|
Enteric Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver, ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,600 serotypes. ''Salmonella'' was named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon. ''Salmonella'' species are non-spore-forming, predominantly motile enterobacteria with cell diameters between about 0.7 and 1.5 μm, lengths from 2 to 5 μm, and peritrichous flagella (all around the cell body, allowing them to move). They are chemotrophs, obtaining their energy from oxidation and reduction reactions, using organic sources. They are also facultative anaerobes, capable of generating ATP with oxygen ("aerobically") when it is available, or using other electron acceptors or fermentation ("anaerobically") when oxygen is not available. ''Salmonella'' spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-generation Cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964. Discovery The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945. Structure Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true. Medical uses Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly against Gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroquinolones
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-Quinolone, 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production. Nearly all quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which contain a fluorine atom in their chemical structure and are effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. One example is ciprofloxacin, one of the most widely used antibiotics worldwide. Medical uses Fluoroquinolones are often used for genitourinary infections and are widely used in the treatment of hospital-acquired infections associated with urinary catheters. In community-acquired infections, they are recommended only when risk factors for multidrug resistance are present or after other antibiotic regimens have failed. However, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
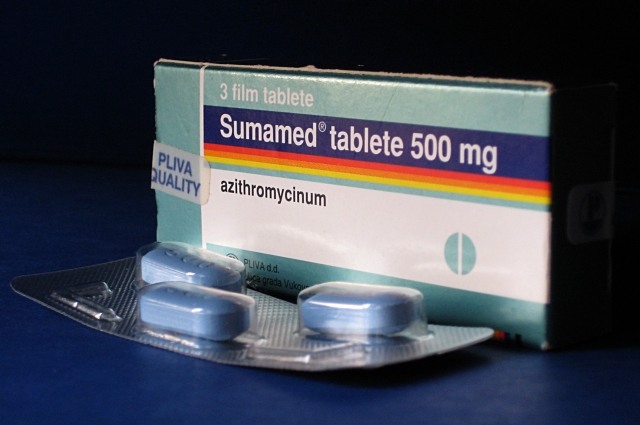
Azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler's diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections. Along with other medications, it may also be used for malaria. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and upset stomach. An allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, QT prolongation, or a type of diarrhea caused by ''Clostridium difficile'' is possible. No harm has been found with its use during pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is not confirmed, but it is likely safe. Azithromycin is an azalide, a type of macrolide antibiotic. It works by decreasing the production of protein, thereby stopping bacterial growth. Azithromycin was discovered in 1980 by the Yugoslav pharmaceutical company Pliva and approved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
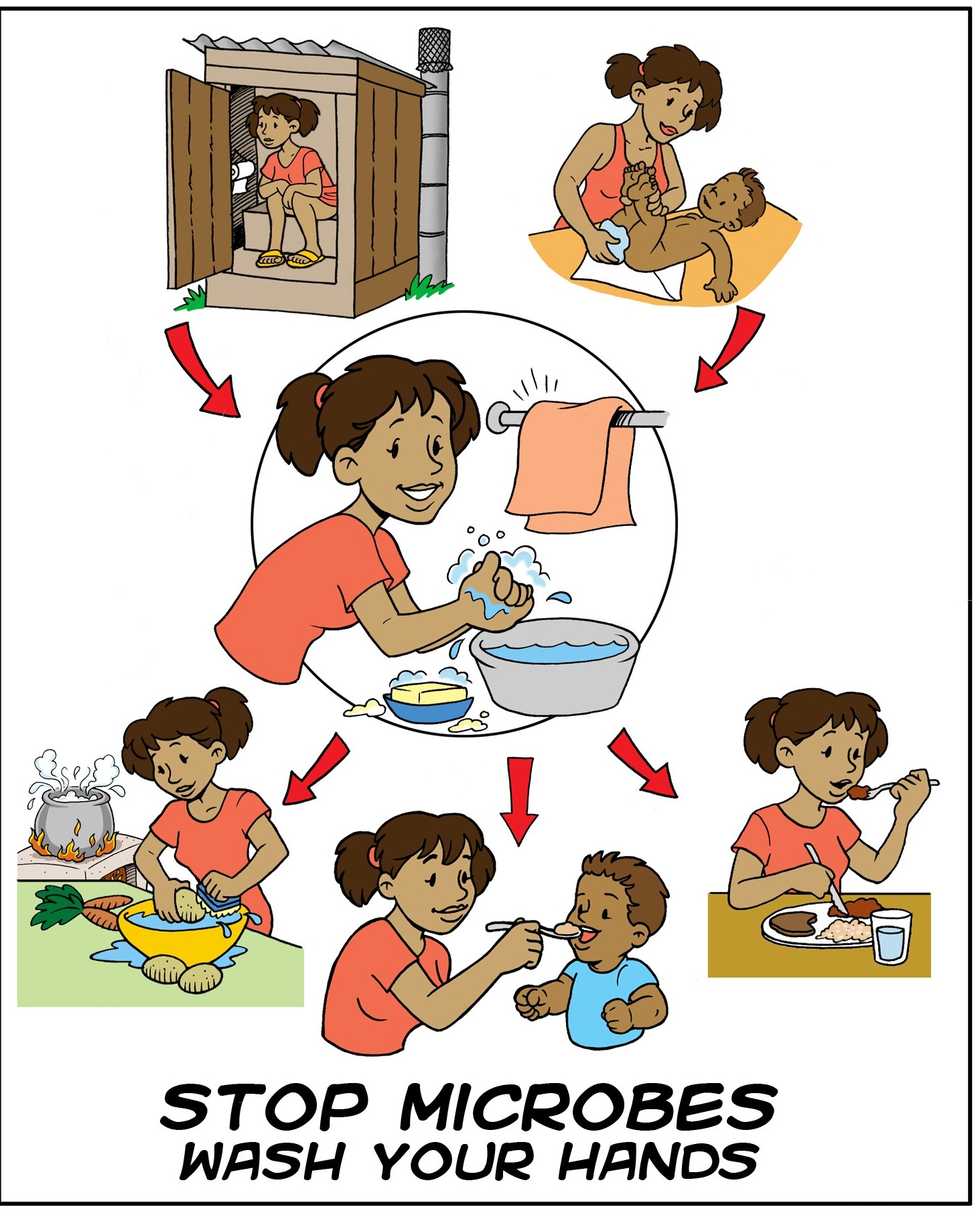
Handwashing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated. If soap and water are unavailable, hand sanitizer that is at least 60% ( v/v) alcohol in water can be used as long as hands are not visibly excessively dirty or greasy. Hand hygiene is central to preventing the spread of infectious diseases in home and everyday life settings. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds before and after certain activities. These include the five critical times during the day where washing hands with soap is important to reduce fecal-oral transmission of disease: after using the toilet (for urination, defecation, menstrual hygiene), after cleaning a child's bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, age, health-related issues, and environmental conditions. This 2004 article focuses on the USA context and uses data collected from the US military. Recent work showed that the most important driver of water turnover which is closely linked to water requirements is energy expenditure. For those who work in a hot climate, up to a day may be required. Typically in developed countries, tap water meets drinking water quality standards, even though only a small proportion is actually consumed or used in food preparation. Other typical uses for tap water include washing, toilets, and irrigation. Greywater may also be used for toilets or irrigation. Its use for irrigation however may be associated with risks. Water may also be unacceptable due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Vaccine
Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a (a live oral vaccine) and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS) (an injectable subunit vaccine). They are about 30 to 70% effective in the first two years, depending on the specific vaccine in question. The Vi-rEPA vaccine has been shown to be efficacious in children. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinating all children in areas where the disease is common. Otherwise they recommend vaccinating those at high risk. Vaccination campaigns can also be used to control outbreaks of disease. Depending on the vaccine, additional doses are recommended every three to seven years. In the United States the vaccine is only recommended in those at high risk such as travelers to areas of the world where the disease is common. The vaccines available as of 2018 are very safe. Minor side effects may occur at the site of injection. The inje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widal Test
The Widal test, developed in 1896 and named after its inventor, Georges-Fernand Widal, is an indirect agglutination test for enteric fever or undulant fever whereby bacteria causing typhoid fever is mixed with a serum containing specific antibodies obtained from an infected individual. In cases of ''Salmonella'' infection, it is a demonstration of the presence of O-soma false-positive result. Test results need to be interpreted carefully to account for any history of enteric fever, typhoid vaccination, and the general level of antibodies in the populations in endemic areas of the world. As with all serological tests, the rise in antibody levels needed to perform the diagnosis takes 7–14 days, which limits its applicability in early diagnosis. Other means of diagnosing ''Salmonella typhi'' (and '' paratyphi'') include cultures of blood, urine and faeces. These organisms produce H2S from thiosulfate and can be identified easily on differential media such as bismuth sulfite agar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
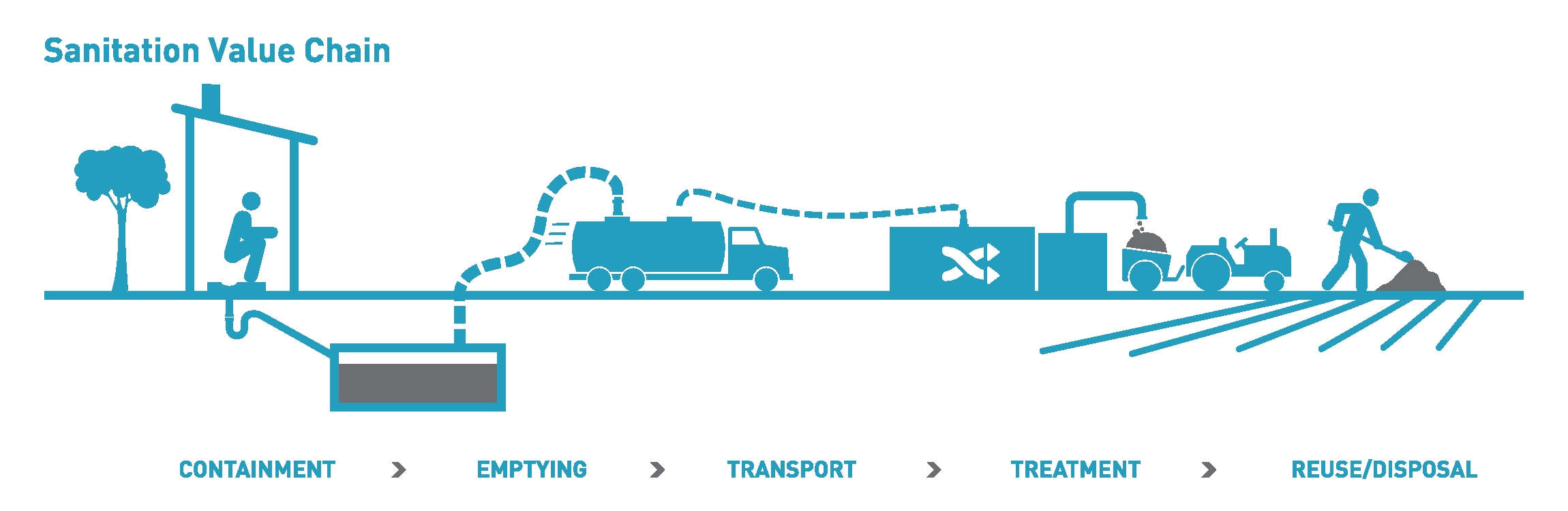
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as fuel or dried and used for construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excreta. Skatole is the principal compound responsible for the unpleasant smell of feces. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Skatole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)