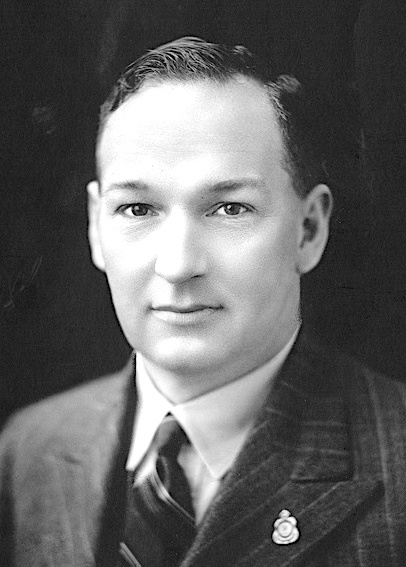|
Even George
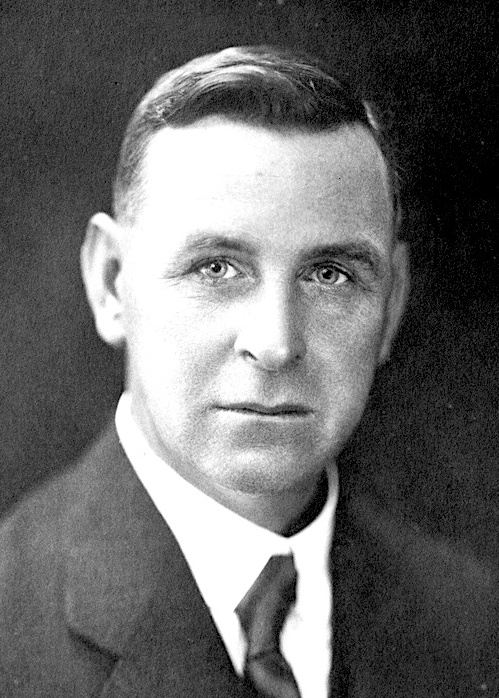
Even Ernest George (1 February 1875 – 1 June 1969) was an Australian politician. He was the Labor member for Burra Burra in the South Australian House of Assembly from 1930 to 1933. George was born at Quorn and educated locally, the son of a farmer who died when he was twelve. His first job was in an office in Port Augusta, after which he spent time working at Wallaroo Mines, where he was involved in the union movement. He also spent three years on the Western Australian goldfields and two years in the pastoral areas of Queensland. However, he was a farmer for the most of his life, and by the 1920s, he had his own farm at North Booborowie. He was auditor of the District Council of Spalding, chairman of the local school committee, a member of the Spalding Repatriation Committee, president of the North Booborowie and Spalding local Labor committees and president of Labor's Burra Burra electorate committee. He was an unsuccessful Labor candidate for the House of Assembly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even George
Even Ernest George (1 February 1875 – 1 June 1969) was an Australian politician. He was the Labor member for Burra Burra in the South Australian House of Assembly from 1930 to 1933. George was born at Quorn and educated locally, the son of a farmer who died when he was twelve. His first job was in an office in Port Augusta, after which he spent time working at Wallaroo Mines, where he was involved in the union movement. He also spent three years on the Western Australian goldfields and two years in the pastoral areas of Queensland. However, he was a farmer for the most of his life, and by the 1920s, he had his own farm at North Booborowie. He was auditor of the District Council of Spalding, chairman of the local school committee, a member of the Spalding Repatriation Committee, president of the North Booborowie and Spalding local Labor committees and president of Labor's Burra Burra electorate committee. He was an unsuccessful Labor candidate for the House of Assembly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 5 April 1930. All 46 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Federation government led by Premier of South Australia Richard L. Butler was defeated by the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Lionel Hill. Each district elected multiple members. This election saw the change from first past the post (plurality) to instant-runoff (preferential) voting, which also meant that electors cast a single vote rather than multiple votes. With 30 of 46 seats in the House of Assembly, the election remains South Australian Labor's biggest seat win. Results See also *Results of the South Australian state election, 1930 (House of Assembly) *Candidates of the South Australian state election, 1930 *Members of the South Australian House of Assembly, 1930–1933 *Members of the South Australian Legislative Council, 1930–1933 This is a list of members of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The South Australian House Of Assembly
This is a list of state elections in South Australia for the bicameral Parliament of South Australia, consisting of the House of Assembly ( lower house) and the Legislative Council (upper house). See also * List of South Australian House of Assembly by-elections * List of South Australian Legislative Council appointments * List of South Australian Legislative Council by-elections * Electoral districts of South Australia * Timeline of Australian elections External linksLower House results 1890-1965 Parliament of SA, www.parliament.sa.gov.au {{South Australian elections [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1969 Deaths
This year is notable for Apollo 11's first landing on the moon. Events January * January 4 – The Government of Spain hands over Ifni to Morocco. * January 5 **Ariana Afghan Airlines Flight 701 crashes into a house on its approach to London's Gatwick Airport, killing 50 of the 62 people on board and two of the home's occupants. * January 14 – An explosion aboard the aircraft carrier USS ''Enterprise'' near Hawaii kills 27 and injures 314. * January 19 – End of the siege of the University of Tokyo, marking the beginning of the end for the 1968–69 Japanese university protests. * January 20 – Richard Nixon is sworn in as the 37th President of the United States. * January 22 – An assassination attempt is carried out on Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev by deserter Viktor Ilyin. One person is killed, several are injured. Brezhnev escaped unharmed. * January 27 ** Fourteen men, 9 of them Jews, are executed in Baghdad for spying for Israel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1875 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the year (Third Class is renamed Second Class in 1956). * January 5 – The Palais Garnier, one of the most famous opera houses in the world, is inaugurated in Paris. * January 12 – Guangxu Emperor, Guangxu becomes the 11th Qing Dynasty Emperor of China at the age of 3, in succession to his cousin. * January 14 – The newly proclaimed King Alfonso XII of Spain (Queen Isabella II's son) arrives in Spain to restore the monarchy during the Third Carlist War. * February 3 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Lácar: Carlist commander Torcuato Mendiri, Torcuato Mendíri secures a brilliant victory, when he surprises and routs a Government force under General Enrique Bargés at Lácar, east of Estella, nearly capturing newly cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert George (politician)
Herbert John George (6 June 1872 – 4 September 1957) was an Australian politician. He was the Labor member for Adelaide in the South Australian House of Assembly from 1926 to 1933 and from 1947 to 1950. He was secretary of the Locomotive Engineers' Union throughout his first term in parliament. His brother, Even George Even Ernest George (1 February 1875 – 1 June 1969) was an Australian politician. He was the Labor member for Burra Burra in the South Australian House of Assembly from 1930 to 1933. George was born at Quorn and educated locally, the son ..., was also a state Labor MP. , - References 1872 births 1957 deaths Members of the South Australian House of Assembly Businesspeople from Adelaide Place of birth missing Australian Labor Party members of the Parliament of South Australia {{Australia-Labor-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 4 March 1950. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Mick O'Halloran. Background Only one seat changed hands, rural Stanley saw the Labor member re-elected as an independent member. Notably, neither major party contested the independent-held seat of Ridley. Results * The primary vote figures were from contested seats, while the statewide two-party-preferred vote figures were estimated from all seats. Post-election pendulum See also * Results of the South Australian state election, 1950 (House of Assembly) * Candidates of the 1950 South Australian state election * Members of the South Australian House of Assembly, 1950-1953 * Members of the South Australian Legislative Council, 1950-1953 *Playmander Notes External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Chronicle (Adelaide)
''The Chronicle'' was a South Australian weekly newspaper, printed from 1858 to 1975, which evolved through a series of titles. It was printed by the publishers of '' The Advertiser'', its content consisting largely of reprints of articles and Births, Marriages and Deaths columns from the parent newspaper. Its target demographic was country areas where mail delivery was infrequent, and businesses which serviced those areas. ''History'' ''South Australian Weekly Chronicle'' When ''The South Australian Advertiser'' was first published, on 12 July 1858, the editor and managing director John H. Barrow also announced the ''South Australian Weekly Chronicle'', which published on Saturdays. ''South Australian Chronicle and Weekly Mail'' On 4 January 1868, with the installation of a new steam press, the size of the paper doubled to four sheets, or sixteen pages and changed its banner to ''The South Australian Chronicle and Weekly Mail''. The editor at this time was William Hay, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1938 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 19 March 1938. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Richard L. Butler defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Andrew Lacey. Background This election was the start of the electoral malapportionment which became known as the Playmander. It consisted of rural districts enjoying a 2-to-1 advantage in the state parliament, even though they contained less than half of the population, as well as a change from multi-member to single-member electorates, and the number of MPs in the lower house was reduced from 46 to 39. Labor remained out of power until the 1965 election. Tom Stott was one of 14 of 39 lower house MPs to be elected as an independent, which as a grouping won 40 percent of the primary vote, more than either of the major parties. Stott was the de facto leader of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 8 April 1933. All 46 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Parliamentary Labor Party government led by Premier Robert Richards was defeated by the opposition Liberal and Country League led by Leader of the Opposition Richard L. Butler. Each district elected multiple members. Background After the ALP government of Premier Lionel Hill endorsed the controversial Premiers' Plan following the start of the Great Depression in Australia and the subsequent Australian Labor Party split of 1931, the ALP state executive expelled 23 of the 30 members of the ALP caucus, including the entire cabinet. The expelled MPs formed the Parliamentary Labor Party (also known as Premiers Plan Labor), with Hill as leader and Premier, and continued in office with the support of the Butler-led Liberal Federation. Amid increasing riots and protests, as well as skyrocketing unemployment, Hill left politics to bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary Labor Party
The Parliamentary Labor Party (also known as the Premiers' Plan Labor Party or Ministerial Labor Party) was a political party active in South Australia from August 1931 until June 1934. The party came into existence as a result of intense dispute, especially within the Australian Labor Party, about the handling of the response to the Great Depression in Australia. In June 1931, a meeting of state premiers agreed on the Premiers' Plan, which involved sweeping austerity measures combined with increases in revenue. When the Premiers' Plan came up for a vote in South Australia, 23 of Labor's 30 House of Assembly members and two of Labor's four Legislative Council members voted for it. In August 1931, the South Australian state conference of the Labor Party expelled all of the MPs who supported the Premiers' Plan, including Premier Lionel Hill and his entire Cabinet. Expelled MPs (23) in the House of Assembly: * Frederick Birrell * Alfred Blackwell *Thomas Butterfield * Clement Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premiers' Plan
The Premiers' Plan was a deflationary economic policy agreed by a meeting of the Premiers of the Australian states in June 1931 to combat the Great Depression in Australia that sparked the 1931 Labor split. Background The Great Depression in Australia saw huge levels of unemployment and economic suffering amid plummeting export income. Although the economic downturn was a product of international events, Australian governments grappled with how to respond. Conventional economists said governments should pursue deflationary policies. Radicals proposed inflationary responses and increased government spending. The James Scullin Labor Government had won office at the 1929 federal election just in time to face the full force of the global crisis—the ‘Wall Street crash’ took place in the first week of his government. Division emerged within the Labor government over how to respond. Scullin invited Sir Otto Niemeyer of the Bank of England to come to Australia to advise on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)