|
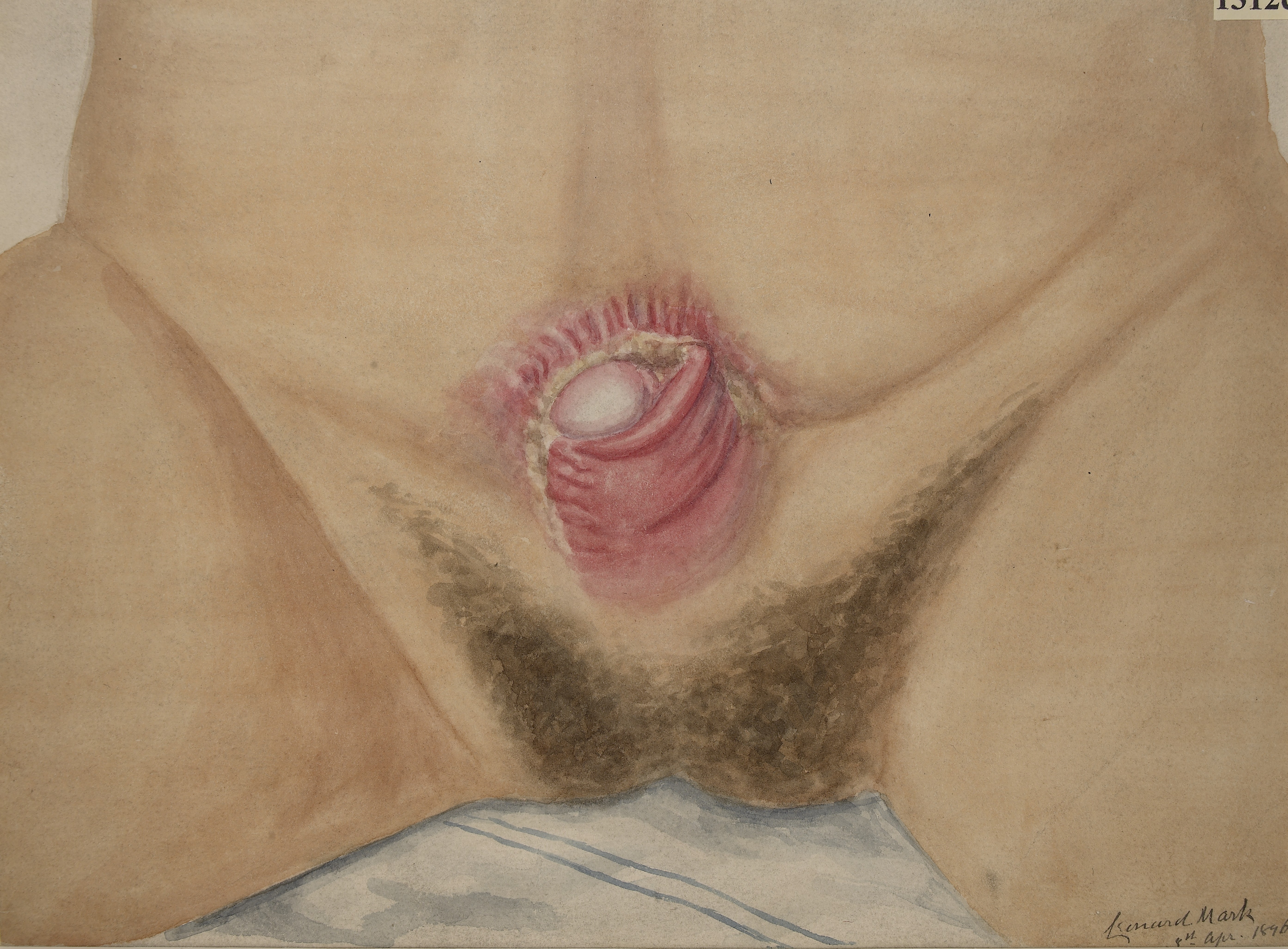
Epispadias
An epispadias is a rare type of malformation in which the urethra ends, in males, in an opening on the upper aspect of the penis, and in females when the urethra develops too far anteriorly. It occurs in around 1 in 120,000 male and 1 in 500,000 female births. Signs and symptoms Most cases involve a small and bifid penis, which requires surgical closure soon after birth, often including a reconstruction of the urethra. Where it is part of a larger exstrophy, not only the urethra but also the bladder (bladder exstrophy) or the entire perineum (cloacal exstrophy) are open and exposed on birth, requiring closure. Many parts of this article are incorrect. Relationship to other conditions Despite the similarity of name, an epispadias is not a type of hypospadias, and involves a problem with a different set of embryologic processes. Women can also have this type of congenital malformation. Epispadias of the female may occur when the urethra develops too far anteriorly, exiting in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Malformation
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifid Penis
A bifid penis (or double penis) is a rare congenital defect where two genital tubercles develop. Many species of male Marsupial#Reproductive system, marsupials have a naturally bifurcated penis, with left and right prongs that they insert into multiple vaginal canals simultaneously. See also * Diphallia * Meatotomy * Penile subincision References Congenital disorders of male genital organs Penis disorders Marsupial anatomy Intersex variations {{Genetic-disorder-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Exstrophy
Bladder exstrophy is a congenital anomaly that exists along the spectrum of the exstrophy-epispadias complex, and most notably involves protrusion of the urinary bladder through a defect in the abdominal wall. Its presentation is variable, often including abnormalities of the Human pelvis, bony pelvis, pelvic floor, and genitalia. The underlying embryologic mechanism leading to bladder exstrophy is unknown, though it is thought to be in part due to failed reinforcement of the cloacal membrane by underlying mesoderm. Exstrophy means the inversion of a hollow organ. Signs and symptoms The classic manifestation of bladder exstrophy presents with: * A defect in the abdominal wall occupied by both the exstrophied bladder as well as a portion of the urethra * A flattened puborectal sling * Separation of the pubic symphysis * Shortening of a pubic ramus (other), pubic rami * External rotation of the pelvis. Females frequently have a displaced and narrowed vagina, vaginal orifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloacal Exstrophy
Cloacal exstrophy (EC) is a severe birth defect wherein much of the abdominal organs (the bladder and intestines) are exposed. It often causes the splitting of the bladder, genitalia, and the anus. It is sometimes called OEIS complex. Diagnostic tests can include ultrasound, voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG), intravenous pyelogram (IVP), nuclear renogram, computerized axial tomography ( CT scan), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Cloacal exstrophy is a rare birth defect, present in 1/200,000 pregnancies and 1/400,000 live births. It is associated with a defect of the ventral body wall and can be caused by inhibited mesodermal migration. The defect can often be comorbid with spinal bifida and kidney abnormalities. See also * Bladder exstrophy Bladder exstrophy is a congenital anomaly that exists along the spectrum of the exstrophy-epispadias complex, and most notably involves protrusion of the urinary bladder through a defect in the abdominal wall. Its presentation is varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting about one of every 250 males at birth. Roughly 90% of cases are the less serious distal hypospadias, in which the urethral opening (the meatus) is on or near the head of the penis (glans). The remainder have proximal hypospadias, in which the meatus is all the way back on the shaft of the penis, near or within the scrotum. Shiny tissue that should have made the urethra extends from the meatus to the tip of the glans; this tissue is called the urethral plate. In most cases, the foreskin is less developed and does not wrap completely around the penis, leaving the underside of the glans uncovered. Also, a downward bending of the penis, commonly referred to as chordee, may occur. Chordee is found in 10% of distal hypospadias and 50% of proximal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitrofanoff
The Mitrofanoff procedure, also known as the Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy, is a surgical procedure in which the appendix is used to create a conduit, or channel, between the skin surface and the urinary bladder. The small opening on the skin surface, or the stoma, is typically located either in the navel or nearby the navel on the right lower side of the abdomen. Originally developed by Professor Paul Mitrofanoff in 1980, the procedure represents an alternative to urethral catheterization and is sometimes used by people with urethral damage or by those with severe autonomic dysreflexia. An intermittent catheter, or a catheter that is inserted and then removed after use, is typically passed through the channel every 3–4 hours and the urine is drained into a toilet or a bottle. As the bladder fills, rising pressure compresses the channel against the bladder wall, creating a one-way valve that prevents leakage of urine between catheterizations. Description of procedure A surgeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders Of Urinary System
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders Of Male Genital Organs
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |