuit in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jadwiga Piłsudska
Jadwiga Piłsudska-Jaraczewska (; 28 February 1920 – 16 November 2014) was a Polish pilot, who served in the Air Transport Auxiliary during the Second World War. She was one of two daughters of Józef Piłsudski. Life and career Piłsudska was born on 28 February 1920 in Warsaw, the younger daughter of Marshal Józef Piłsudski, Poland's Chief of State (1918–22) and dictator (1926–1935), by the woman who would later become his second wife, Aleksandra Piłsudska (née Aleksandra Szczerbińska). In 1937 Piłsudska began flying gliders and obtained a pilot's licence. In 1939 she graduated from secondary school and decided to study aircraft engineering at the Warsaw Polytechnic. In September 1939, Poland was invaded by Germany, initiating the Second World War, and her family realized that under the circumstances it would be prudent to leave the country immediately. Piłsudska fled with her mother and elder sister, Wanda, to Lithuania and eventually arrived in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarvis Offutt
First Lieutenant Jarvis Jenness Offutt (October 26, 1894 – August 13, 1918) was an American aviator from Omaha, Nebraska, who died in World War I. Offutt Air Force Base is named in his honor. Early life Born and raised in Omaha, Offutt was the younger son of Bertha() and Charles Offutt. Charles (1856–1898) was an attorney and a former speaker of the Kentucky General Assembly, from He relocated to Omaha in 1888 and married four years later. The middle of three children, Jarvis had an older brother (Casper) and a younger sister (Virginia). He attended Central High School and graduated from the Lawrenceville Preparatory School in New Jersey in 1913. He went to college at Yale University in Connecticut and graduated in 1917. Offutt was a member of Yale's Varsity Club, Glee Club, Alpha Delta Phi fraternity, and was a track man, winning his honors in the high hurdles. He was also inducted into the Phi Beta Kappa Society, an organization which recognizes high academic ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Olds
Robert Olds (June 15, 1896 – April 28, 1943) was a general officer in the United States Army Air Forces, theorist of strategic air power, and proponent of an independent United States Air Force. Olds is best known today as the father of Brig. Gen. Robin Olds, a " triple ace" fighter pilot of World War II and the Vietnam War. He became an instructor at the Air Corps Tactical School between 1928 and 1931, the crucial period when the theory of strategic bombardment achieved ascendancy within the Air Corps as the most effective use of airpower. With eight colleagues at the ACTS, he was a member of the " Bomber Mafia," whose influence led to adoption of the theory as the doctrine of daylight precision bombing during World War II. Olds was a persuasive, sometimes controversial figure in the unsuccessful campaign during the 1930s to promote air force independence, but the bombardment doctrine the clique championed ultimately became the foundation for separation from the Army. Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |