|
Extended Projection Principle
The extended projection principle (EPP) is a linguistic hypothesis about subjects. It was proposed by Noam Chomsky as an addendum to the projection principle. The basic idea of the EPP is that clauses must contain a noun phrase or determiner phrase in the subject position (i.e. in the specifier of a tense phrase or inflectional phrase or in the specifier of a verb phrase in languages in which subjects don't raise to TP/IP, e.g. Welsh). Details Most verbs require meaningful subjects—for example, "kick" in "Tom kicked the ball" takes the subject "Tom". However, other verbs do not require (and in fact, do not permit) meaningful subjects—for example, one can say "it rains" but not "the sky rains". The EPP states that regardless of whether the main predicate assigns a meaningful theta role to a subject, a subject must be present syntactically. As a result, verbs that do not assign external theta roles will appear with subjects that are either dummy pronouns (e.g. expletive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Role
Theta roles are the names of the participant roles associated with a predicate: the predicate may be a verb, an adjective, a preposition, or a noun. If an object is in motion or in a steady state as the speakers perceives the state, or it is the topic of discussion, it is called a theme. The participant is usually said to be an argument of the predicate. In generative grammar, a theta role or θ-role is the formal device for representing syntactic argument structure—the number and type of noun phrases—required syntactically by a particular verb. For example, the verb ''put'' requires three arguments (i.e., it is trivalent). The formal mechanism for implementing a verb's argument structure is codified as theta roles. The verb ''put'' is said to "assign" three theta roles. This is coded in a theta grid associated with the lexical entry for the verb. The correspondence between the theta grid and the actual sentence is accomplished by means of a bijective filter on the grammar k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-sentence
A pro-sentence is a sentence where the subject pronoun has been dropped and therefore the sentence has a null subject. Overview Languages differ within this parameter, some languages such as Italian and Spanish have constant pro-drop, Finnish and Hebrew for example are partial pro-drop languages and Japanese and Tamil fall into the category of discourse or radical pro-drop languages. There are also languages such as English, German and Swedish that only allow pro-drop within very strict stylistic conditions. A pro-sentence is a kind of pro-form and is therefore anaphoric. In English, ''yes'', ''no'' and '' okay'' are common pro-sentences. In response to the question "Does Mars have two moons?", the sentence "Yes" can be understood to abbreviate "Mars does have two moons." Pro-sentences are sometimes seen as grammatical interjections, since they are capable of very limited syntactical relations. But they can also be classified as a distinct part of speech, given that (ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null-subject Language
In linguistic typology, a null-subject language is a language whose grammar permits an independent clause to lack an explicit subject; such a clause is then said to have a null subject. In the principles and parameters framework, the null subject is controlled by the pro-drop parameter, which is either on or off for a particular language. Typically, null-subject languages express person, number, and/or gender agreement with the referent on the verb, rendering a subject noun phrase redundant. For example, in Italian the subject "she" can be either explicit or implicit: The subject "(s)he" of the second sentence is only implied in Italian. English and French, on the other hand, require an explicit subject in this sentence. Null-subject languages include Arabic, most Romance languages, Chinese, Greek, Hebrew, the Indo-Aryan languages, Japanese, Korean, Persian, the Slavic languages, Tamil, and the Turkic languages. Characterization Languages which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
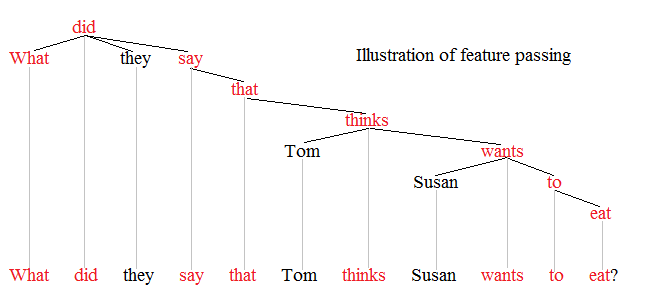
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRO (linguistics)
In generative linguistics, PRO (called "big PRO", distinct from ''pro'', "small pro" or " little pro") is a pronominal determiner phrase (DP) without phonological content. As such, it is part of the set of empty categories. The null pronoun PRO is postulated in the subject position of non-finite clauses. One property of PRO is that, when it occurs in a non-finite complement clause, it can be bound by the main clause subject ("subject control") or the main clause object ("object control"). The presence of PRO in non-finite clauses lacking overt subjects allows a principled solution for problems relating to binding theory. Within government and binding theory, the existence and distribution of PRO followed from the PRO theorem, which states that PRO may not be governed. More recent analyses have abandoned the PRO theorem. Instead, PRO is taken to be in complementary distribution with overt subjects because it is the only item that is able to carry ''null case'' which is checked for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Category
In linguistics, an empty category, which may also be referred to as a covert category, is an element in the study of syntax that does not have any phonological content and is therefore unpronounced.Kosta, Peter, and Krivochen, Diego Gabriel. ''Eliminating Empty Categories: A Radically Minimalist View on Their Ontology and Justification''. Frankfurt: Peter Lang GmbH, 2013. Print. Empty categories exist in contrast to overt categories which are pronounced. When representing empty categories in tree structures, linguists use a null symbol (∅) to depict the idea that there is a mental category at the level being represented, even if the word(s) are being left out of overt speech. The phenomenon was named and outlined by Noam Chomsky in his 1981 Lectures on Government and Binding: The Pisa Lectures, LGB framework, and serves to address apparent violations of Locality (linguistics), locality of selection — there are different types of empty categories that each appear to account for lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pro-drop
A pro-drop language (from "pronoun-dropping") is a language in which certain classes of pronouns may be omitted when they can be pragmatically or grammatically inferable. The precise conditions vary from language to language, and can be quite intricate. The phenomenon of "pronoun-dropping" is part of the larger topic of zero or null anaphora. The connection between pro-drop languages and null anaphora relates to the fact that a dropped pronoun has referential properties, and so is crucially not a null dummy pronoun. Pro-drop is a problem when translating to a non-pro-drop language such as English, which requires the pronoun to be added, especially noticeable in machine translation. It can also contribute to transfer errors in language learning. An areal feature of some European languages is that pronoun dropping is not, or seldom, possible (see Standard Average European); this is the case for English, French, German, and Emilian, among others. In contrast, Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dummy Pronoun
A dummy pronoun, also known as an expletive pronoun, is a deictic pronoun that fulfills a syntactical requirement without providing a contextually explicit meaning of its referent. As such, it is an example of exophora. A dummy pronoun is used when a particular verb argument (or preposition) is nonexistent, but when a reference to the argument (a pronoun) is nevertheless syntactically required. This is commonly the case if the verb is an impersonal verb, but it could also be that the argument is unknown, irrelevant, already understood, or otherwise taboo (as in naming taboo). For example, in the phrase " is obvious that the violence will continue", the term 'it' is a dummy pronoun, not referring to any agent. Unlike a regular pronoun of English, it cannot be replaced by any noun phrase. The term 'dummy pronoun' refers to the function of a word in a particular sentence, not a property of individual words. For example, 'it' in the example from the previous paragraph is a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales by about 18% of the population, by some in England, and in (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). It is spoken by smaller numbers of people in Canada and the United States descended from Welsh immigrants, within their households (especially in Nova Scotia). Historically, it has also been known in English as "British", "Cambrian", "Cambric" and "Cymric". The Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011 gave the Welsh language official status in Wales. Welsh and English are ''de jure'' official languages of the Senedd (the Welsh parliament), with Welsh being the only ''de jure'' official language in any part of the United Kingdom, with English being merely ''de facto'' official. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject (grammar)
A subject is one of the two main parts of a Sentence (linguistics), sentence (the other being the Predicate (grammar), predicate, which modifies the subject). For the simple Sentence (linguistics), sentence ''John runs'', ''John'' is the subject, a person or thing about whom the statement is made. Traditionally the subject is the word or phrase which controls the verb in the clause, that is to say with which the verb Agreement (linguistics), agrees (''John is'' but ''John and Mary are''). If there is no verb, as in ''Nicola what an idiot!'', or if the verb has a different subject, as in ''John I can't stand him!'', then 'John' is not considered to be the grammatical subject, but can be described as the ''Topic and comment, topic'' of the sentence. While these definitions apply to simple English sentences, defining the subject is more difficult in more complex sentences and languages. For example, in the sentence ''It is difficult to learn French'', the subject seems to be the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |