|
Euthyrox
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken by mouth or given by intravenous injection. Maximum effect from a specific dose can take up to six weeks to occur. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to triiodothyronine (T3). Levothyroxine was first made in 1927. It is on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid nodules are nodules (raised areas of tissue or fluid) which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant. Small, asymptomatic nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptoms may eventually need medical care. A goitre may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse. Signs and symptoms Often these abnormal growths of thyroid tissue are located at the edge of the thyroid gland and can be felt as a lump in the throat. When they are large, they can sometimes be seen as a lump in the front of the neck. Sometimes a thyroid nodule presents as a fluid-filled cavity called a thyroid cyst. Often, solid components are mixed with the fluid. Thyroid cysts most commonly result from degenerating thyroid adenomas, which are benign, but they occasionally contain malignant solid components. Diagnosis A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) due to decreased blood flow in the coronary arteries such that part of the heart muscle is unable to function properly or dies. The most common symptom is centrally located pressure-like chest pain, often radiating to the left shoulder or angle of the jaw, and associated with nausea and sweating. Many people with acute coronary syndromes present with symptoms other than chest pain, particularly women, older people, and people with diabetes mellitus. Acute coronary syndrome is subdivided in three scenarios depending on the duration of symptoms, the presence of ECG changes and blood test results: ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%). Generally, when symptoms occur for less than 30 minutes, it is unstable angina. When symptoms are prolonged for more than 30 minutes, the diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. ACS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
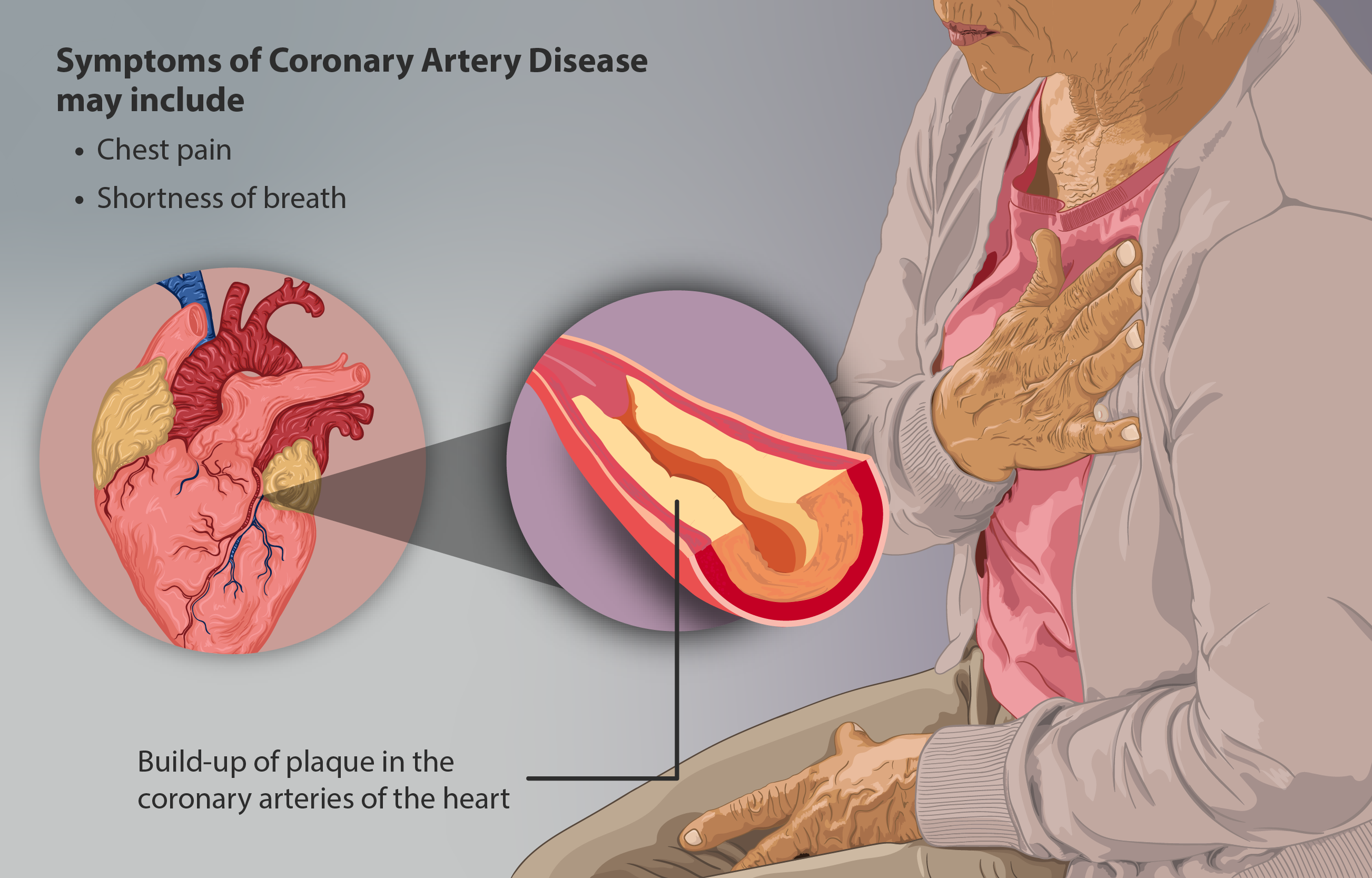
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall. The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount ... in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Stress (psychological), stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compliance (medicine)
In medicine, patient compliance (also adherence, capacitance) describes the degree to which a patient correctly follows medical advice. Most commonly, it refers to medication or drug compliance, but it can also apply to other situations such as medical device use, self care, self-directed exercises, or therapy sessions. Both patient and health-care provider affect compliance, and a positive physician-patient relationship is the most important factor in improving compliance. Access to care plays a role in patient adherence, whereby greater wait times to access care contributing to greater absenteeism. The cost of prescription medication also plays a major role. Compliance can be confused with concordance, which is the process by which a patient and clinician make decisions together about treatment. Worldwide, non-compliance is a major obstacle to the effective delivery of health care. 2003 estimates from the World Health Organization indicated that only about 50% of patients with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' (bile) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LDL Cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 220–275 angstroms in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins, or reasons behind the way that things are, or the way they function, or it can refer to the causes themselves. The word is commonly used in medicine (pertaining to causes of disease) and in philosophy, but also in physics, psychology, government, geography, spatial analysis, theology, and biology, in reference to the causes or origins of various phenomena. In the past, when many physical phenomena were not well understood or when histories were not recorded, myths often arose to provide etiologies. Thus, an etiological myth, or origin myth, is a myth that has arisen, been told over time or written to explain the origins of various social or natural phenomena. For example, Virgil's ''Aeneid'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sum Activity Of Peripheral Deiodinases
The sum activity of peripheral deiodinases (''GD'', also referred to as deiodination capacity, total deiodinase activity or, if calculated from levels of thyroid hormones, as SPINA-GD) is the maximum amount of triiodothyronine produced per time-unit under conditions of substrate saturation. It is assumed to reflect the activity of deiodinases outside the central nervous system and other isolated compartments. GD is therefore expected to reflect predominantly the activity of type I deiodinase. How to determine GD ''GD'' can be determined experimentally by exposing a cell culture system to saturating concentrations of T4 and measuring the T3 production. Whole body deiodination activity can be assessed by measuring production of radioactive iodine after loading the organism with marked thyroxine. However, both approaches are faced with draw-backs. Measuring deiodination in cell culture delivers little, if any, information on total deiodination activity. Using marked thyroxine exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI may be determined using a table or chart which displays BMI as a function of mass and height using contour lines or colours for different BMI categories, and which may use other units of measurement (converted to metric units for the calculation). The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as ''underweight'', ''normal weight'', ''overweight'', or ''obese'' based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult BMI classifications are underweight (under 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9), overweight (25 to 29.9), and obese (30 or more). When used to predict an individual's health, rather than as a statistical measurement for groups, the BMI has limitations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)