|
Esimiphaios
Sumyafaʿ (or Sumūyafaʿ) Ashwaʿ (Greek: ''Esimiphaios'', Latin: ''Esimiphaeus'') was the king of Ḥimyar under the Aksumite Empire from 525/531 until 535. There is an inscription commemorating the refortification of Qanīʾ from February 530 or 531 by a Sumūyafaʿ Ashwaʿ and his sons Shuriḥbiʾīl Yakmul and Maʿdīkarib Yaʿfur. He was the son of Laḥayʿat Yarkham, from western Ḥimyar and had been in exile in Aksum, only returning with the Aksumite invasion force. It is not certain that this was the same Sumūyafaʿ Ashwaʿ who was or became king of Ḥimyar. It is not possible to be precise about the date of accession of Sumūyafaʿ Ashwaʿ. A native Ḥimyarite and a Christian, he was appointed by the Aksumite king Caleb, who had defeated and killed the previous king of Ḥimyar, Dhū Nuwās, sometime between Pentecost 525 and February 531. A fragmentary inscription appears to give his full title as "king of Sabaʾ, of dhu-Raydān, of Ḥaḍramawt, and of Yamnat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraha
Abraha ( Ge’ez: አብርሃ) (also spelled Abreha, died after CE 570;Stuart Munro-Hay (2003) "Abraha" in Siegbert Uhlig (ed.) ''Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: A-C''. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. r. 525–at least 553S. C. Munro-Hay (1991) ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity''. Edinburgh: University Press. p. 87. ), also known as Abrahah al-Ashram ( ar, أَبْرَهَة ٱلْأَشْرَم), was an Aksumite army general, then the viceroy of South Arabia for the Kingdom of Aksum, and later declared himself an independent King of Himyar. Abraha ruled much of present-day Arabia and Yemen from at least 531–547 CE to 555–570 CE. Life Dhu Nuwas, the Jewish Himyarite ruler of Yemen, in the period c. 523–525"Abraha." ''Dictionary of African Christian Biographies''. 2007. (last accessed 11 April 2007) or c. 518–20 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in what is now northern Ethiopia, and spanning modern-day Eritrea, northern Djibouti, and eastern Sudan, it extended at its height into much of modern-day southern Arabia during the reign of King Kaleb. Axum served as the kingdom's capital for many centuries but relocated to Jarma in the 9th century due to declining trade connections and recurring external invasions. Emerging from the earlier Dʿmt civilization, the kingdom was likely founded in the early 1st century. Pre-Aksumite culture developed in part due to a South Arabian influence, evident in the use of the Ancient South Arabian script and the practice of Ancient Semitic religion. However, the Geʽez script came into use by the 4th century, and as the kingdom became a major power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaleb Of Axum
Kaleb (), also known as Saint Elesbaan, was King of Aksum, which was situated in modern-day Eritrea and Ethiopia Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er .... Procopius calls him "Hellestheaeus", a variant of grc-koi, Ελεσβόάς version of his regnal name, gez, እለ አጽብሐ, translit=ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa (''Histories'', 1.20). Variants of his name are Hellesthaeus, Ellestheaeus, Eleshaah, Ellesboas, Elesbaan, and Elesboam. At Aksum, in inscription RIE 191, his name is rendered in unvocalized Gə‘əz as KLB ’L ’ṢBḤ WLD TZN (Kaleb ʾElla ʾAṣbeḥa, son of Tazena). In vocalized Gə‘əz, it is (Kaleb ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa). Kaleb, a name derived from the Biblical character Caleb, was his given name; on both his coins and inscriptions he lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhū Nuwās
Dhū Nuwās, ( ar, ذُو نُوَاس), real name "Yūsuf Asʾar Yathʾar" ( Musnad: 𐩺𐩥𐩪𐩰 𐩱𐩪𐩱𐩧 𐩺𐩻𐩱𐩧, ''Yws¹f ʾs¹ʾr Yṯʾr''), "Yosef Nu'as" ( he, יוסף נואס), or "Yūsuf ibn Sharhabīl" ( ar, يُوْسُف ٱبْن شَرْحَبِيْل, link=no), also known as "Masruq" in Syriac, and ''Dounaas'' () in Medieval Greek, was a Jewish king of Himyar between 517 and 525–527 AD, who came to renown on account of his persecutions of peoples of other religions, notably Christians, living in his kingdom. History Ibn Hisham's ''Sirat Rasul Allah'' (better known in English as ''the Life of Muhammad''), describes the exploits of Yūsuf Dhū Nuwās. Ibn Hisham explains that Yūsuf was a convert Jew who grew out his sidelocks (''nuwas''), and who became known as "he of sidelocks." The historicity of Dhū Nuwās is affirmed by Philostorgius and by Procopius (in the latter's ''Persian War''). Procopius writes that in 525, the armies of the Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Language
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rulers Of Yemen
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, line gauge, or scale, is a device used in geometry and technical drawing, as well as the engineering and construction industries, to measure distances or draw straight lines. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Some are wooden. Plastics have also been used since they were invented; they can be molded with length markings instead of being scribed. Metal is used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. in length is useful for a ruler to be kept on a desk to help in drawing. Shorter rulers are convenient for keeping in a pocket. Longer rulers, e.g., , are necessary in some cases. Rigid wooden or plastic yardsticks, 1 yard long, and meter sticks, 1 meter long, are also used. Classically, long measuring rods were used for larger projects, now superseded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Himyar
Kings or King's may refer to: * Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings *One of several works known as the "Book of Kings": **The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts **The '' Shahnameh'', an 11th-century epic Persian poem **The Morgan Bible, a French medieval picture Bible **The Pararaton, a 16th-century Javanese history of southeast Asia *The plural of any king Business *Kings Family Restaurants, a chain of restaurants in Pennsylvania and Ohio *Kings Food Markets, a chain supermarket in northern New Jersey * King's Favourites, a brand of cigarettes * King's Variety Store, a chain of stores in the USA * King's (defunct discount store), a defunct chain of discount stores in the USA Education * King's College (other), various colleges * King's School (other), various schools * The King's Academy (other), various academies Electoral districts *King's (New Brunswick electoral district) ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Arabs
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irfan Shahîd
Irfan Arif Shahîd ( ar, عرفان عارف شهيد ; Nazareth, Mandatory Palestine, January 15, 1926 – Washington, D.C., November 9, 2016), born as Erfan Arif Qa'war (), was a scholar in the field of Oriental studies. He was from 1982 until his death professor emeritus at Georgetown University, where he had been the Oman Professor of Arabic and Islamic Literature. Shahîd was also a Fellow of the Medieval Academy of America since 2012. Biography Erfan Arif was born in Nazareth, Mandatory Palestine to a Palestinian Christian family. He left in 1946 to attend St John's College, Oxford, where he read classics and Greco-Roman history. He studied under renowned antiquities historian A. N. Sherwin-White. He received his Ph.D. from Princeton University in Arabic and Islamic Studies. His doctorate thesis was “Early Islam and Poetry.” Shahîd'Erfan's research was primarily focused on three major areas: the area where the Greco-Roman world, especially the Byzantine Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael The Syrian
Michael the Syrian ( ar, ميخائيل السرياني, Mīkhaʾēl el Sūryani:),( syc, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܣܽܘܪܝܳܝܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Sūryoyo), died 1199 AD, also known as Michael the Great ( syr, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܪܰܒ݁ܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Rabo) or Michael Syrus or Michael the Elder, to distinguish him from his nephew, was a patriarch of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 1166 to 1199. He is best known today as the author of the largest medieval ''Chronicle'', which he wrote in the Syriac language. Some other works and fragments written by him have also survived. Life The life of Michael is recorded by Bar Hebraeus. He was born ca. 1126 in Melitene (today Malatya), the son of the Priest Eliya (Elias), of the Qindasi family. His uncle, the monk Athanasius, became bishop of Anazarbus in Cilicia in 1136. At that period Melitene was part of the kingdom of the Turkoman Danishmend dynasty, and, when that realm was divided in two in 1142, it became the capital of on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophanes Of Byzantium
Theophanes of Byzantium ( el, Θεόφανης ὁ Βυζάντιος; fl. 6th century) was a Byzantine historian. He wrote, in ten books, the history of the Eastern Empire during the Persian war under Justin II, beginning from the second year of Justin (567), in which the truce made by Justinian I with Khosrau I was broken, and going down to last year of the war. The work has not survived, but Patriarch PhotiusPhotius, ''Bibl. Cod.'' 64 gives an account of the work of Theophanes, and he repeats the author's statement that, besides adding other books to the ten which formed the original work, he had written another work on the history of Justinian. Among the historical statements preserved by Photius from Theophanes is the discovery, in the reign of Justinian, of the fact that silk was the product of a worm, which had not been before known to the people of the Roman Empire. A certain Persian, he tells us, coming from the land of the Seres Seres are the people of Serica, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
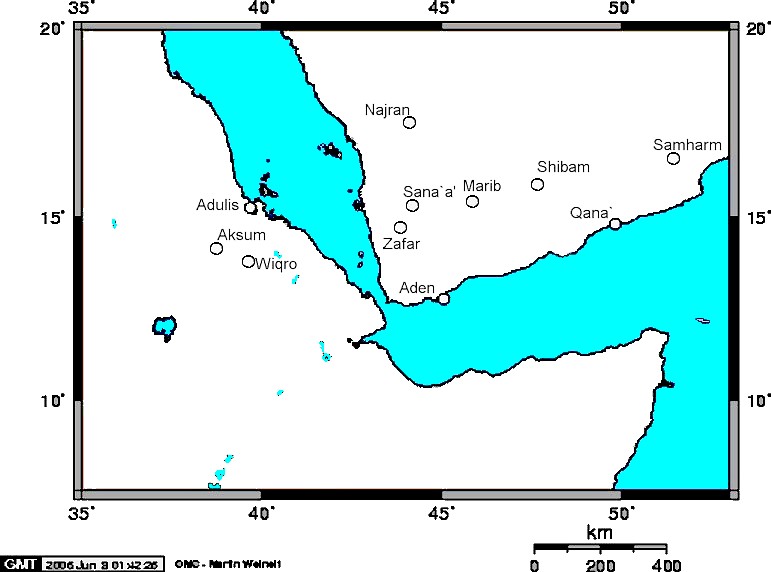
Gregentios
Gregentios ( Greek: Γρηγέντιος) was the purported archbishop of Ẓafār, the capital of the kingdom of Ḥimyar, in the mid-6th century, according to a hagiographical dossier compiled in the 10th century. This compilation is essentially legendary and fictitious, although a few parts of it are of historical value. Written in Greek, it survives also in a Slavonic translation. The three works in the dossier are conventionally known as the ''Bios'' (Life), ''Nomoi'' (Laws) and ''Dialexis'' (Debate). The whole dossier is sometimes known as the ''Acts'' of Gregentios. Name The name Gregentios is unknown apart from the ''Bios'' and related texts. According to the ''Bios'', he received his name from a local holy man. Several later scribes, encountering an unheard of name, changed it to Gregorios (Gregory). This is the name that appears in all the Slavonic versions, as well as an Arabic translation of the ''Dialexis''. It also appears in the fresco depicting Gregentios in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)