|
Entomopoxvirinae
''Entomopoxvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae''. Insects, human, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 31 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera with one species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: impairment of motility and development. Structure The virions are generally enveloped though the intracellular mature virion form of the virus, which contains a different envelope, is also infectious. They vary in their shape depending upon the species but are generally shaped like a brick or as an oval form similar to a rounded brick because they are wrapped by the endoplasmic reticulum. The genome is exceptionally large, around 250-380kb in length and the virion diameter is around 350 nm. It carries its genome in a single, linear, double-stranded segment of DNA. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomopoxvirinae
''Entomopoxvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae''. Insects, human, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 31 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera with one species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: impairment of motility and development. Structure The virions are generally enveloped though the intracellular mature virion form of the virus, which contains a different envelope, is also infectious. They vary in their shape depending upon the species but are generally shaped like a brick or as an oval form similar to a rounded brick because they are wrapped by the endoplasmic reticulum. The genome is exceptionally large, around 250-380kb in length and the virion diameter is around 350 nm. It carries its genome in a single, linear, double-stranded segment of DNA. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poxviridae
''Poxviridae'' is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses. Vertebrates and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 83 species in this family, divided among 22 genera, which are divided into two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include smallpox. Four genera of poxviruses may infect humans: ''Orthopoxvirus'', ''Parapoxvirus'', ''Yatapoxvirus'', ''Molluscipoxvirus''. ''Orthopoxvirus'': smallpox virus (variola), vaccinia virus, cowpox virus, monkeypox virus; ''Parapoxvirus'': orf virus, pseudocowpox, bovine papular stomatitis virus; ''Yatapoxvirus'': tanapox virus, yaba monkey tumor virus; ''Molluscipoxvirus'': molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). The most common are vaccinia (seen on the Indian subcontinent) and molluscum contagiosum, but monkeypox infections are rising (seen in west and central African rainforest countries). The similarly named disease chickenpox is not a true poxvirus and is caused by the herpesvirus varicella zoster. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
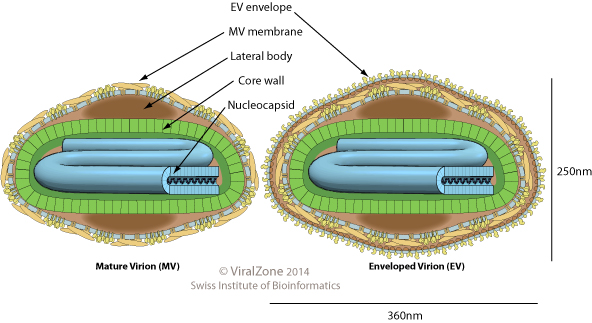
Intracellular Mature Virion
''Poxviridae'' is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses. Vertebrates and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 83 species in this family, divided among 22 genera, which are divided into two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include smallpox. Four genera of poxviruses may infect humans: ''Orthopoxvirus'', ''Parapoxvirus'', ''Yatapoxvirus'', ''Molluscipoxvirus''. ''Orthopoxvirus'': smallpox virus (variola), vaccinia virus, cowpox virus, monkeypox virus; ''Parapoxvirus'': orf virus, pseudocowpox, bovine papular stomatitis virus; ''Yatapoxvirus'': tanapox virus, yaba monkey tumor virus; ''Molluscipoxvirus'': molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). The most common are vaccinia (seen on the Indian subcontinent) and molluscum contagiosum, but monkeypox infections are rising (seen in west and central African rainforest countries). The similarly named disease chickenpox is not a true poxvirus and is caused by the herpesvirus varicella zoster. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betaentomopoxvirus
''Betaentomopoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae'', in the subfamily ''Entomopoxvirinae ''Entomopoxvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae''. Insects, human, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 31 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera with one species unassign ...''. Lepidoptera and orthoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are 16 species in this genus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * '' Acrobasis zelleri entomopoxvirus'' * '' Adoxophyes honmai entomopoxvirus'' * '' Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus'' * '' Arphia conspersa entomopoxvirus'' * '' Choristoneura biennis entomopoxvirus'' * '' Choristoneura conflicta entomopoxvirus'' * '' Choristoneura diversuma entomopoxvirus'' * '' Choristoneura fumiferana entomopoxvirus'' * '' Choristoneura rosaceana entomopoxvirus'' * '' Chorizagrotis auxiliaris entomopoxvirus'' * '' Heliothis armigera entomopoxvirus'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaentomopoxvirus
''Alphaentomopoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae'', in the subfamily ''Entomopoxvirinae ''Entomopoxvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae''. Insects, human, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 31 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera with one species unassign ...''. Coleoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are seven species in this genus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * '' Anomala cuprea entomopoxvirus'' * '' Aphodius tasmaniae entomopoxvirus'' * '' Demodema bonariensis entomopoxvirus'' * '' Dermolepida albohirtum entomopoxvirus'' * '' Figulus sublaevis entomopoxvirus'' * '' Geotrupes sylvaticus entomopoxvirus'' * '' Melolontha melolontha entomopoxvirus'' Structure Viruses in ''Alphaentomopoxvirus'' are enveloped, with ovoid geometries. The diameter is around 250 nm. Genomes are linear, around 260-370kb in length. Life cycle Viral replicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gammaentomopoxvirus
''Gammaentomopoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae'', in the subfamily ''Entomopoxvirinae ''Entomopoxvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses, in the family ''Poxviridae''. Insects, human, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 31 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera with one species unassign ...''. Lepidoptera and orthoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * '' Aedes aegypti entomopoxvirus'' * '' Camptochironomus tentans entomopoxvirus'' * '' Chironomus attenuatus entomopoxvirus'' * '' Chironomus luridus entomopoxvirus'' * '' Chironomus plumosus entomopoxvirus'' * '' Goeldichironomus holoprasinus entomopoxvirus'' Structure Viruses in ''Gammaentomopoxvirus'' are enveloped, with ovoid geometries. The diameter is around 230 nm. Genomes are linear, around 250-380kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the Order (biology), order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily (zoology), superfamily Papilionoidea, which contains at least one former group, the skippers (formerly the superfamily "Hesperioidea"), and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies (formerly the superfamily "Hedyloidea"). Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, as like most insects they undergo Holometabolism, complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_male_in_flight.jpg)
