|
Erythropoietic Porphyria
Erythropoietic porphyria is a type of porphyria associated with erythropoietic cells. In erythropoietic porphyrias, the enzyme deficiency occurs in the red blood cells. Types There are three types: Presentation X-linked dominant erythropoietic protoporphyria is a relatively mild version of porphyria with the predominant symptom being extreme photosensitivity causing severe itching and burning sensation of the skin due to the buildup of protoporphyrin IX. One possible treatment was discovered when treating an individual with supplemental iron for a gastric ulcer. Levels of free protoporphyrin decreased significantly as there was iron available for the FECH to produce heme. Levels of zinc-protoporphyrin, however did not decrease. Cause X-linked sideroblastic anemia or "X-linked dominant erythropoietic protoporphyria", associated with ALAS2 (aminolevulinic acid synthase), has also been described. X-linked dominant erythropoietic protoporphyria (XDEPP) is caused by a gain of functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, ''porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological functions incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Porphyria
Hepatic porphyrias is a form of porphyria in which toxic porphyrin molecules build up in the liver. Hepatic porphyrias can result from a number of different enzyme deficiencies. Examples include (in order of synthesis pathway): * Acute intermittent porphyria * Porphyria cutanea tarda Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ... and Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria * Hereditary coproporphyria * Variegate porphyria See also * Erythropoietic porphyria * Givosiran References External links * * www.drugs-porphyria.com * www.porphyria-europe.com Porphyrias {{endocrine-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoporphyrin IX
Protoporphyrin IX is an organic compound, classified as a porphyrin, that plays an important role in living organisms as a precursor to other critical compounds like heme (hemoglobin) and chlorophyll. It is a deeply colored solid that is not soluble in water. The name is often abbreviated as PPIX. Protoporphyrin IX contains a porphine core, a tetrapyrrole macrocycle with a marked aromatic character. Protoporphyrin IX is essentially planar, except for the N-H bonds that are bent out of the plane of the rings, in opposite (trans) directions. Nomenclature The general term protoporphyrin refers to porphine derivatives that have the outer hydrogen atoms in the four pyrrole rings replaced by other functional groups. The prefix proto often means 'first' in science nomenclature (such as carbon protoxide), hence Hans Fischer is thought to have coined the name protoporphyrin as the first class of porphyrins. Fischer described iron-deprived heme becoming the "proto-" porphyrin, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of ''Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
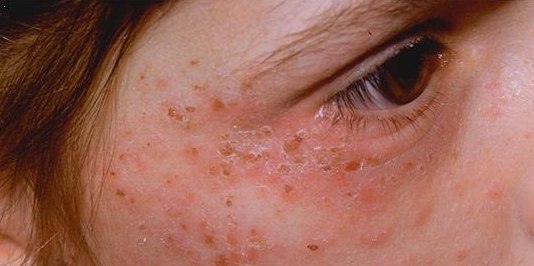
Erythropoietic Protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria (or commonly called EPP) is a form of porphyria, which varies in severity and can be very painful. It arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the red blood cells (erythrocytes), plasma, skin, and liver. The severity varies significantly from individual to individual. A clinically similar form of porphyria, known as X-Linked dominant protoporphyria, was identified in 2008. Presentation EPP usually presents in childhood with the most common mode of presentation as acute photosensitivity of the skin. It affects areas exposed to the sun and tends to be intractable. A few minutes of exposure to the sun induces pruritus, erythema, swelling and pain. Longer periods of exposure may induce second degree burns. After repetitive exposure, patients may present with lichenification, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation and scarring of the skin. EPP usually first presents in childhood, and most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues earlier along the protein sequence. The alpha helix is also called a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. The name 3.613-helix is also used for this type of helix, denoting the average number of residues per helical turn, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond. Among types of local structure in proteins, the α-helix is the most extreme and the most predictable from sequence, as well as the most prevalent. Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were drastic changes in the X-ray fiber diffraction of moist wool or hair fibers upon significant stretching. The data suggested that the unstretched fibers had a coiled molecular structure with a characteristic repeat of ≈. Astb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types The most common secondary structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
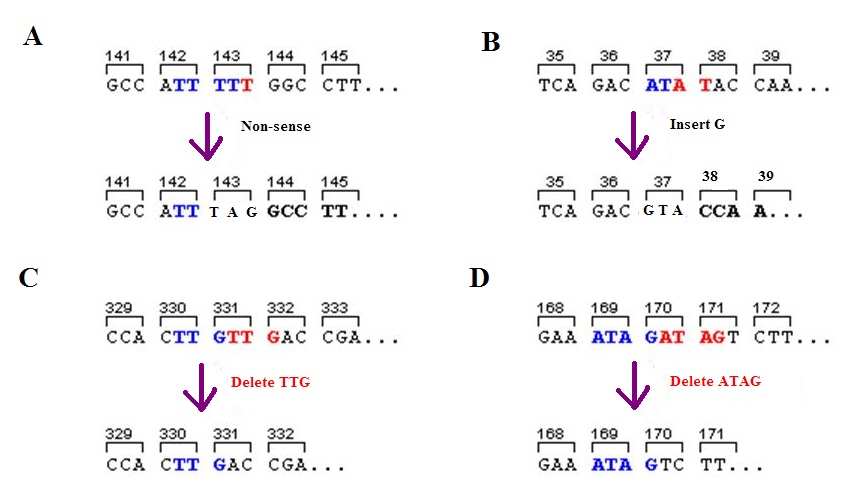
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminolevulinic Acid Synthase
Aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALA synthase, ALAS, or delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase) is an enzyme () that catalyzes the synthesis of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) the first common precursor in the biosynthesis of all tetrapyrroles such as hemes, cobalamins and chlorophylls. The reaction is as follows: :succinyl-CoA + glycine \rightleftharpoons δ-aminolevulinic acid + CoA + CO2 This enzyme is expressed in all non-plant eukaryotes and the α-class of proteobacteria and the reaction it catalyses is sometimes referred to as the Shemin pathway for ALA formation. Other organisms produce ALA through a three enzyme pathway known as the C5 pathway. ALA is synthesized through the condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA. In humans, transcription of ALA synthase is tightly controlled by the presence of Fe2+-binding elements, to prevent accumulation of porphyrin intermediates in the absence of iron. There are two forms of ALA synthase in the body. One form is expressed in red blood cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |