|
Euparkeriidae
Euparkeriidae is an extinct family of small carnivorous archosauriforms which lived from the Early Triassic to the Middle Triassic (Anisian). While most other early archosauriforms walked on four limbs, euparkeriids were probably facultative bipeds that had the ability to walk on their hind limbs at times. The most well known member of Euparkeriidae is the species '' Euparkeria capensis'', which was named by paleontologist Robert Broom from the Karoo Basin of South Africa in 1913 and is known from several nearly complete skeletons. The family name was first proposed by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1920; Huene classified euparkeriids as members of Pseudosuchia, a traditional name for crocodilian-line archosaurs from the Triassic (Pseudosuchia means "false crocodiles"). However, phylogenetic analyses performed in the 21st century place Euparkeriidae as a group of Archosauriformes, a position outside Pseudosuchia and close to the ancestry of both crocodile-line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorosuchus
''Dorosuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform previously assigned to the family Euparkeriidae. It lived during the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic. Fossil material is known from Sol-Iletsk in Orenburg Oblast, Russia. The type species is ''D. neoetus'', named in 1989. Description ''Dorosuchus'' was considered to be a relative of euparkeriid ''Euparkeria'' based on the features of the limbs and pelvic girdle. Most specimens are known from a single block of siltstone from a location known as the Berdyanka I locality by Berdyanka River. Limb and hip elements, sacral and caudal vertebrae, and a braincase are preserved in the block and represent four individuals. A partial ilium is known from another locality. Classification ''Dorosuchus'' was initially classified as a euparkeriid in 1989 with its first description. The family Euparkeriidae is best represented by the genus ''Euparkeria'' from the Early Triassic of South Africa. Several other genera in the past have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
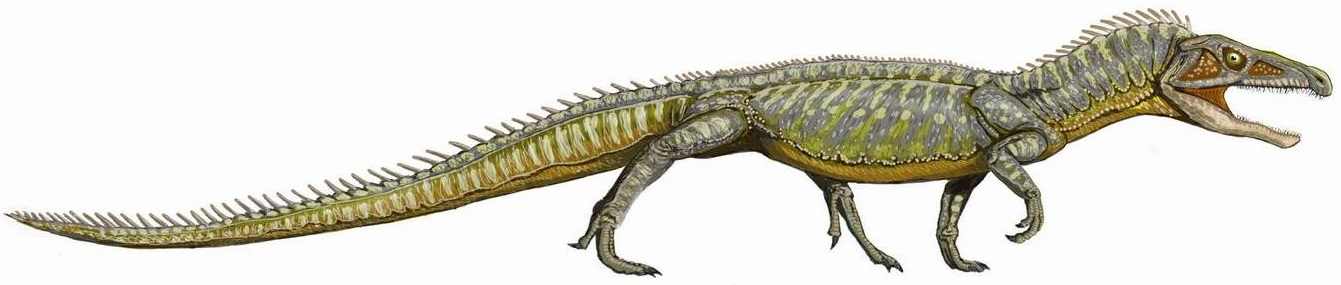
Euparkeria Capensis
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that it cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euparkeria
''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, birds and crocodilians. ''Euparkeria'' had hind limbs that were slightly longer than its forelimbs, which has been taken as evidence that it may have been able to rear up on its hind legs as a facultative biped. Although ''Euparkeria'' is close to the ancestry of fully bipedal archosaurs such as early dinosaurs, it probably developed bipedalism independently. ''Euparkeria'' was not as well adapted to bipedal locomotion as dinosaurs and its normal movement was probably more analogous to a crocodilian high walk. Palaeobiology Locomotion The hind limbs of ''Euparkeria'' are somewhat longer than its forelimbs, which has led many researchers to conclude that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and extinct relatives of crocodilians. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives, and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphological characteristics, such as an antorbital fenestra in the skull, serrated teeth, and an upright stance. Some extinct reptiles, such as proterosuchids and euparkeriids, possessed these features yet originated pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmolskina
left, 210px, Fossil elements. ''Osmolskina'' is a genus of archosauriform reptile which lived during the Early Triassic in what is now Poland. The type species, ''Osmolskina czatkowicensis'', was described by Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka and Susan Evans in 2003. The generic name honors the late female Polish paleontologist Halszka Osmólska. ''Osmolskina'' closely resembles the well-known genus ''Euparkeria''. The authors of the 2003 paper considered classifying ''Osmolskina'' within the family Euparkeriidae, noting the animal's close resemblance to ''Euparkeria ''Euparkeria'' (; meaning "Parker's good animal", named in honor of W.K. Parker) is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close ...'', but concluded that "Euparkeriidae remains monotypic because no other genus can be assigned to it with confidence." References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4189167 Prehis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halazhaisuchus
''Halazhaisuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Early Triassic of China. It is known from a single species, ''Halazhaisuchus qiaoensis'', which was named in 1982 from the lower Ermaying Formation in Shaanxi. It was assigned to the family Euparkeriidae as a close relative of the genus ''Euparkeria'' from South Africa. ''Halazhaisuchus'' is known from a single holotype specimen called V6027, which was discovered in 1977 and includes a portion of the vertebral column, some ribs, two scapulae and two humeri, the right radius and ulna, and a left coracoid. Two rows of plate-like bones called osteoderms run along the length of the vertebrae. When it was first described in 1982, ''Halazhaisuchus'' was considered a close relative of ''Euparkeria'' because it has primitive features like small intercentra bones between the vertebrae and a large coracoid, not seen in later archosaurs. However, these features are common to many early archosauriforms and are not unique to Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate groups like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Grade
A grade is a taxon united by a level of morphological or physiological complexity. The term was coined by British biologist Julian Huxley, to contrast with clade, a strictly phylogenetic unit. Definition An evolutionary grade is a group of species united by morphological or physiological traits, that has given rise to another group that has major differences from the ancestral condition, and is thus not considered part of the ancestral group, while still having enough similarities that we can group them under the same clade. The ancestral group will not be phylogenetically complete (i.e. will not form a clade), so will represent a paraphyletic taxon. In order to fully understand evolutionary grades, one must first get a better understanding of Phylogenetics, defined as "''In biology, is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among individuals or groups of organisms (e.g. species, or populations). These relationships are discovered through phylogenetic i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were insectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |