|
Erasmus Smith's Professor Of Natural And Experimental Philosophy
Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy at Trinity College Dublin is a chair in physics founded in 1724 and funded by the Erasmus Smith Trust, which was established by Erasmus Smith, a wealthy London merchant, who lived from 1611–1691. It is one of the oldest dedicated chairs of physics in Britain and Ireland. Originally, the holder was to be elected from the members of the college by an examination to determine the person best qualified for the professorship. Since 1851, the professorship has been supported by Trinity College. Of the 22 holders of this chair, seven were Fellows of the Royal Society while one, Ernest Walton, won the Nobel Prize for Physics. The inaugural Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy was Richard Helsham (1724), who was also the Donegal Lecturer in Mathematics (1723-30) as well as the Regius Professor of Physic (1733-38) at Trinity College. He is best known for his book, ''A Course of Lectures in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
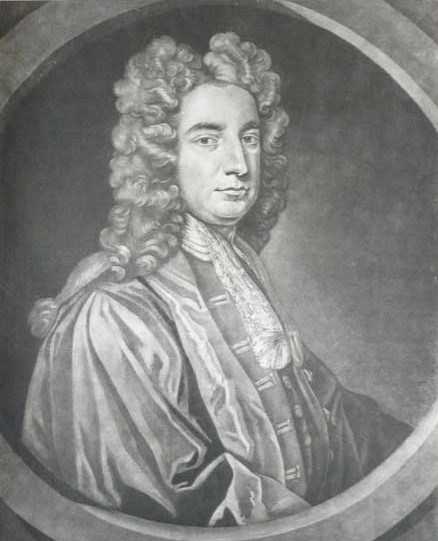
Richard Helsham Beard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Chair Of Natural Philosophy (1847)
The University Chair of Natural Philosophy is a professorship in the School of Mathematics at Trinity College Dublin. It was established in 1847. From 1724 to 1847 the Erasmus Smith's Professorship of Natural and Experimental Philosophy had a mathematical and theoretical orientation, with many holders being also mathematicians. Several, such as Bartholomew Lloyd (1822) and James MacCullagh (1843), previously held the Erasmus Smith's Professor of Mathematics position. In 1847 the University Chair of Natural Philosophy was founded and took on the applied mathematics and theoretical physics role, while Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy (1724) effectively became the chair of experimental physics. List of the professors * 1847–1870: John Jellett (1817–1888) * 1870–1884: Richard Townsend (1821–1884) * 1884–1890: Benjamin Williamson (1827–1916) * 1890–1902: Francis Tarleton (1841–1920) * 1902–1910: Frederick Purser (1839–1910) * 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Coleman (physicist)
Jonathan Coleman is the Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy in the School of Physics and a Principal Investigator in CRANN at Trinity College Dublin. Coleman's research focuses on solution-processing of nanomaterials and their use in applications. He is most well-known for the development of liquid phase exfoliation, a widely used method for preparing two-dimensional nanosheets. Early life and education Coleman attended the King's Hospital School, before studying for a BA in Experimental Physics in Trinity College Dublin. He graduated with First Class Honours and a gold medal in 1995. He completed a Doctor of Philosophy, PhD in Physics in TCD in 1999 under Prof Werner Blau. Research and Career Coleman became a lecturer in Physics at TCD in 2001 and was the Professor of Chemical Physics from 2011 to 2022 before moving to his current chair. He is currently (2022) the Head of the School of Physics in TCD and a member of the University Council. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Coey
John Michael David Coey (born 24 February 1945), known as Michael Coey, is a Belfast-born experimental physicist working in the fields of magnetism and spintronics. He got a BA in Physics at Jesus College, Cambridge (1966), and a PhD from University of Manitoba (1971) for a thesis on "Mössbauer Effect of 57Fe in Magnetic Oxides" with advisor Allan H. Morrish.Lifland (2009) Trinity College Dublin (TCD), where he has been in the physics department since 1978, awarded him ScD (1987) and the University of Grenoble awarded him Dip. d'Habilitation (1986) and an honorary doctorate (1994). He served as Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy at TCD from 2007 to 2012. Career Mike Coey has been a Professor of Physics at TCD since 1987, and was the last appointed Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy (2007–2012), a chair that dates from 1724. He has supervised over 50 PhD students, and authored or edited 5 volumes. Recognised as a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
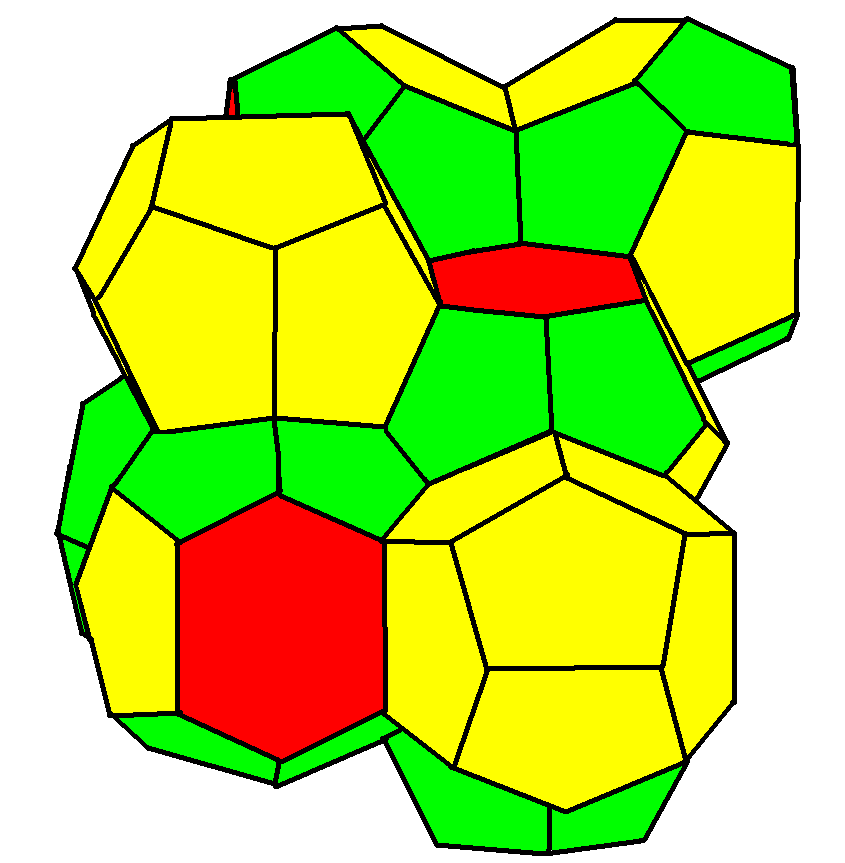
Weaire–Phelan Structure
In geometry, the Weaire–Phelan structure is a three-dimensional structure representing an idealised foam of equal-sized bubbles, with two different shapes. In 1993, Denis Weaire and Robert Phelan found that this structure was a better solution of the Kelvin problem of tiling space by equal volume cells of minimum surface area than the previous best-known solution, the Kelvin structure. History and the Kelvin problem In two dimensions, the subdivision of the plane into cells of equal area with minimum average perimeter is given by the hexagonal tiling, but although the first record of this honeycomb conjecture goes back to the ancient Roman scholar Marcus Terentius Varro, it was not proven until the work of Thomas C. Hales in 1999. In 1887, Lord Kelvin asked the corresponding question for three-dimensional space: how can space be partitioned into cells of equal volume with the least area of surface between them? Or, in short, what was the most efficient soap bubble foam? This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its contemporary form. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883, was its president 1890–1895, and in 1892 was the first British scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords. Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in his honour. While the existence of a coldest possible temperature ( absolute zero) was known prior to his work, Kelvin is known for determining its correct value as approximately −273.15 degrees Celsius or −459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. The Joule–Thomson effect is also named in his honour. He worked closely with mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Weaire
Denis Lawrence Weaire FRS (born 17 October 1942 in Dalhousie, Simla, India) is an Irish physicist and an emeritus professor of Trinity College Dublin (TCD). Educated at the Belfast Royal Academy and Clare College, Cambridge, he held positions at University of California, University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale, ultimately holding professorships at Heriot-Watt, and University College Dublin before becoming, in 1984, Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy at TCD.Erasmus Smith's professors of Mathematics Mathematics at TCD 1592–1992 Together with his graduate student Robert Phelan, Weaire came up with a counter-example to |
Brian Henderson (academic)
Brian Henderson (26 March 1936 – 20 August 2017) was an English solid-state spectroscopic physicist whose career included spells at Atomic Energy Research Establishment (AERE), Keele University, Trinity College Dublin (TCD), and the University of Strathclyde. Life and career Brian Henderson was born near Doncaster, and was educated at Maltby Grammar School, then in the West Riding of Yorkshire. He attended the University of Birmingham, obtaining his BSc (in physical metallurgy) in 1958 and PhD in 1960 with a thesis on "The Lattice Spacings of Alloys with Reference to Electronic Constitution". The Royal Society of Edinburgh He became senior scientific officer at the Basic Ceramics Group at AERE (Harwell) in 1962, and joined the staff at Keele University in 1968, being promoted to Reader in Physics t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cockcroft
Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, (27 May 1897 – 18 September 1967) was a British physicist who shared with Ernest Walton the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1951 for splitting the atomic nucleus, and was instrumental in the development of nuclear power. After service on the Western Front with the Royal Field Artillery during the Great War, Cockcroft studied electrical engineering at Manchester Municipal College of Technology whilst he was an apprentice at Metropolitan Vickers Trafford Park and was also a member of their research staff. He then won a scholarship to St. John's College, Cambridge, where he sat the tripos exam in June 1924, becoming a wrangler. Ernest Rutherford accepted Cockcroft as a research student at the Cavendish Laboratory, and Cockcroft completed his doctorate under Rutherford's supervision in 1928. With Ernest Walton and Mark Oliphant he built what became known as a Cockcroft–Walton generator. Cockcroft and Walton used this to perform the first artifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates: # The laws of physics are invariant (that is, identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no acceleration). # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source or the observer. Origins and significance Special relativity was originally proposed by Albert Einstein in a paper published on 26 September 1905 titled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".Albert Einstein (1905)''Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper'', ''Annalen der Physik'' 17: 891; English translatioOn the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodiesby George Barker Jeffery and Wilfrid Perrett (1923); Another English translation On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies by Megh Nad Saha (1920). The incompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula , which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius". In 1905, a year sometimes described as his ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)