|
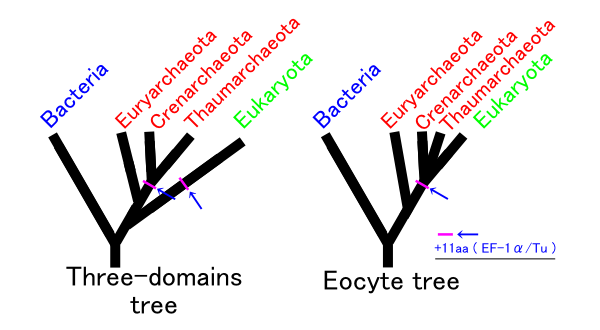
Eocyte Hypothesis
The eocyte hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposes the origin of eukaryotes from a group of prokaryotes called eocytes (later classified as Thermoproteota, a group of archaea). After his team at the University of California, Los Angeles discovered eocytes in 1984, James A. Lake formulated the hypothesis as "eocyte tree" that proposed eukaryotes as part of archaea. Lake hypothesised the Tree of life (biology), tree of life as having only two primary branches: Parkaryoates that include Bacteria and Archaea, and karyotes that comprise Eukaryotes and eocytes. Parts of this early hypothesis were revived in a newer two-domain system of biological classification which named the primary domains as Archaea and Bacteria. Lake's hypothesis was based on an analysis of the structural components of ribosomes. It was largely ignored, being overshadowed by the three-domain system which relied on more precise genetic analysis. In 1990, Carl Woese and his colleagues proposed that cellular life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoarchaeum Equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of this microbe were also found on the Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, and in the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park. Since it grows in temperatures approaching boiling, at about 80 degrees Celsius, it is considered to be a thermophile. It grows best in environments with a pH of 6, and a salinity concentration of 2%. ''Nanoarchaeum'' appears to be an obligate symbiont on the archaeon ''Ignicoccus''; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive. ''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' cannot synthesize lipids but obtains them from its host. Its cells are only 400 nm in diameter, making it the smallest known living organism, and the smallest known archaeon. ''N. equitans'' genome consists of a single circular chromosome, and has an average G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Of Life (biology)
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, model and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Tree diagrams originated in the medieval era to represent genealogical relationships. Phylogenetic tree diagrams in the evolutionary sense date back to the mid-nineteenth century. The term phylogeny for the evolutionary relationships of species through time was coined by Ernst Haeckel, who went further than Darwin in proposing phylogenic histories of life. In contemporary usage, ''tree of life'' refers to the compilation of comprehensive phylogenetic databases rooted at the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth. Two public databases for the tree of life are ''TimeTree'', for phylogeny and divergence times, and the ''Open Tree of Life'', for phylogeny. Early natural classifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogens
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (spherical shaped) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacteria
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Kingdom
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla. Traditionally, some textbooks from the United States and Canada used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria/Eubacteria) while textbooks in Great Britain, India, Greece, Brazil and other countries use five kingdoms only (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, ''funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms When Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature into biology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Henderson
Eric Charles Henderson (born January 8, 1983) is an American football coach who is the defensive line coach and run game coordinator for the Los Angeles Rams of the National Football League (NFL). He previously served as an assistant coach for the Los Angeles Chargers. Henderson played college football at Georgia Tech as a defensive end and was signed by the Cincinnati Bengals as an undrafted free agent in 2006 and played professionally for six seasons. Playing career College While playing for the Georgia Tech Yellow Jackets, Henderson set a team career record with 59.5 tackles-for-loss (TFL), and he ranks fourth in school history in sacks (25). He had a breakout sophomore season in 2003, starting all 13 games and earning first-team All-Atlantic Coast Conference honors with 11 sacks and 24 TFL. He earned second-team All-ACC nods as both a junior and a senior. As a senior, he led the team with six sacks, despite missing four games with an ankle injury, and caused four fumbles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequences commonly forms stem-loop configurations. The length and position of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese (; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique that has revolutionized microbiology. He also originated the RNA world hypothesis in 1967, although not by that name. Woese held the Stanley O. Ikenberry Chair and was professor of microbiology at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. Life and education Carl Woese was born in Syracuse, New York on July 15, 1928. Woese attended Deerfield Academy in Massachusetts. He received a bachelor's degree in mathematics and physics from Amherst College in 1950. During his time at Amherst, Woese took only one biology course (Biochemistry, in his senior year) and had "no scientific interest in plants and animals" until advised by William M. Fairbank, then an assistant professor of physics at Amherst, to pursue biophysics at Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-domain System
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis in 1990 that divides cellular life forms into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota or Eukarya. The key difference from earlier classifications such as the two-empire system and the five-kingdom classification is the splitting of archaea from bacteria as completely different organism. It has been challenged by the two-domain system that divides organisms into Bacteria and Archaea only, as eukaryotes are considered as one group of archaea. Background Woese argued, on the basis of differences in 16S rRNA genes, that bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes each arose separately from an ancestor with poorly developed genetic machinery, often called a progenote. To reflect these primary lines of descent, he treated each as a domain, divided into several different kingdom (biology), kingdoms. Originally his split of the prokaryotes was into ''Eubacteria'' (now ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |