|
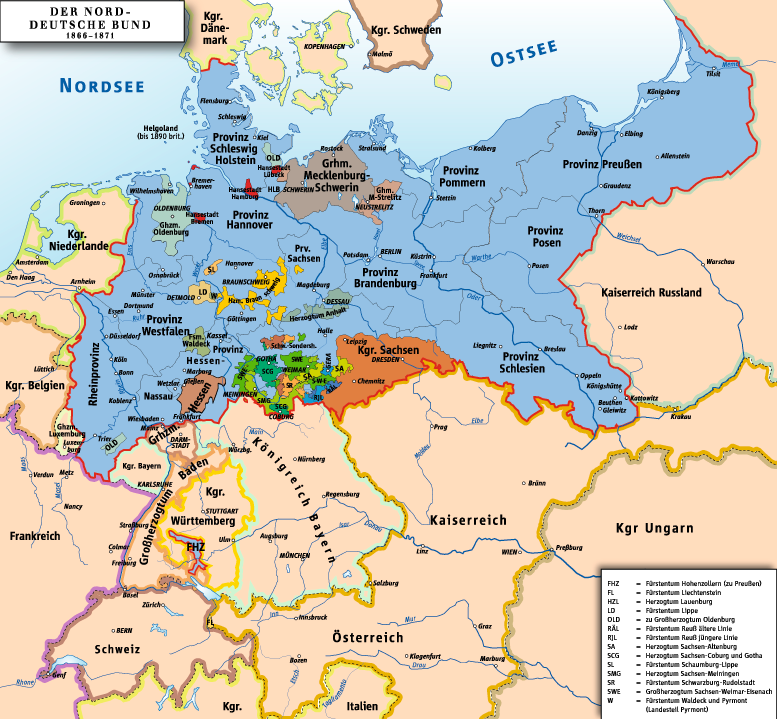
February 1867 North German Federal Election
Elections to the Constituent Reichstag of the North German Confederation were held on 12 February 1867, with run-off elections during the following weeks. The National Liberal Party emerged as the largest party, winning 80 seats and receiving strong support in Hanover, Kassel and Nassau.Helmut Walser Smith (2011) ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern German History'' Oxford University Press, p294 Voter turnout was around 65% in Prussian constituencies. After the Constituent Reichstag had drawn up and agreed a constitution, fresh elections were held in August. Electoral system The North German Confederation were divided into 297 single-member electoral constituencies. Elections were conducted under the two-round system. All men over the age of 25, who were in full enjoyment of their civil rights, who were resident in the place of election and had nationality in one of the States belonging to the Confederation for at least three years, who were not under guardianship or curate, who wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag (North German Confederation)
The Reichstag () of the North German Confederation was the federal state's lower house of parliament. The popularly elected Reichstag was responsible for federal legislation together with the Bundesrat, the upper house whose members were appointed by the governments of the individual states to represent their interests. Executive power lay with the Bundesrat and the king of Prussia acting as ''Bundespräsidium'', or head of state. The Reichstag debated and approved or rejected taxes and expenditures and could propose laws in its own right. To become effective, all laws required the approval of both the Bundesrat and the Reichstag. Voting rights in Reichstag elections were advanced for the time, granting universal, equal, and secret suffrage to men above the age of 25. When the German Empire was established in 1871, the North German Reichstag formed the basis of the new Reichstag of the German Empire. Background The draft constitution Following Prussia's victory in the 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August 1867 North German Federal Election
Elections to the Reichstag of the North German Confederation were held on 31 August 1867,Jonathan Steinberg (2011) ''Bismarck: A Life'', Oxford University Press with run-off elections during the following weeks. The National Liberal Party continued to serve as the largest party, winning 81 seats. These were the first regular and last elections during the North German Confederation. In July 1870 the Reichstag members decided not to hold new elections during the Franco-Prussian war, in spite of the three-year period. Electoral system The North German Confederation were divided into 297 single-member electoral constituencies, of which 236 were in Prussia. All men over the age of 25 and not in receipt of public assistance were eligible to vote. Results References {{German elections 1867 08 Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1867 Elections In Europe
Events January–March * January 1 – The Covington–Cincinnati Suspension Bridge opens between Cincinnati, Ohio, and Covington, Kentucky, in the United States, becoming the longest single-span bridge in the world. It was renamed after its designer, John A. Roebling, in 1983. * January 8 – African-American men are granted the right to vote in the District of Columbia. * January 11 – Benito Juárez becomes Mexican president again. * January 30 – Emperor Kōmei of Japan dies suddenly, age 36, leaving his 14-year-old son to succeed as Emperor Meiji. * January 31 – Maronite nationalist leader Youssef Bey Karam leaves Lebanon aboard a French ship for Algeria. * February 3 – ''Shōgun'' Tokugawa Yoshinobu abdicates, and the late Emperor Kōmei's son, Prince Mutsuhito, becomes Emperor Meiji of Japan in a brief ceremony in Kyoto, ending the Late Tokugawa shogunate. * February 7 – West Virginia University is established in Morgantown, West Virginia. * February 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Elections In Germany
Elections in Germany include elections to the Bundestag (Germany's federal parliament), the Landtags of the various states, and local elections. Several articles in several parts of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany govern elections and establish constitutional requirements such as the secret ballot, and requirement that all elections be conducted in a free and fair manner. The Basic Law also requires that the federal legislature enact detailed federal laws to govern elections; electoral law(s). One such article is Article 38, regarding the election of deputies in the federal Bundestag. Article 38.2 of the Basic Law establishes universal suffrage: "Any person who has attained the age of eighteen shall be entitled to vote; any person who has attained the age of majority may be elected." German federal elections are for all members of the Bundestag, which in turn determines who is the chancellor of Germany. The most recent federal election was held in 2021. German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General German Workers' Association
The General German Workers' Association (german: Allgemeiner Deutscher Arbeiter-Verein, ADAV) was a German political party founded on 23 May 1863 in Leipzig, Kingdom of Saxony by Ferdinand Lassalle. It was the first organized mass working-class party in European history. The organization existed by this name until 1875, when it combined with the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (SDAP) to form the Socialist Workers' Party of Germany. This unified organization was renamed soon thereafter the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), which presently remains in existence and dates its origins to the founding of the ADAV. Its Austrian part would become the SPÖ. The ADAV was the first German Labour Party, formed in Prussia prior to the establishment of the German Empire. It was active in the German Confederation, which included the Austrian Empire. Organizational history Establishment The ADAV was founded in Leipzig by Ferdinand Lassalle and twelve delegates from so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon People's Party
The Saxon People's Party (german: Sächsische Volkspartei) was a left-liberal and radical democratic party with socialist leanings in Germany, founded by Wilhelm Liebknecht and August Bebel on 19 August 1866 in Chemnitz, and integrated into the newly-founded Social Democratic Workers' Party (SDAP) on 8 August 1869. It was an alliance between liberal, anti-Prussian bourgeois and socialist workers' organizations in Saxony. It is considered one of the precursors to the Social Democratic Party of Germany. In the preamble to the Chemnitz program of the Saxon People's Party, they committed themselves to " ..fighting the enemies of German freedom and unity under all circumstances and in all areas ... It called for " ..the unrestricted right of self-determination of the German people .., the promotion of " ..general prosperity .. and " ..the liberation of work and the workers from any pressure and any bondage ..]". Founding Immediately after Prussia's victory against Austrian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Party
The Danish Party (german: Dänische Partei) was a political party in the German Empire. History The party was established in 1871 to represent the 50,000-strong Danish population of North Schleswig, who remained opposed to their separation from Denmark following the Second Schleswig War in 1864.Vincent E McHale (1983) ''Political parties of Europe'', Greenwood Press, p415 It won a seat in every Reichstag elected between 1871 and 1912. Its best performance was in the 1881 elections, the only occasion on which it won two seats. The party disappeared after World War I, following the Schleswig Plebiscites The Schleswig plebiscites were two plebiscites, organized according to section XII, articles 100 to 115 of the Treaty of Versailles of 28 June 1919, in order to determine the future border between Denmark and Germany through the former Duchy of S ... and the return of Northern Schleswig to Denmark. References {{German Empire political parties Defunct regional parties in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-Hanoverian Party
The German-Hanoverian Party (german: Deutsch-Hannoversche Partei, DHP), also known as the Guelph Party (german: Welfenpartei), was a conservative, federalist political party in the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. History The party was founded in 1867 in protest of the annexation of the Kingdom of Hanover by the Kingdom of Prussia in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War.Vincent E McHale (1983) ''Political parties of Europe'', Greenwood Press, p420 They wanted the revival of the Kingdom of Hanover and the restoration of the sequestrated assets of the former ruling House of Welf. The party therefore was also called the ''Welfen'', and drew its strongest support from the rural areas around Hannover. In the Reichstag DHP deputies usually acted as allies of the anti-Prussian Centre Party parliamentary group under Ludwig Windthorst, who although a Catholic and leader of the Centre Party was a former Hanoverian Justice Minister who was loyal to the House of Welf. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Liberals
The Old Liberals ( ''German'': Altliberale) were 19th-century liberals who, after 1849, stood in the tradition of the moderate, constitutional liberalism of the Vormärz and the revolution of 1848/49. In a narrower sense, the term refers to a parliamentary group in the Prussian House of Representatives. Its origin was the Vincke faction in the 1850s. After 1866, if they had not gone over to the German Progress Party in 1861, their deputies became part of the National Liberal Party or the Free Conservative Party. The term altliberal is contemporary and was used by Robert von Mohl after 1849 to describe the supporters of a constitutional system of government. Literature * Gerd Fesser : ''Old Liberals (Al) 1849–1876.'' In: Dieter Fricke and others (ed.): ''Encyclopedia of party history.'' Vol. 1. Bibliographic Institute, Leipzig 1983, DNBbr>850223156, pp. 59–65. * Walter Tormin : ''History of the German parties since 1848.'' 2nd edition. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart et al. 1967, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Progress Party
The German Progress Party (german: Deutsche Fortschrittspartei, DFP) was the first modern political party in Germany, founded by liberal members of the Prussian House of Representatives () in 1861 in opposition to Minister President Otto von Bismarck. History Upon the failed Revolutions of 1848, several deputies in the Landtag diet of Prussia maintained the idea of constitutionalism as it had been developed in the ''Vormärz'' era. In the 1850s, these Old Liberals gathered in a parliamentary group around Georg von Vincke, an originally conservative Prussian official and landowner ('' Junker''). Vincke, former member of the Frankfurt Parliament, a polished orator and firebrand, had fallen out with Prime Minister Otto Theodor von Manteuffel over his reactionary policies and in 1852 even fought a duel with Bismarck after a heated verbal exchange in parliament (both men missed). When under the regency of William I of Prussia from 1858 the Prussian policies of the new era turned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Conservative Party
The Free Conservative Party (german: Freikonservative Partei, FKP) was a liberal-conservative political party in Prussia and the German Empire which emerged from the Prussian Conservative Party in the Prussian Landtag in 1866. In the federal elections to the Reichstag parliament from 1871, it ran as the German Reich Party (german: Deutsche Reichspartei, DRP). DRP was classified as centrist or centre-right by political standards at the time, and it also put forward the slogan " conservative progress". The Free Conservative Association achieved party status in 1867, comprising German nobles and East Elbian Junkers (land owners) like Duke Victor of Ratibor and Karl Rudolf Friedenthal, industrialists and government officials like Johann Viktor Bredt, Hermann von Hatzfeldt, Hermann von Dechend, Prince Karl Max von Lichnowsky or General Hans Hartwig von Beseler and scholars like Hans Delbrück and Otto Hoetzsch. It was distinguished from the German Conservative Party established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Party (Prussia)
The Conservative Party was a party in Prussia founded in 1848 from the relatively loose cooperation of conservative associations, groups and members of parliament. The party split into the German Conservative Party and the Free Conservative Party in 1876. Chairmen * Ernst Ludwig von Gerlach Ernst Ludwig von Gerlach (7 March 1795 – 18 February 1877) was a Prussian politician, editor and judge. He is considered one of the main founders and leading thinkers of the Conservative Party in Prussia and was for many years its leader in the P ... Electoral results German Reichstag/Bundestag References {{Party-stub Defunct political parties in Germany Political parties established in 1848 Politics of the German Empire 1876 disestablishments in Germany Political parties disestablished in 1876 Defunct conservative parties Politics of Prussia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |