|
Eurotrochilus Inexpectatus
''Eurotrochilus'' is an extinct genus of stem group hummingbirds (Trochilidae) and are the closest known relatives of the crown group Trochilidae. Despite ''Eurotrochilus'' being morphologically very similar to modern hummingbirds, they still retained several primitive features and are not closely related to any specific extant hummingbird in the crown group. There are currently two described species of ''Eurotrochilus'': ''E. inexpectatus'' and ''E. noniewiczi''. ''Eurotrochilus'' has been dated back to the Rupelian age of the early Oligocene era, which occurred during the Paleogene period. While there is some debate over exactly when ''Eurotrochilus'' was present, the most recent estimate is suggested to be 28 to 34 million years ago. The discovery of ''Eurotrochilus'' fossils in Germany, France, and Poland was extremely important because today all 328 of the extant species of hummingbirds only occur in the New World but the fossils of ''Eurotrochilus'' suggest an Old World or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Oligocene
The Rupelian is, in the geologic timescale, the older of two ages or the lower of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between . It is preceded by the Priabonian Stage (part of the Eocene) and is followed by the Chattian Stage. Name The stage is named after the small river Rupel in Belgium, a tributary to the Scheldt. The Belgian Rupel Group derives its name from the same source. The name Rupelian was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The separation between the group and the stage was made in the second half of the 20th century, when stratigraphers saw the need to distinguish between lithostratigraphic and chronostratigraphic names. Stratigraphic definition The base of the Rupelian Stage (which is also the base of the Oligocene Series) is at the extinction of the foraminiferan genus ''Hantkenina''. An official GSSP for the base of the Rupelian has been assigned in 1992 (Massignano, Italy). The transi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochilus
The streamertails are hummingbirds in the genus ''Trochilus'', that are endemic to Jamaica. It is the type genus of the family Trochilidae. Today most authorities consider the two taxa in this genus as separate species, but some (e.g. AOU) continue to treat them as conspecific, in which case ''scitulus'' is a subspecies of ''T. polytmus''. A wide range of common names apply to this combined species, including green-and-black streamertail, Jamaican streamertail or simply streamertail. The name ''streamertail'' is a reference to the greatly elongated rectrices of the males. Taxonomy and species list The genus ''Trochilus'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his '' Systema Naturae''. The genus name is from the Ancient Greek τροχιλος/''trokhilos'', a small unidentified bird mentioned by Aristotle. Later authors assumed the word referred to a wren. The type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiesloch
Wiesloch (, locally ; South Franconian: ''Wissloch''), is a town in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated 13 kilometres south of Heidelberg. After Weinheim, Sinsheim and Leimen it is the fourth largest town in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis. It shares Wiesloch-Walldorf station with its neighbouring town Walldorf. Also in the vicinity of Wiesloch are Dielheim, Malsch (bei Wiesloch), Mühlhausen, Rauenberg and Sankt Leon-Rot. Wiesloch's population grew to more than 20,000 when the administration of the area was reorganised in the 1970s. Wiesloch became a ''Große Kreisstadt'' on 1 January 1973, when Altwiesloch, Baiertal, Frauenweiler and Schatthausen were amalgamated with Wiesloch to form the present municipality. History The settlement that is now Wiesloch town centre originated during the expansion of silver mining in the vicinity in the 10th century. Fossil site The fossil remains of the oldest hummingbird found to date, ''Eurotrochilus inexpectatus'', were found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpometacarpus
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless birds, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely. It forms the tip of the wing skeleton in birds. To it, most of the primary remiges attach. The alula, by contrast, is formed by the thumb, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bones. To non-biologists the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings come in two basic sizes, a large angled one containing three major bones, and a smaller flat one containing only two. The bone missing in the latter is the carpometacarpus. See also * Carpometacarpal joint The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek κόραξ, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In dinosaurs the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa (geology)
In planetary nomenclature, a fossa (pl. fossae ) is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben. On Mars The Tharsis quadrangle is home to large troughs (long narrow depressions) called fossae in the geographical language used for Mars. This term is derived from Latin; therefore fossa is singular and fossae is plural. Troughs form when the crust is stretched until it breaks. The stretching can be due to the large weight of a nearby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
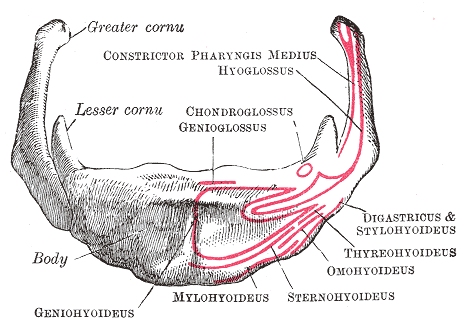
Hyoid Bones
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchokinesis
Cranial kinesis is the term for significant movement of skull bones relative to each other in addition to movement at the joint between the upper and lower jaw. It is usually taken to mean relative movement between the upper jaw and the braincase. Most vertebrates have some form of kinetic skull. Cranial kinesis, or lack thereof, is usually linked to feeding. Animals which must exert powerful bite forces, such as crocodiles, often have rigid skulls with little or no kinesis, for maximum strength. Animals which swallow large prey whole (snakes), which grip awkwardly shaped food items (parrots eating nuts), or, most often, which feed in the water via suction feeding often have very kinetic skulls, frequently with numerous mobile joints. In the case of mammals, which have akinetic skulls (except for perhaps hares), the lack of kinesis is most likely to be related to the secondary palate, which prevents relative movement. This in turn is a consequence of the need to be able to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar plays a crucial role in the foraging economics and evolution of nectar-eating species; for example, nectar foraging behavior is largely responsible for the divergent evolution of the African honey bee, ''A. m. scutellata'' and the western honey bee. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of parasitoid wasps (e.g. the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(19840424759).jpg)