|
Eupterodactyloidea
Eupterodactyloidea (meaning "true Pterodactyloidea") is an extinct group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs that existed from the latest Late Jurassic to the latest Late Cretaceous periods (Tithonian to Maastrichtian stages). Eupterodactyloids lived on all continents except Antarctica. Classification Eupterodactyloidea was named by S. Christopher Bennett in 1994 as an infraorder of the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Bennett defined it as an apomorphy-based clade. However, in 2010, Brian Andres re-defined the group as a stem-based taxon in his dissertation, and then formalized the definition in 2014 as all pterosaurs more closely related to ''Pteranodon longiceps'' than to ''Pterodactylus antiquus''. The slightly more exclusive group Ornithocheiroidea was re-defined in 2003 by Alexander Kellner. He defined it as the least inclusive clade containing ''Anhanguera blittersdorffi'', ''Pteranodon longiceps'', ''Dsungaripterus weii'', and ''Quetzalcoatlus northropi''. Ornithocheiroidea has often b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloidea
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloid
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were insectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheiroidea
Ornithocheiroidea (or ornithocheiroids) is a group of pterosaurs within the extinct suborder Pterodactyloidea. They were typically large pterosaurs that lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Maastrichtian stages), with fossil remains found all over the world except Antarctica. Ornithocheiroids were the most advanced group of pterosaurs, as the group includes the clade Azhdarchoidea, of which its members lived until the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous, around 66 million years ago. Notable pterosaurs from this group include the pteranodontians ''Pteranodon'' and ''Nyctosaurus'', the ornithocheirid ''Ornithocheirus'', the anhanguerid ''Tropeognathus'', as well as the azhdarchids ''Hatzegopteryx'' and ''Quetzalcoatlus''. Classification The name Ornithocheiroidea was originally defined as an apomorphy-based taxon by Christopher Bennett in 1994. It was given a relationship-based definition in 2003 by Alexander Kellner, who defined it as the least in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheirid
Ornithocheiridae (or ornithocheirids, meaning "bird hands") is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Turonian stages), around 140 to 90 million years ago. Ornithocheirids are generally infamous for having an enormously controversial and very confusing taxonomy. Although agreements that these animals were related, and therefore similar to istiodactylids and pteranodontians, there is still no virtual consensus over the exact content and interrelationships of this group. Ornithocheirids were the most successful pterosaurs during their reign, they were also the largest pterosaurs before the appearance of the azhdarchids such as '' Quetzalcoatlus''. Ornithocheirids were excellent fish hunters, they used various flight techniques to catch their prey, and they are also capable of flying great distances without f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haopterus Gracilis
''Haopterus'' is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Barremian- Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China. Its fossil remains dated back 124.6 million years ago. Discovery and naming It was in 2001 named by Wang Xiaolin and Lü Junchang. The type species is ''Haopterus gracilis''. The genus name honors Professor Hao Yichun and combines her name with a Latinized Greek ''pteron'', "wing". The specific name, "slender-built" in Latin, refers to the condition of the metatarsals. The genus is based on holotype IVPP V11726, a crushed fossil found in 1998 at the Sihetun-locality. The layer it was discovered in, was argon-dated at an age of 124.6 million years. It was the first Chinese pterosaur fossil preserving the skull. It consists of the front half of a subadult, including a skull, lower jaws, pectoral girdle, sternum, wings, cervical and dorsal vertebrae, partial pelvis and metatarsals. Description The skull of ''Haopterus'' is with a length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
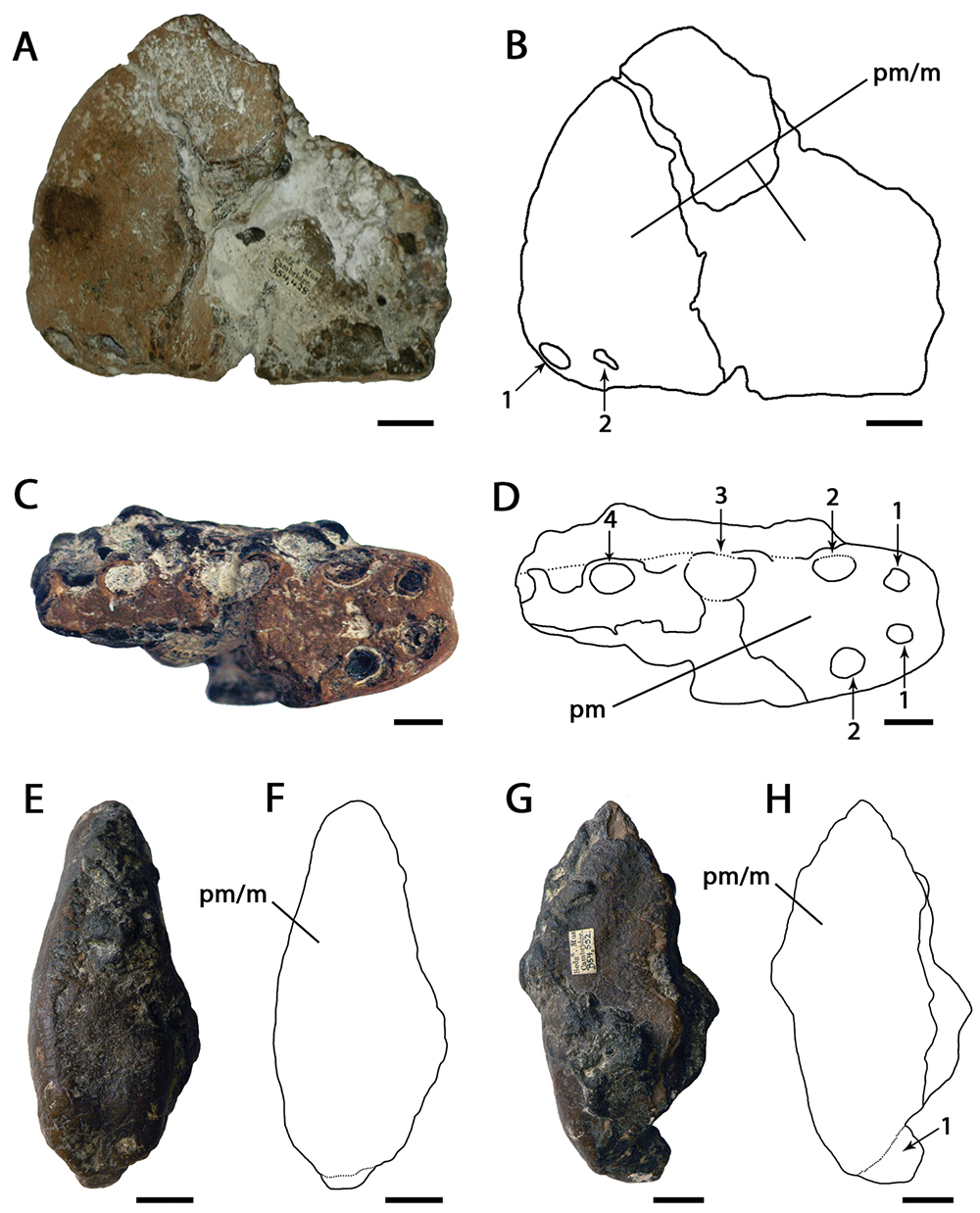
Piksi Barbarulna
''Piksi'' is a potential pterosaurLongrich, N.R., Martill, D.M., and Andres, B. (2018). Late Maastrichtian pterosaurs from North Africa and mass extinction of Pterosauria at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. PLoS Biology, 16(3): e2001663. genus containing the single species ''Piksi barbarulna'' (meaning "strange elbowed big bird", from Blackfoot ''piksi'', "big bird" or, specifically, "chicken" and Latin ''barbarus'' "strange, outlandish" + ''ulna'', elbow). It lived roughly 75 million years ago in what is now Montana, United States. Known from parts of a right wing – the humerus, ulna and radius (bone), radius bones – the only specimens found so far are housed in the Museum of the Rockies (collection number MOR 1113). The genus ''Piksi'' is monotypic at present. The fossils were found in 1991 by Gloria Jean Siebrecht in the Blackfeet Indian Reservation, namely at Bob's Vacation Site locality TM-088, Glacier County. Recovered from an old stratum of the upper Two Medicine Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |