|
Entinostat
Entinostat, also known as SNDX-275 and MS-275, is a benzamide histone deacetylase inhibitor undergoing clinical trials for treatment of various cancers. Entinostat inhibits class I HDAC1 and HDAC3 Histone deacetylase 3 is an enzyme encoded by the ''HDAC3'' gene in both humans and mice. Function Histones are highly alkaline proteins that package and order DNA into structural units called nucleosomes, which comprise the major protein comp ... with IC50 of 0.51 μM and 1.7 μM, respectively. Syndax pharmaceuticals currently holds the rights to Entinostat and recently received $26.6 million in funds to advance treatments of resistant cancers using epigenetic tools.http://www.syndax.com/assets/130827%20Syndax%20Series%20B%20news%20release.pdf References Benzamides Carbamates Histone deacetylase inhibitors 3-Pyridyl compounds Orphan drugs {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamide
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, .... In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAC inhibitors, HDACi, HDIs) are chemical compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases. HDIs have a long history of use in psychiatry and neurology as mood stabilizers and anti-epileptics. More recently they are being investigated as possible treatments for cancers, parasitic and inflammatory diseases. Cellular biochemistry/pharmacology To carry out gene expression, a cell must control the coiling and uncoiling of DNA around histones. This is accomplished with the assistance of histone acetyl transferases (HAT), which acetylate the lysine residues in core histones leading to a less compact and more transcriptionally active euchromatin, and, on the converse, the actions of histone deacetylases (HDAC), which remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin. Reversible modification of the terminal tails of core histones constitutes the major epigenetic mechanism for re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamides
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, wh .... In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDAC1
Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HDAC1'' gene. Function Histone acetylation and deacetylation, catalyzed by multisubunit complexes, play a key role in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family and is a component of the histone deacetylase complex. It also interacts with retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor protein and this complex is a key element in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Together with metastasis-associated protein-2 MTA2, it deacetylates p53 and modulates its effect on cell growth and apoptosis. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of HDAC1 function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Hdac1tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease to inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDAC3
Histone deacetylase 3 is an enzyme encoded by the ''HDAC3'' gene in both humans and mice. Function Histones are highly alkaline proteins that package and order DNA into structural units called nucleosomes, which comprise the major protein component of chromatin. The posttranslational and enzymatically mediated lysine acetylation and deacetylation of histone tails changes the local chromatin structure through altering the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged DNA backbone and histones. HDAC3 is a Class I member of the histone deacetylase superfamily (comprising four classes based on function and DNA sequence homology) that is recruited to enhancers to modulate both the epigenome and nearby gene expression. HDAC3 is found exclusively in the cell nucleus where it is the sole endogenous histone deacetylase biochemically purified in the nuclear-receptor corepressor complex containing NCOR and SMRT (NCOR2). Thus, HDAC3 unlike other HDACs, has a unique role in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC50
The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. drug) is needed to inhibit, ''in vitro'', a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microorganism. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration. IC50 is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency in pharmacological research. IC50 is comparable to other measures of potency, such as EC50 for excitatory drugs. EC50 represents the dose or plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect ''in vivo''. IC50 can be determined with functional assays or with competition binding assays. Sometimes, IC50 values are converted to the pIC50 scale. :\ce = -\log_ \ce Due to the minus sign, higher values of pIC50 indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
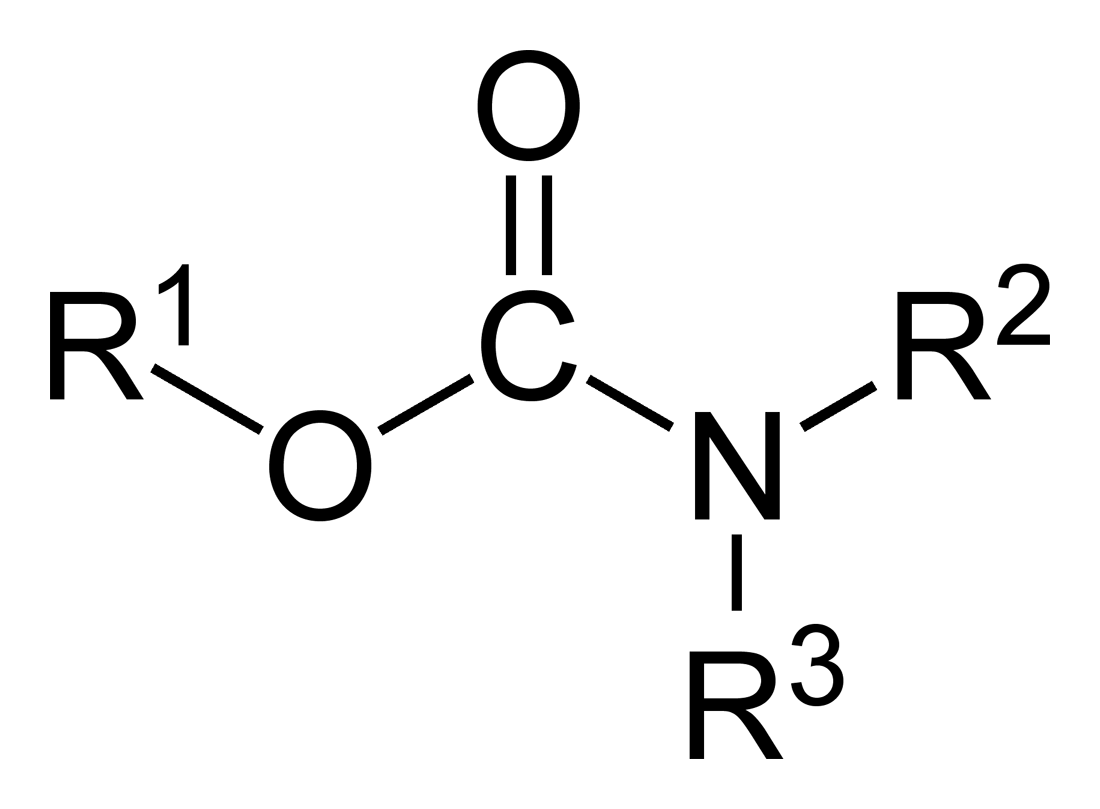
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediately, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30- nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wrapping of DNA around hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |