|
Eusthenopteron
''Eusthenopteron'' (from el, εὖ , 'good', el, σθένος , 'strength', and el, πτερόν 'wing' or 'fin') is a genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian (often called lobe-finned fishes) which has attained an iconic status from its close relationships to tetrapods. Early depictions of this animal show it emerging onto land; however, paleontologists now widely agree that it was a strictly aquatic animal.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi'' ''Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. The genus ''Eusthenopteron'' is known from several species that lived during the Late Devonian period, about 385 million years ago. ''Eusthenopteron'' was first described by J. F. Whiteaves in 1881, as part of a large collection of fishes from Miguasha, Quebec. Some 2,000 ''Eusthenopteron'' specimens have been collected from Miguasha, one of which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusthenopteron Foordi 1
''Eusthenopteron'' (from el, εὖ , 'good', el, σθένος , 'strength', and el, πτερόν 'wing' or 'fin') is a genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian (often called lobe-finned fishes) which has attained an iconic status from its close relationships to tetrapods. Early depictions of this animal show it emerging onto land; however, paleontologists now widely agree that it was a strictly aquatic animal.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi'' ''Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. The genus ''Eusthenopteron'' is known from several species that lived during the Late Devonian period, about 385 million years ago. ''Eusthenopteron'' was first described by J. F. Whiteaves in 1881, as part of a large collection of fishes from Miguasha, Quebec. Some 2,000 ''Eusthenopteron'' specimens have been collected from Miguasha, one of which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Fish
The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include ''Haikouichthys''. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans. The earliest jawed vertebrates probably developed during the late Ordovician period. They are first represented in the fossil record from the Silurian by two groups of fish: the armoured fish known as placoderms, which evolved from the ostracoderms; and the Acanthodii (or spiny sharks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Jarvik
Anders Erik Vilhelm Jarvik (30 November 1907 – 11 January 1998) was a Swedish paleontologist who worked extensively on the sarcopterygian (or lobe-finned) fish ''Eusthenopteron''. In a career that spanned some 60 years, Jarvik produced some of the most detailed anatomical work on this fish, making it arguably the best known fossil vertebrate. Jarvik was born at a farm in Utby Parish near Mariestad in northern Västergötland. He studied botany, zoology, geology, and paleontology at Uppsala University, where he took his licentiate's degree in 1937. In 1942, he completed his PhD with the dissertation ''On the structure of the snout of Crossopterygians and lower Gnathostomes in general''. He participated in the Greenland expedition of Gunnar Säve-Söderbergh in 1932 and was appointed assistant in the Department of Palaeozoology of the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm in 1937; he eventually succeeded Erik Stensiö as professor and head of the department in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gogonasus
''Gogonasus'' (meaning "snout from Gogo") was a lobe-finned fish known from three-dimensionally preserved 380-million-year-old fossils found from the Gogo Formation in Western Australia. It lived in the Late Devonian period, on what was once a 1,400-kilometre coral reef off the Kimberley coast surrounding the north-west of Australia. ''Gogonasus'' was a small fish reaching 30–40 cm (1 ft) in length. Its skeleton shows several features that were like those of a four-legged land animal (tetrapod). They included the structure of its middle ear, and its fins show the precursors of the forearm bones, the radius and ulna. Researchers believe it used its forearm-like fins to dart out of the reef to catch prey. ''Gogonasus'' was first described from a single snout (ethmosphenoid) by John A. Long (1985). On Long's 1986 expedition to Gogo the first relatively complete skull of ''Gogonasus'' was found by Chris Nelson and after being prepared solved a scientific controversy by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
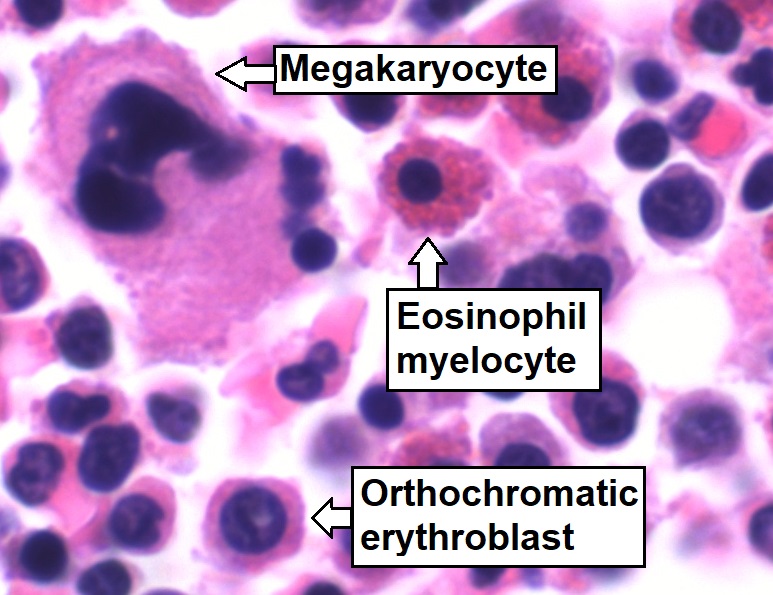
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as well as possible hydrodynamic advantages. The term ''scale'' derives from the Old French , meaning a shell pod or husk. Scales vary enormously in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it came from. Scales originated within the jawless ostracoderms, ancestors to all jawed fishes today. Most bony fishes are covered with the cycloid scales of salmon and carp, or the ctenoid scales of perch, or the ganoid scales of sturgeons and gars. Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) are covered with placoid scales. Some species are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorpha
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyostega
''Ichthyostega'' (from el, ἰχθῦς , 'fish' and el, στέγη , 'roof') is an extinct genus of limbed tetrapodomorphs from the Late Devonian of Greenland. It was among the earliest four-limbed vertebrates in the fossil record, and was one of the first with weight-bearing adaptations for terrestrial locomotion. ''Ichthyostega'' possessed lungs and limbs that helped it navigate through shallow water in swamps. Although ''Ichthyostega'' is often labelled a 'tetrapod' due to the possession of limbs and fingers, it evolved long before true crown group tetrapods, and could more accurately be referred to as a stegocephalian or stem tetrapod. Likewise, while undoubtedly of amphibian build and habit, it is not considered a true member of the group in the narrow sense, as the first modern amphibians (members of the group Lissamphibia) appeared in the Triassic Period. Until finds of other early stegocephalians and closely related fishes in the late 20th century, ''Ichthyostega'' st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouvelle, Quebec
Nouvelle is a municipality in eastern Quebec, Canada, on the south shore of the Gaspé Peninsula at the mouth of the Nouvelle River, where the Restigouche River widens into Chaleur Bay. In addition to Nouvelle itself, the municipality also includes the communities of Allard, Brébeuf (Dugal), Drapeau, Miguasha, Miguasha-Ouest, Nouvelle-Ouest, and Provancher. Nouvelle's graphic seal is a world globe overlaid by '' Eusthenopteron foordi'', whose fossil discovery brought worldwide fame to the Miguasha National Park, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site within the municipality. The seal's red and gray colours represent the colors of the rocks present on the fossil site. History Nouvelle was first settled by Acadians fleeing the deportation of 1755, fish merchants from Jersey, Channel Islands and some Irish. The name Nouvelle (French meaning "new") was used as early as the end of the 18th century and stood for the "new land" being made available west of the town that is now called Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
