|
Evolution By Gene Duplication
Evolution by gene duplication is an event by which a gene or part of a gene can have two identical copies that can not be distinguished from each other. This phenomenon is understood to be an important source of novelty in evolution, providing for an expanded repertoire of molecular activities. The underlying mutational event of duplication may be a conventional gene duplication mutation within a chromosome, or a larger-scale event involving whole chromosomes (aneuploidy) or whole genomes (polyploidy). A classic view, owing to Susumu Ohno, which is known as Ohno model, he explains how duplication creates redundancy, the redundant copy accumulates beneficial mutations which provides fuel for innovation.Andersson DI, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Näsvall J. Evolution of new functions de novo and from preexisting genes. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2015 Jun 1;7(6):a017996. Knowledge of evolution by gene duplication has advanced more rapidly in the past 15 years due to new g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination, retrotransposition event, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and replication slippage. Mechanisms of duplication Ectopic recombination Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes. The products of this recombination are a duplication at the site of the exchange and a reciprocal deletion. Ectopic recombination is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination, retrotransposition event, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and replication slippage. Mechanisms of duplication Ectopic recombination Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes. The products of this recombination are a duplication at the site of the exchange and a reciprocal deletion. Ectopic recombination is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Evolution
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, neutral evolution vs. natural selection, origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of speciation, evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genomic and phenotypic changes. History The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with comparative biochemistry, and the use of "fingerprinting" methods such as immune assays, gel electrophoresis and paper chromatography in the 1950s to explore homologous proteins. The field of molecular evolution came into its own in the 1960s and 1970s, following the rise of molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
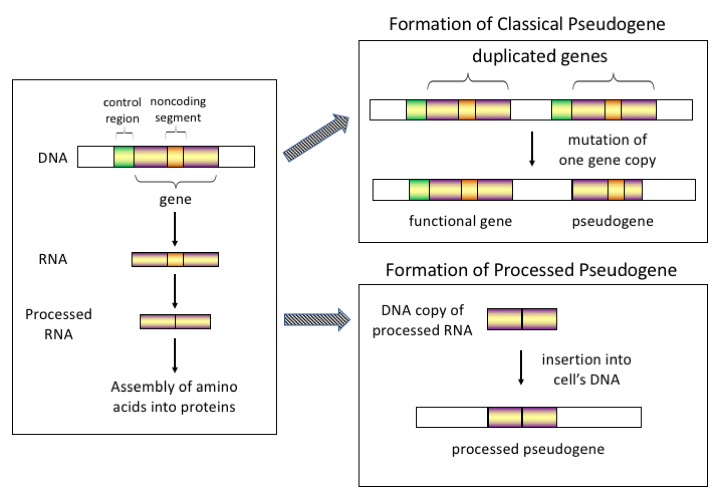
Pseudogenes
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many mutational changes that they are no longer recognizable as former genes. Analysis of these degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Promiscuity
Enzyme promiscuity is the ability of an enzyme to catalyse a fortuitous side reaction in addition to its main reaction. Although enzymes are remarkably specific catalysts, they can often perform side reactions in addition to their main, native catalytic activity. These promiscuous activities are usually slow relative to the main activity and are under neutral selection. Despite ordinarily being physiologically irrelevant, under new selective pressures these activities may confer a fitness benefit therefore prompting the evolution of the formerly promiscuous activity to become the new main activity. An example of this is the atrazine chlorohydrolase (''atzA'' encoded) from '' Pseudomonas sp.'' ADP that evolved from melamine deaminase (''triA'' encoded), which has very small promiscuous activity toward atrazine, a man-made chemical. Introduction Enzymes are evolved to catalyse a particular reaction on a particular substrate with a high catalytic efficiency (''kcat/KM'', ''cf''. Michae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neofunctionalization
Neofunctionalization, one of the possible outcomes of functional divergence, occurs when one gene copy, or paralog, takes on a totally new function after a gene duplication event. Neofunctionalization is an adaptive mutation process; meaning one of the gene copies must mutate to develop a function that was not present in the ancestral gene. In other words, one of the duplicates retains its original function, while the other accumulates molecular changes such that, in time, it can perform a different task. The process The process of Neofunctionalization begins with a gene duplication event, which is thought to occur as a defense mechanism against the accumulation of deleterious mutations. Following the gene duplication event there are two identical copies of the ancestral gene performing exactly the same function. This redundancy allows one the copies to take on a new function. In the event that the new function is advantageous, natural selection positively selects for it and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Divergence
Functional divergence is the process by which genes, after gene duplication, shift in function from an ancestral function. Functional divergence can result in either subfunctionalization, where a paralog specializes one of several ancestral functions, or neofunctionalization, where a totally new functional capability evolves. It is thought that this process of gene duplication and functional divergence is a major originator of molecular novelty and has produced the many large protein families that exist today. Functional divergence is just one possible outcome of gene duplication events. Other fates include nonfunctionalization where one of the paralogs acquires deleterious mutations and becomes a pseudogene and superfunctionalization (reinforcement), where both paralogs maintain original function. While gene, chromosome, or whole genome duplication events are considered the canonical sources of functional divergence of paralogs, orthologs (genes descended from speciation events) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by Reverse transcriptase, reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for Transcription (biology), transcription or Translation (biology), translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to Frameshift mutation, frameshifts or premature stop codons. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many mutational cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a ''euploid'' cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of some genetic disorders. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells (nondisjunction). Most cases of aneuploidy in the autosomes result in miscarriage, and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18 and 13. Chromosome abnormalities are detected in 1 of 160 live human births. Autosomal aneuploidy is more dangerous than sex chromosome aneuploidy, as autosomal aneuploidy is almost always lethal to embryos that cease develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |