|
Eulerian Coherent Structure
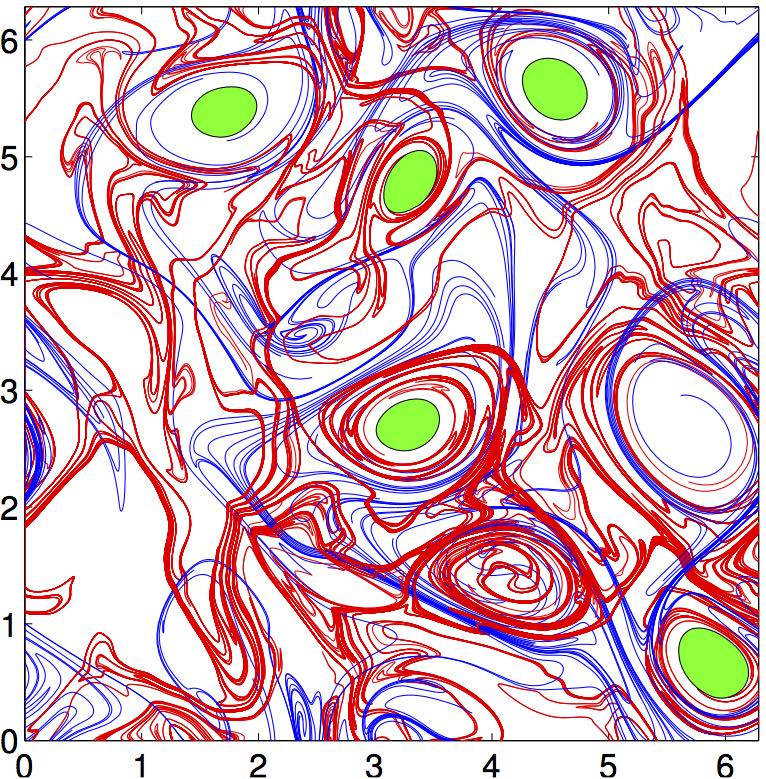
In applied mathematics, objective Eulerian coherent structures (OECSs) are the instantaneously most influential surfaces or curves that exert a major influence on nearby trajectories in a dynamical system over short time-scales, and are the short-time limit of Lagrangian coherent structure Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs) are distinguished surfaces of trajectories in a dynamical system that exert a major influence on nearby trajectories over a time interval of interest. The type of this influence may vary, but it invariably cr ...s (LCSs). Such influence can be of different types, but OECSs invariably create a short-term coherent trajectory pattern for which they serve as a theoretical centerpiece. While LCSs are intrinsically tied to a specific finite time interval, OECSs can be computed at any time instant regardless of the multiple and generally unknown time scales of the system. In observations of tracer patterns in nature, one readily identifies short-term variability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface (mathematics)
In mathematics, a surface is a mathematical model of the common concept of a surface. It is a generalization of a plane, but, unlike a plane, it may be curved; this is analogous to a curve generalizing a straight line. There are several more precise definitions, depending on the context and the mathematical tools that are used for the study. The simplest mathematical surfaces are planes and spheres in the Euclidean 3-space. The exact definition of a surface may depend on the context. Typically, in algebraic geometry, a surface may cross itself (and may have other singularities), while, in topology and differential geometry, it may not. A surface is a topological space of dimension two; this means that a moving point on a surface may move in two directions (it has two degrees of freedom). In other words, around almost every point, there is a ''coordinate patch'' on which a two-dimensional coordinate system is defined. For example, the surface of the Earth resembles (ideally) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (geometry), point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'': "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image (mathematics), image of an interval (mathematics), interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space
In dynamical system theory, a phase space is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state corresponding to one unique point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of position and momentum variables. It is the outer product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs. Introduction In a phase space, every degree of freedom or parameter of the system is represented as an axis of a multidimensional space; a one-dimensional system is called a phase line, while a two-dimensional system is called a phase plane. For every possible state of the system or allowed combination of values of the system's parameters, a point is included in the multidimensional space. The system's evolving state over time traces a path (a phase-space trajectory for the system) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
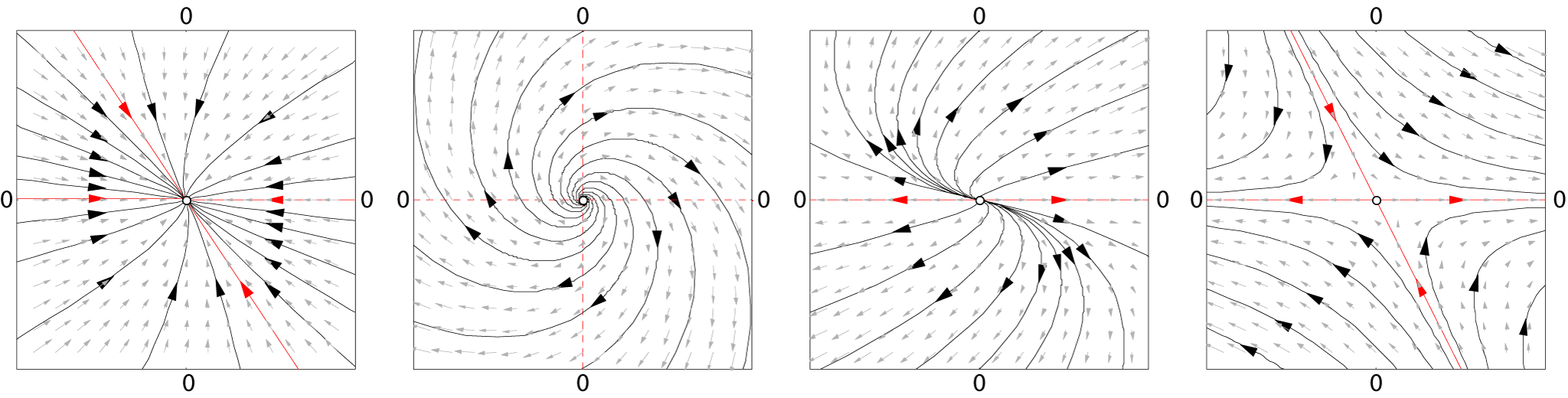
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Coherent Structure
Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs) are distinguished surfaces of trajectories in a dynamical system that exert a major influence on nearby trajectories over a time interval of interest. The type of this influence may vary, but it invariably creates a coherent trajectory pattern for which the underlying LCS serves as a theoretical centerpiece. In observations of tracer patterns in nature, one readily identifies coherent features, but it is often the underlying structure creating these features that is of interest. As illustrated on the right, individual tracer trajectories forming coherent patterns are generally sensitive with respect to changes in their initial conditions and the system parameters. In contrast, the LCSs creating these trajectory patterns turn out to be robust and provide a simplified skeleton of the overall dynamics of the system. The robustness of this skeleton makes LCSs ideal tools for model validation, model comparison and benchmarking. LCSs can also be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometrical manif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |