|
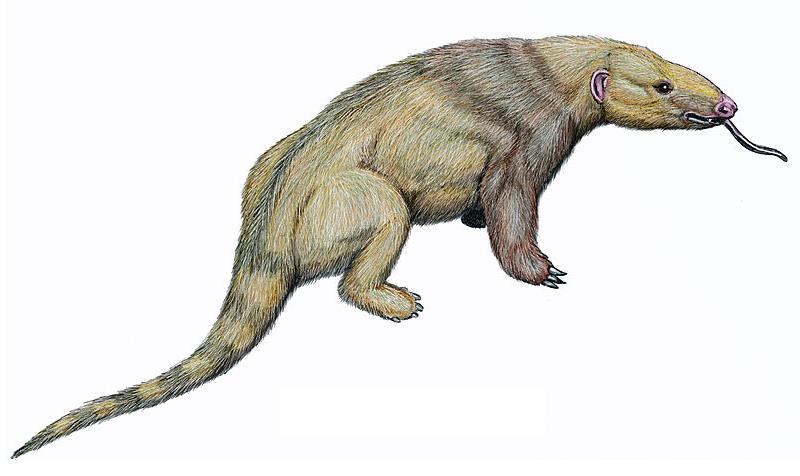
Ernanodon
''Ernanodon antelios'' ("a growing sprouts of toothless animals") is an extinct placental mammal from the middle Paleocene Nongshan Formation of China. It was a relatively small animal about in length, not including the tail. When it was first discovered and examined, it was thought to be a primitive anteater. ''E. antelios'' and ''Eurotamandua'' of Eocene Germany helped to support a now-abandoned hypothesis that there was movement between the faunas of South America (the homeland of anteaters and other Xenarthrans), and the faunas of Europe and Asia, by way of North America. This was further supported by the alleged European Phorusrhacid ''Strigogyps'', also of Eocene Germany. The view of ''E. antelios'' being an anteater has been discarded, and the idea that there was any extensive Paleocene faunal interchange with South America has been rethought due to ''Eurotamandua'' being now regarded as a scaleless relative of the modern-day pangolin, and the various European Phorus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeanodonta
Palaeanodonta ("ancient toothless animals") is an extinct clade of stem- pangolins. They were insectivorous, possibly fossorial, and lived from the Early Paleocene to Early Oligocene in North America, Europe and East Asia. While the taxonomic grouping of Palaeanodonta has been debated,Averianov, A. O. & Lopatin, A. V. (2014."High-level systematics of placental mammals: Current status of the problem."Biology Bulletin, 41(9), 801–816. it is widely thought that they are a sister group to pangolins. Anatomy Skull Palaeanodonts generally have low and caudally-broad skulls, with notable lambdoid crests and inflated bullae and squamosals. Teeth Despite the name of the group and contrary to their pangolin relatives, palaeanodonts are known to have had teeth. Early palaeanodonts retained minimal tribosphenic post-canines while later species had peglike or otherwise reduced molar crowns. Many also had large, characteristic cuspids. Classification and phylogeny Traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidotamorpha
Pholidotamorpha ("pangolin-shaped") is a clade of mammals that includes the orders Palaeanodonta and Pholidota (the pangolins). In the past both orders were formerly classified with various other orders of ant-eating mammals, most notably Xenarthra, which includes the true anteaters, sloths, and the armadillos which pangolins superficially resemble. Newer genetic evidence, however, indicates their closest living relatives are the Carnivora with which they form the clade Ferae. Some palaeontologists, placing family Ernanodontidae in a separate suborder Ernanodonta of Cimolesta near Pholidota, have classified the pangolins in the order Cimolesta, together with several extinct groups indicated (†) below, though this idea has fallen out of favor since it was determined that cimolestids were not placental mammals. A 2012 study from new remains found in Late Paleocene Mongolian strata have led to the assessment that ''Ernanodon'' is closely related to ''Metacheiromys'' within the orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacheiromys
''Metacheiromys'' ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct genus of palaeanodont mammal from the paraphyletic subfamily Metacheiromyinae within paraphyletic family Metacheiromyidae, that lived in North America (what is now Wyoming) during the early to middle Eocene. ''Metacheiromys'' was a small creature, and measured around long. It had long claws and a narrow head similar in shape to that of an armadillo or an anteater (though it was actually related to the modern pangolins). The shape of its claws suggests that it probably dug through the soil in search of food, most likely small invertebrates. Unlike modern anteaters or pangolins, it had powerful canine teeth, but only a very few cheek teeth, instead using horny pads in its mouth to crush its food. The generic name means "next to ''Cheiromys''" because the scientist who saw the bones mistakenly thought that the animal was a primate with hands like those of the aye-aye (''Daubentonia madagascariensis''), one synonym be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoicotheriidae
Epoicotheriidae ("strange beasts") is an extinct family of insectivorous mammals which were endemic to North America from the early Eocene to the early Oligocene 55.8—30.9 Ma existing for approximately . Epoicotheriids were highly specialized animals that were convergent with the golden moles Golden moles are small insectivorous burrowing mammals endemic to Sub-Saharan Africa. They comprise the family Chrysochloridae and as such they are taxonomically distinct from the true moles, family Talpidae, and other mole-like families, a ... of Africa in the structure of their skulls and forelimbs, and would have had a similar lifestyle as subterranean burrowers.Kenneth D. Rose, Robert J. Emry (1983"Extraordinary fossorial adaptations in the oligocene palaeanodonts ''Epoicotherium'' and ''Xenocranium'' (Mammalia)"Journal of Morphology 175(1):33 - 56 Classification and phylogeny Taxonomy Epoicotheriidae was named by Simpson in 1927. It was assigned to the Palaeanodonta by Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escavadodon
''Escavadodon'' ("tooth from Escavada") is an extinct genus of pangolin-like insectivorous mammal which was endemic to North America during the Early Paleocene ( Torrejonian in the NALMA classification), from approximately 63.8 to 60.9 Ma, existing for approximately . It contains a single species, ''Escavadodon zygus''. Taxonomy The monotypic family Escavadodontidae was erected by Rose and Lucas in 2000 to hold the type species, recovered from the Nacimiento Formation of New Mexico ) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke .... Phylogenetic tree The phylogenetic relationships of genus ''Escavadodon'' is shown in the following cladogram: References Palaeanodonta Paleocene mammals of North America Torrejonian Fossils of the United States Paleontology in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin Hardwicke (white Background)
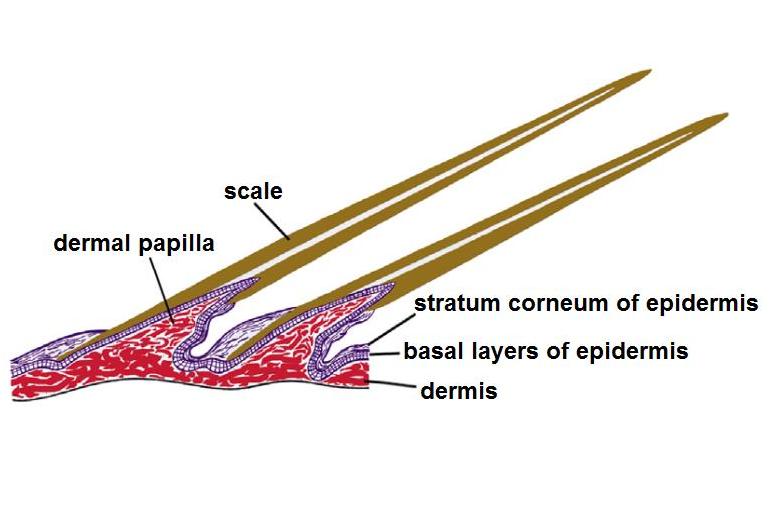
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises the four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . A number of extinct pangolin species are also known. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. They live in hollow trees or burrows, depending on the species. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises the four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . A number of extinct pangolin species are also known. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. They live in hollow trees or burrows, depending on the species. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotamandua
''Eurotamandua'' ("european ''Tamandua''") is an extinct genus of mammal from extinct family Eurotamanduidae that lived some 40-35 million years ago, during the middle Eocene. A single fossil is known, coming from the Messel Pit in southwestern Germany. ''Eurotamandua'' was about long. Most palaeontologists now classify ''Eurotamandua'' as a pangolin. When its fossils were first discovered, ''Eurotamandua'' was originally thought to be an anteater, as it lacked the characteristic fused-hair scales of other pangolins. ''Eurotamandua'' placement within the pangolins was made primarily because of a lack of the characteristic "xenarthran" joints found in all xenarthrans, including tamanduas. There is still much ambiguity in the taxonomy of all mammals prior to the Eocene, so there is the possibility that ''Eurotamandua'' was a primitive xenarthran. However, this is highly unlikely because all known fossil evidence indicates that xenarthrans existed exclusively in South America from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises the four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . A number of extinct pangolin species are also known. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. They live in hollow trees or burrows, depending on the species. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phorusrhacid
Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct clade of large carnivorous flightless birds that were one of the largest species of apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era; their conventionally accepted temporal range covers from 62 to 0.1 million years ( Ma) ago. They ranged in height from . Their closest modern-day relatives are believed to be the seriemas. ''Titanis walleri'', one of the larger species, is known from Texas and Florida in North America. This makes the phorusrhacids the only known large South American predator to migrate north in the Great American Interchange that followed the formation of the Isthmus of Panama land bridge (the main pulse of the interchange began about 2.6 Ma ago; ''Titanis'' at 5 Ma was an early northward migrant). It was once believed that ''T. walleri'' became extinct in North America around the time of the arrival of humans, but subsequent datings of ''Titanis'' fossils provided no evidence for their survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
