|
Extracellular Matrix Protein 1
Extracellular matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ECM1'' gene. This gene encodes an extracellular protein containing motifs with a cysteine pattern characteristic of the cysteine pattern of the ligand-binding "double-loop" domains of the albumin protein family. This gene maps outside the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC), a cluster of three gene families involved in epidermal differentiation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. Diseases ECM1 is implicated in breast cancer, thyroid cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and other cancers, and also in ulcerative colitis Germline mutations in ECM-1 cause the genetic disease lipoid proteinosis. Autoimmune attack on ECM-1 is responsible for lichen sclerosus.(see the Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology,). See also * Lipoid proteinosis Lipoid may refer to: * Lipid Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Differentiation Complex
The epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) is a gene complex comprising over fifty genes encoding proteins involved in the terminal differentiation and cornification of keratinocytes, the primary cell type of the epidermis. In humans, the complex is located on a 1.9 Mbp stretch within chromosome 1q21. The proteins encoded by EDC genes are closely related in terms of function, and evolutionarily they belong to three distinct gene families: the cornified envelope precursor family, the S100 protein family and the S100 fused type protein (SFTP) family. It has been hypothesized that the clustering of EDC genes occurred due to duplication events which were evolutionarily favored during the adaptation to terrestrial environments. EDC proteins have been involved in a variety of skin disorders including ichthyosis vulgaris, atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. History The epidermal differentiation complex was first described in 1993, and further characterized in 1996, when Dietmar Mischke an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
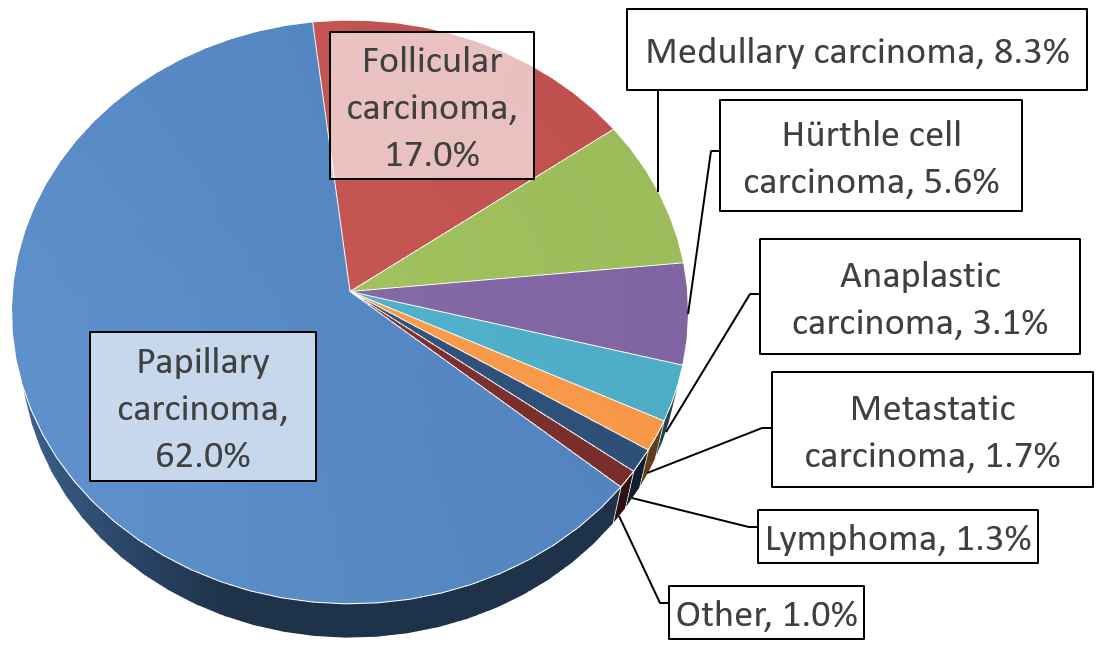
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer. Risk factors include radiation exposure at a young age, having an enlarged thyroid, and family history. The four main types are papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Diagnosis is often based on ultrasound and fine needle aspiration. Screening people without symptoms and at normal risk for the disease is not recommended as of 2017. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy including radioactive iodine, chemotherapy, thyroid hormone, targeted therapy, and watchful waiting. Surgery may involve removing part or all of the thyroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation, and is most closely linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection (hepatitis B or C) or exposure to toxins such as alcohol, aflatoxin, or pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, markedly increase the risk of developing HCC. Metabolic syndrome and NASH are also increasingly recognized as risk factors for HCC. As with any cancer, the treatment and prognosis of HCC vary depending on the specifics of tumor histology, size, how far the cancer has spread, and overall health. The vast majority of HCC cases and the lowest survival rates after treatment occur in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, in countries where hepatitis B infection is endem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer. The cause of UC is unknown. Theories involve immune system dysfunction, genetics, changes in the normal gut bacteria, and environmental factors. Rates tend to be higher in the developed world with some proposing this to be the result of less exposure to intestinal infections, or to a Western diet and lifestyle. The removal of the appendix at an early age may be protective. Diagnosis is typically by colonoscopy with tissue biopsies. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urbach–Wiethe Disease
Urbach–Wiethe disease is a very rare recessive genetic disorder, with approximately 400 reported cases since its discovery. It was first officially reported in 1929 by Erich Urbach and Camillo Wiethe, although cases may be recognized dating back as early as 1908. The symptoms of the disease vary greatly from individual to individual. They may include a hoarse voice, lesions and scarring on the skin, easily damaged skin with poor wound healing, dry, wrinkly skin, and beading of the papules around the eyelids. All of these are results of a general thickening of the skin and mucous membranes. In some cases there is also a hardening of brain tissue in the medial temporal lobes, which can lead to epilepsy and neuropsychiatric abnormalities. The disease is typically not life-threatening and patients do not show a decreased life expectancy, life span. Because Urbach–Wiethe disease is an autosomal recessive condition individuals can be genetic carrier, carriers of the disease but s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus (LS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease of unknown cause which can affect any body part of any person but has a strong preference for the genitals (penis, vulva) and is also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO) when it affects the penis. Lichen sclerosus is not contagious. There is a well-documented increase of skin cancer risk in LS, potentially improvable with treatment. LS in adult age women is normally incurable, but improvable with treatment, and often gets progressively worse if not treated properly. Most males with mild or intermediate disease restricted to prepuce or glans can be cured by either medical or surgical treatment. Signs and symptoms LS can occur without symptoms. White patches on the LS body area, itching, pain, dyspareunia (in genital LS), easier bruising, cracking, tearing and peeling, and hyperkeratosis are common symptoms in both men and women. In women, the condition most commonly occurs on the vulva and around the anus with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Of Genetics And Cytogenetics In Oncology And Haematology
The Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology, created in 1997 by Jean-Loup Huret (with bioinformatics by Philippe Dessen) is a collection of resources on genes, chromosomes anomalies, leukemias, solid tumours, and cancer-prone diseases. The project is accessible through Internet and is made of encyclopedic-style files, as well as traditional overviews, links towards websites and databases devoted to cancer and/or genetics, case reports in haematology. It also encompasses teaching items in various languages. Starting first from cytogenetics in the nineteens, the Atlas now combines different types of knowledge in a single web site: genes and their function, cell biology (ex: Apoptosis), pathological data, diseases and their clinical implications, cytogenetics, but also medical genetics, with hereditary disorders associated with an increased risk of cancer. This gives a wider and more global view of cancer genetics, while these data are usually dispersed. It inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoid Proteinosis
Lipoid may refer to: * Lipid Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids includ ..., a fatlike substance * Lipoid proteinosis, also known as Urbach–Wiethe disease {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |