|
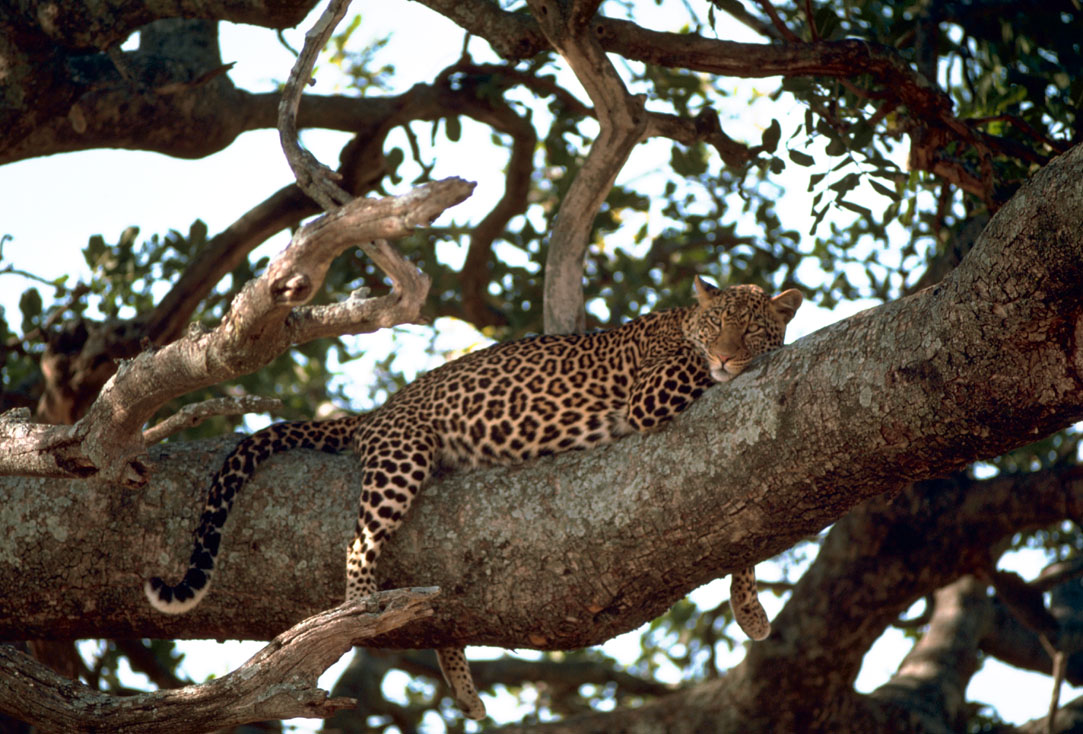
Eoscansor
''Eoscansor'' (EE-oh-SKAN-sor; meaning "dawn climber") is a species of small varanopid amniote that lives from the upper Pennsylvanian subperiod in northern New Mexico, United States 305 million years ago. The species ''Eoscansor cobrensis'' was 24.5 centimeters (9.6 inches) long and weighed 58.3 grams. The tetrapods teeth indicated that it was insectivorous. The small size and grasping limbs means that was ''E. cobrensis'' highly agile and likely arboreal (tree climbing). The name ''Eoscansor'' means "dawn climber", derived from Greek with "Eo" meaning dawn and "scansor" meaning climber. ''E. cobrensis'' is currently the oldest specialised climbing tetrapod animal pushing back the original record by 15 million years. The species was discovered in the El Cobre Canyon Formation in northern New Mexico near the village of Chama in 2005 but was not prepared until 2015. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 pushed study back until 2022 where it was described as a new genus and species. ''Eosc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopidae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arboreal Locomotion
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving through them and lead to a variety of anatomical, behavioral and ecological consequences as well as variations throughout different species.Cartmill, M. (1985). Climbing. In ''Functional Vertebrate Morphology'', eds. M. Hildebrand D. M. Bramble K. F. Liem and D. B. Wake, pp. 73–88. Cambridge: Belknap Press. Furthermore, many of these same principles may be applied to climbing without trees, such as on rock piles or mountains. Some animals are exclusively arboreal in habitat, such as the tree snail. Biomechanics Arboreal habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving in them, which have been solved in diverse ways. These challenges include moving on narrow branches, mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Cobre Canyon Formation
The El Cobre Canyon Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the late Pennsylvanian to early Permian periods. Description The El Cobre Canyon Formation consists of siliciclastic red beds with a total thickness of roughly . These lie on Proterozoic basement and are in turn overlain by the Arroyo del Agua Formation. At its type section, the formation is 66% siltstone and 21% sandstone, with minor conglomerate (9%) sandy shale (2%), and calcrete (1%). The beds are pale reddish brown in color, and can readily be distinguished from the orange beds of the overlying Arroyo del Agua Formation. The siltstone beds contain many rhizoliths, while the sandstone beds are coarse grained, arkosic, and micaceous, with trough crossbedding. The sandstones form thick cliffs and benches. The conglomerates are composed mostly of fragments of basement rock. The formation correlates with the Atrasado Formation and lower Abo Formation to the south. Fossils Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
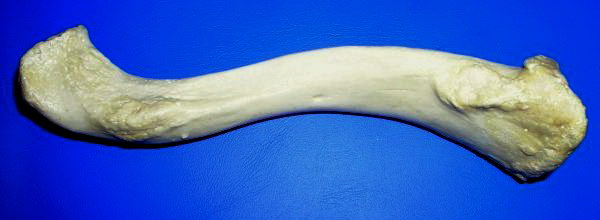
Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interclavicle
An interclavicle is a bone which, in most tetrapods, is located between the clavicles. Therian mammals ( marsupials and placentals) are the only tetrapods which never have an interclavicle, although some members of other groups also lack one. In therians, it is replaced by the sternum which is similar in shape and function but forms via endochondral ossification (cartilage forming bone). The interclavicle, on the other hand, develops through intramembranous ossification of the skin. Monotreme Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...s, although part of the mammalian class, do have interclavicles. References Bones of the upper limb Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastralia
Gastralia (singular gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptiles, gastralia provide support for the abdomen and attachment sites for abdominal muscles. The possession of gastralia may be ancestral for Tetrapoda and were possibly derived from the ventral scales found in animals like rhipidistians, labyrinthodonts, and ''Acanthostega'', and may be related to ventral elements of turtle plastrons. Similar, but not homologous cartilagenous elements, are found in the ventral body walls of lizards and anurans. These structures have been referred to as inscriptional ribs, based on their alleged association with the inscriptiones tendinae (the tendons that form the six pack in humans). However, the terminology for these gastral-like structures remains confused. Both types, along with sternal ribs ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Carboniferous
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manus (anatomy)
The manus (Latin for ''hand'', plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions. It can be represented by the hand of primates, the lower front limb of hoofed animals or the fore paw and is represented in the wing of birds, bats and prehistoric flying reptiles (pterosaurs), the flipper of marine mammals and the 'paddle' of extinct marine reptiles, such as plesiosaurs and ichthyosaurs. In cephalopods, the ''manus'' is the end, broader part of a tentacle, and its suckers are often larger and arranged differently from those on the other arms. See also *Pes (anatomy) The pes (Latin for ''foot'') is the zoological term for the distal portion of the hind limb of tetrapod animals. It is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metatarsals and digits (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |